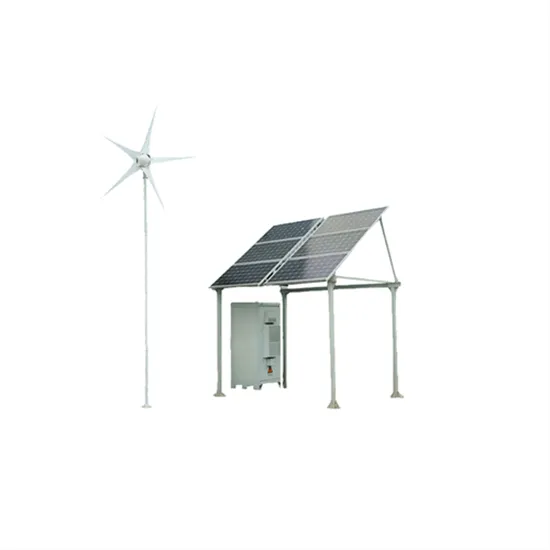
Best battery setup for 5000w inverter : r/preppers
Although if you''re already looking at a harbor freight 5000 watt inverter you''re probably not going to want to hear spend the money on the quality pure sine wave, That uses a 24 or 48 volt
Get a quote
How Much Power Does An Inverter Draw With No Load?
Yes, inverters drain batteries if not in use and the amount of power drained depends on the design and size of the inverter. Generally, it is said
Get a quote
How many volts of battery should I choose for solar energy
It is imperative to select an inverter that is compatible with the chosen battery voltage to optimize energy use. Sizing the inverter correctly based on the voltage can help
Get a quote
What Size Battery Do I Need for a 1000W Inverter?
To power a 1000W inverter, you typically need a battery with a minimum capacity of 100Ah if you plan to run it for about one hour. However, the actual size may vary based on
Get a quote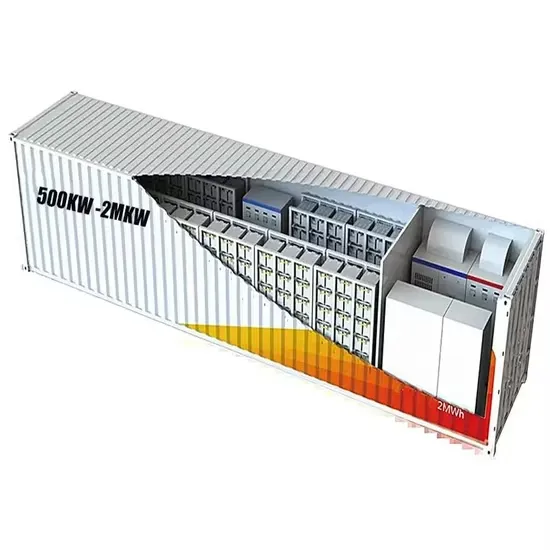
How Many Amps Does a 600 Watt Inverter Draw?
A 600W inverter is ideal if you need a portable system that is affordable and practical to carry. Although it has its limits, a 600W inverter can run small and medium sized appliances,
Get a quote
How Many Batteries Do I Need for My Inverter?
