Definition of Inverter Specifications
Maximum Input Voltage DC (V). This indicates the maximum voltage that can be input on the DC side of the inverter. Nominal Voltage (AC). This indicates the nominal voltage that is output
Get a quote
Power Inverters: The Need-to-Know Essentials
Inverters are devices that transform direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). They take power from the DC source and convert it to electrical power; they do not create any
Get a quote
Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What Is The
What is an Inverter Input? Inverter input is a resource that enters the inverter in the form of direct current (DC) supplied from DC sources such as batteries, solar panels, PV, wind turbines, or
Get a quote
Control of Grid Side Inverter
The inverter is a voltage source; this means that currents in the AC side will be a function of the voltages impressed by the inverter and the configuration of the grid it is connected to.
Get a quote
Photovoltaic Inverters: Key Parameters and connection for home
Inversion is the opposite process to rectification, which is the process of converting DC power into AC power. Photovoltaic inverter refers to a circuit that completes the inverter
Get a quote
DC OVERLOADING OF INVERTERS & COMPATIBILITY
DC side overloading is a good option to improve AC power output of SPV Plant. It allows solar plant to increase generation during non peak hours and optimize overall performance.
Get a quote
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
This article investigates the basic principles of inverters, different types of DC-to-AC conversion, and common applications for generating AC
Get a quote
What''s Inside Your Inverter? Main Components for
Inverters are the heart of solar systems and power solutions, converting DC power into AC power to power your home or business. But not
Get a quote
Inverter AC vs DC Side: What to Ground, Bond, or Isolate?
The AC Side: Connecting to Your Home''s Electrical System The AC side connects the inverter''s output to your home''s main electrical panel and, if applicable, the utility grid. As
Get a quote
Basics of troubleshooting DC faults within PV systems
How do we troubleshoot DC Errors? Most inverters look for errors in similar ways, no matter who the manufacturer is, they still use either isolation testing, or a current sensor to
Get a quote
DC and AC Inverters: What You Need to Know
What is the main difference between a DC inverter and an AC inverter? The main difference is that a DC inverter converts direct current (DC)
Get a quote
Inverter Protection and Ride-Through : RNWBL
I will explore the inverter protection mechanisms used to keep DC side faults and AC side faults from causing damage to the inverter. Inverter
Get a quote
DC side voltage harmonics and spectrum. (a)
The harmonic spectrum of the dc side voltage is shown in Fig. 7 (a) and (b) shows the variation of the 12th, 24th, 48th and 96th harmonics of the dc output
Get a quote
PV Power Plant DC Side Design
This chapter presents the main components of DC side and the corresponding design methods. It discusses how to design main equipment of the DC side of a large-scale
Get a quote
What''s Inside Your Inverter? Main Components for Reliable Power
Inverters are the heart of solar systems and power solutions, converting DC power into AC power to power your home or business. But not all inverters are created equal. The
Get a quote
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
This article investigates the basic principles of inverters, different types of DC-to-AC conversion, and common applications for generating AC voltage in manufacturing.
Get a quote
Choosing the Right DC SPD for Solar Applications
Different SPDs for AC & DC sides in solar/PV system It is important to protect both AC & DC sides from lightning strikes by using a
Get a quote
Ground Fault Protection | Information by Electrical Professionals
A source of some confusion for me is the idea of GFP for inverters interconnected on the load side of a service entrance OCPD. 705.32 says: Where protection is installed in
Get a quote
PV Power Plant DC Side Design
Download Citation | PV Power Plant DC Side Design | This chapter presents the main components of DC side and the corresponding design methods. It discusses how to
Get a quote
An advanced guide to Understanding DC to AC inverters
Choosing the right inverter for your DC electronics and appliances would be best. Different products need different inverters, so it''s crucial that you have the right specs to
Get a quote
DC and AC Inverters: What You Need to Know
What is the main difference between a DC inverter and an AC inverter? The main difference is that a DC inverter converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), while
Get a quote
Side Discharge Condenser Vs Top Discharge
Side-discharge designs are quite popular among Asian manufacturers, including Daikin, Fujitsu, and Mitsubishi. Interestingly, it was in Japan that the brilliant idea of applying
Get a quote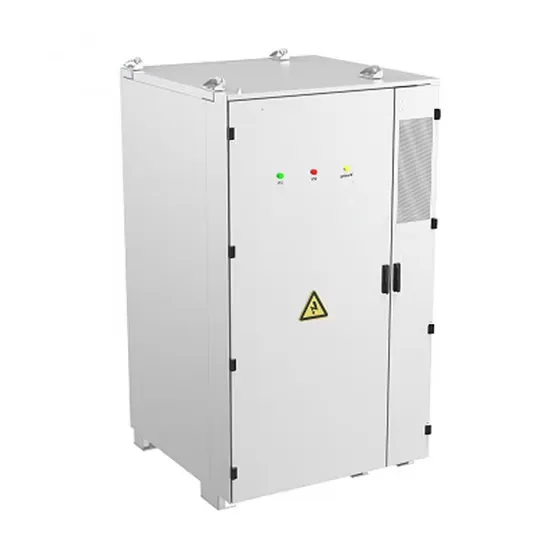
Load‐side Inverters | part of Design of Three-phase AC Power
This chapter is on the design of three‐phase load‐side PWM DC/AC inverters. Inverters can be used to serve loads as in the case of motor drives, or to interface with the grid or other sources
Get a quote