Let''s say you need 5 hours of total run time for appliances totaling 1000 watts, and you have 12 DC volts. The calculation would look like this: (5 x 1000)/12 =
Get a quote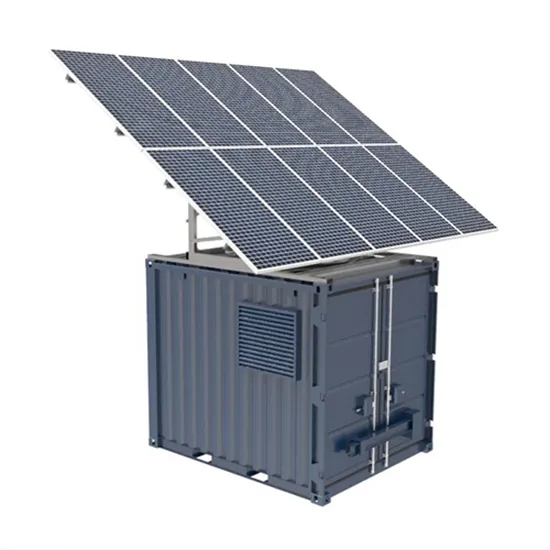
12V, 24V, or 48V Solar Power System: Which Voltage Is Best for
Therefore, you CANNOT use these batteries to create a 24 or 48V system. Inverters The whole point of a higher voltage system is to be able to run higher wattage AC appliances without over
Get a quote
When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings
Typically, residential inverters have a maximum input voltage between 500V and 1000V. Choosing one with a higher rating ensures greater flexibility and better
Get a quote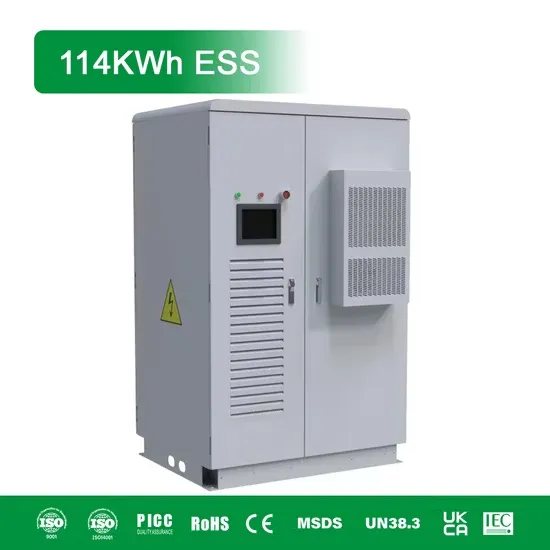
How Big Of an Inverter Can My Car Handle | Expert Guide
The inverter is the device that converts power from battery-powered electronics to the voltage used by your car (120 volts). The greater wattage an inverter can handle, the more devices
Get a quote
Frequently Asked Questions About Power Inverters | DonRowe
Power Inverter FAQ Frequently Asked Questions about Power Inverters What does a power inverter do, and what can I use one for? Using an inverter for basic emergency home backup
Get a quote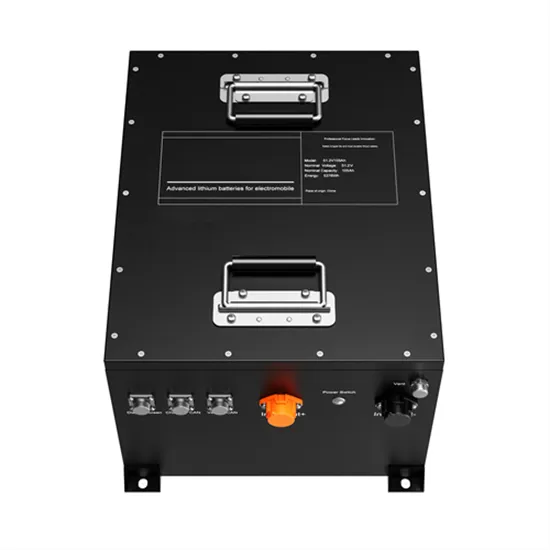
Calculator
Powerful Calculators: Inverter Size, Battery Capacity and Battery Backup Time Calculators Are you tired of struggling with complex calculations for inverter size, battery capacity, and battery
Get a quote
Lithium Battery for Inverter: Pros, Specs, and Tips
When selecting a lithium battery for inverter use, it is essential to understand the key specifications: Voltage (V): Most inverter systems use
Get a quote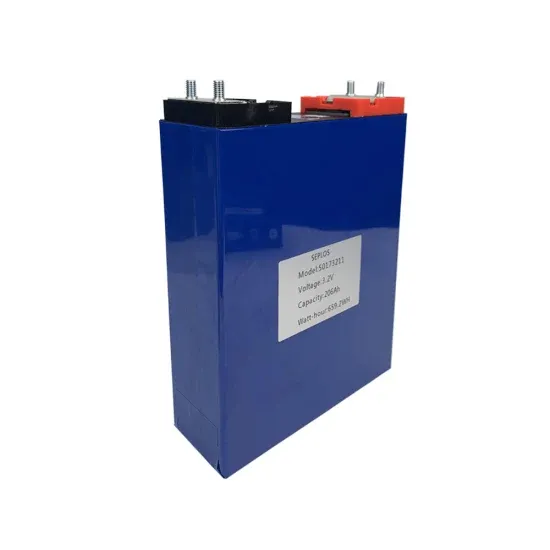
How Many Batteries For A 1000 Watt Inverter?
Most readers of my website will have a 12V battery, so we will use 12V as an example. 1,000W/12V= 83A. The inverter will draw a current of 83A
Get a quote
How many amps does a 1000 watt inverter draw?
Generally, a 1000 Watt inverter can draw up to 120 Amps if the battery bank is rated at 12 Volts, or up to 60 Amps if the battery bank is rated
Get a quote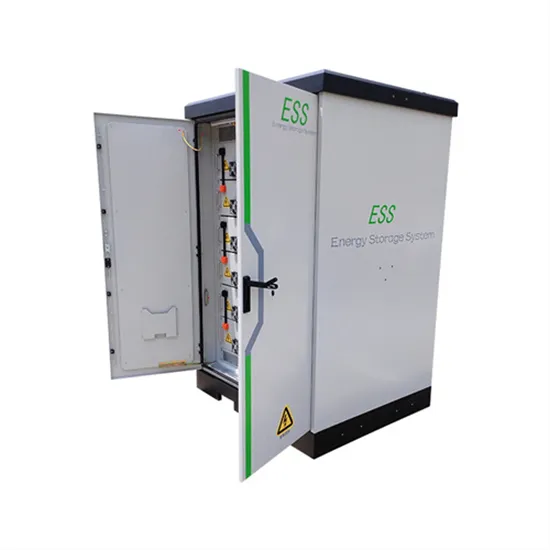
How Many Batteries Do I Need for My Inverter?
How many batteries do I need for my inverter? The calculation for figuring out how many batteries you need for your inverter is (Total Hours Needed
Get a quote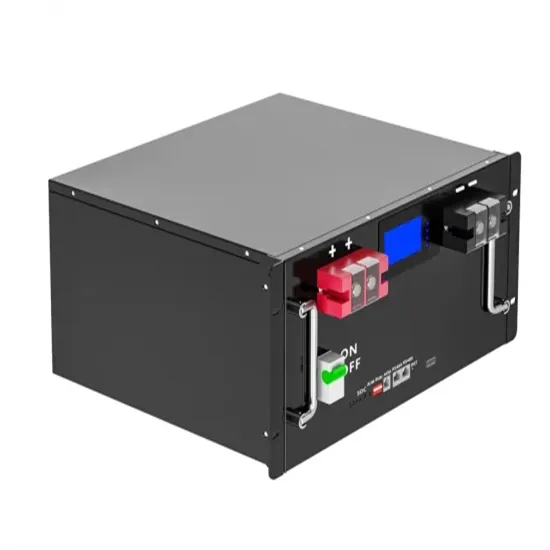
Understanding inverter voltage
The cut-off inverter voltage is a crucial parameter that determines when the inverter should cease operating to prevent damage to the connected battery. For a 12V inverter, the
Get a quote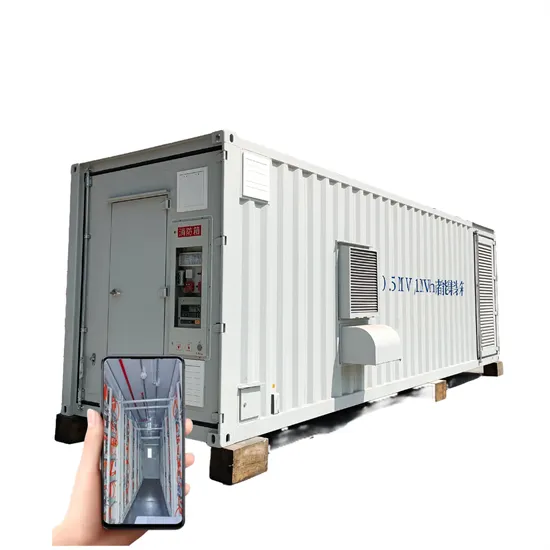
Inverter Battery Voltage: How Many Volts Are Needed For
An inverter battery typically operates at 12V, 24V, or 48V. These voltages represent the nominal direct current (DC) needed for the inverter''s function.
Get a quote
Calculate Battery Size For Any Size Inverter (Using Our Calculator)
Inverter capacity (W)*Runtime (hrs)/solar system voltage = Battery Size*1.15. Multiply the result by 2 for lead-acid type battery, for lithium battery type it would stay the
Get a quote
When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings should you pay
Typically, residential inverters have a maximum input voltage between 500V and 1000V. Choosing one with a higher rating ensures greater flexibility and better performance in different
Get a quote
How to Choose the Right Inverter Battery Voltage for Your Needs
Understanding inverter battery voltage is key to creating a strong and dependable power system. This detailed guide explores how to choose the right voltage, offers tips for
Get a quote
How Many Batteries For A 1000 Watt Inverter?? + Diagrams
Most readers of my website will have a 12V battery, so we will use 12V as an example. 1,000W/12V= 83A. The inverter will draw a current of 83A from the battery. If we
Get a quote
How Many Batteries Do I Need for My Inverter?
Let''s say you need 5 hours of total run time for appliances totaling 1000 watts, and you have 12 DC volts. The calculation would look like this: (5 x 1000)/12 = 417 amps. You would need a
Get a quote
Is your RV converter charging your batteries?
Many RVs come with a thin gauge wire between the charger and the battery. This will give you voltage loss that needs to be accounted for. I
Get a quote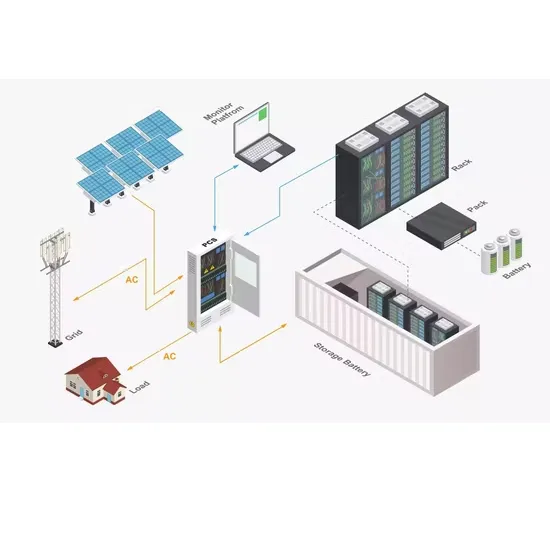
6 FAQs about [How many volts should the inverter battery use ]
What voltage should a 12V inverter run on?
The input voltage of the inverter should match the battery voltage. (For example 12v battery for 12v inverter, 24v battery for 24v inverter and 48v battery for 48v inverter Summary What Will An Inverter Run & For How Long?
Do solar inverters have multiple battery voltage options?
Most inverters now come with multiple battery voltage options, allowing for greater flexibility in system design. Understanding the voltage ratings of your inverter ensures safe, efficient, and reliable solar energy production.
How many volts does an inverter need?
For grid-tied systems, this is typically 220V or 230V in most countries. For off-grid systems, it might be 48V or 24V, depending on your battery configuration. Ensuring this rating matches your power system's output guarantees that your inverter will efficiently convert energy without risk of damage.
How much current does a 12V inverter draw from a battery?
The current draw depends on the battery voltage. Most readers of my website will have a 12V battery, so we will use 12V as an example. 1,000W/12V= 83A The inverter will draw a current of 83A from the battery. If we repeat the same calculations for a 24V and 48V battery system: 1,000W/24V= 41A 1,000W/48V= 20A
How much battery do I need to run a 3000-watt inverter?
You would need around 24v 150Ah Lithium or 24v 300Ah Lead-acid Battery to run a 3000-watt inverter for 1 hour at its full capacity Here's a battery size chart for any size inverter with 1 hour of load runtime Note! The input voltage of the inverter should match the battery voltage.
What is the input voltage of an inverter?
Understanding the inverter voltage is crucial for selecting the right equipment for your power system. Inverter voltage typically falls into three main categories: 12V, 24V, and 48V. These values signify the nominal direct current (DC) input voltage required for the inverter to function optimally. What is the rated input voltage of an inverter?
Guess what you want to know
-
 How many volts of battery can the inverter use
How many volts of battery can the inverter use
-
 How big an inverter can I use with a 72v 20a lithium battery
How big an inverter can I use with a 72v 20a lithium battery
-
 How big an inverter should I use for a 60 volt battery
How big an inverter should I use for a 60 volt battery
-
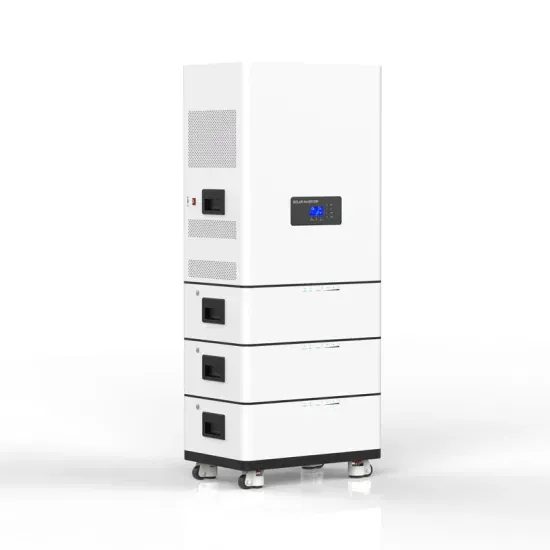 How big an inverter can I use with a 12v 50AH lithium battery
How big an inverter can I use with a 12v 50AH lithium battery
-
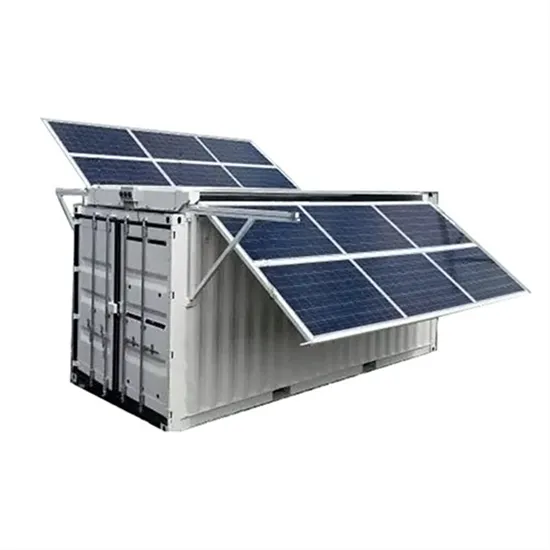 How big an inverter should I use for one battery
How big an inverter should I use for one battery
-
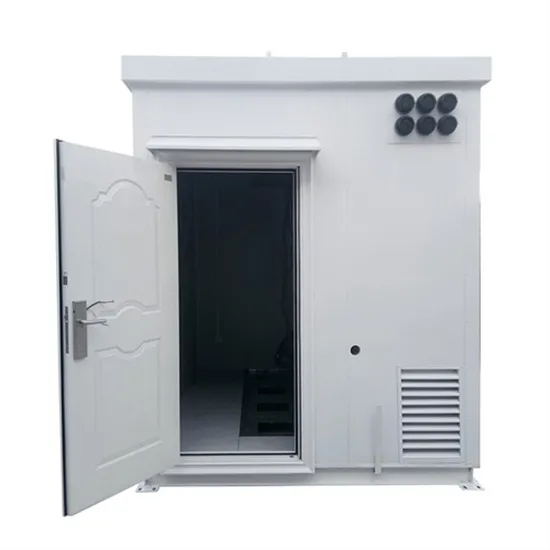
 How to use electricity in photovoltaic backup battery cabinet
How to use electricity in photovoltaic backup battery cabinet
-
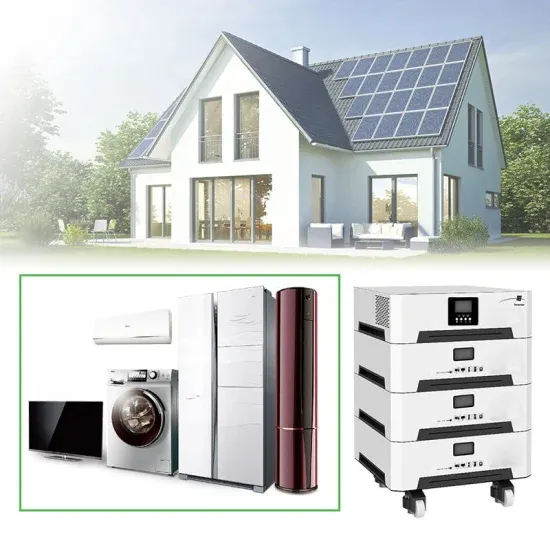 How many watts of battery does a 25w solar all-in-one machine use
How many watts of battery does a 25w solar all-in-one machine use
-
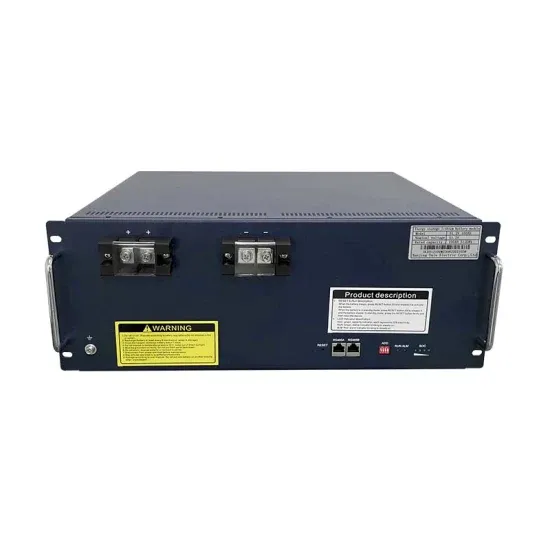 How big a photovoltaic panel should I use for a 50a32650 battery
How big a photovoltaic panel should I use for a 50a32650 battery
-
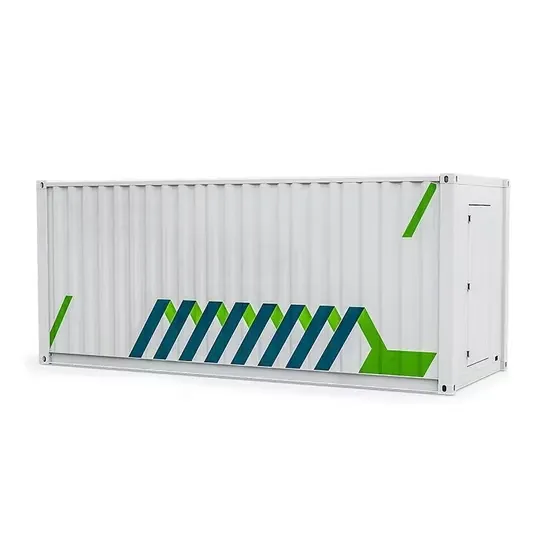 What size battery should I use with an 8600w inverter
What size battery should I use with an 8600w inverter
-
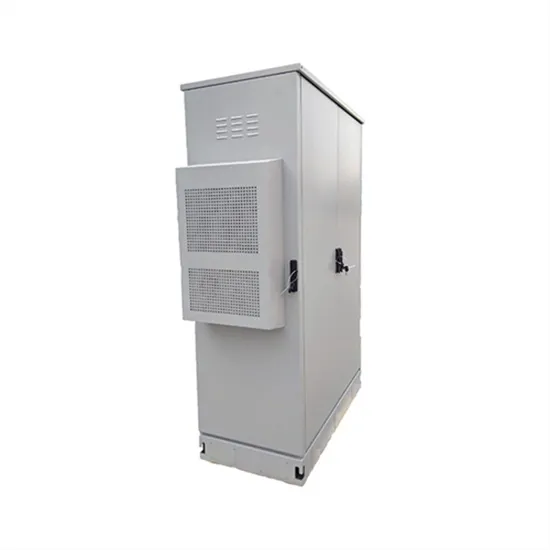 How big an inverter can I use with 60v
How big an inverter can I use with 60v
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


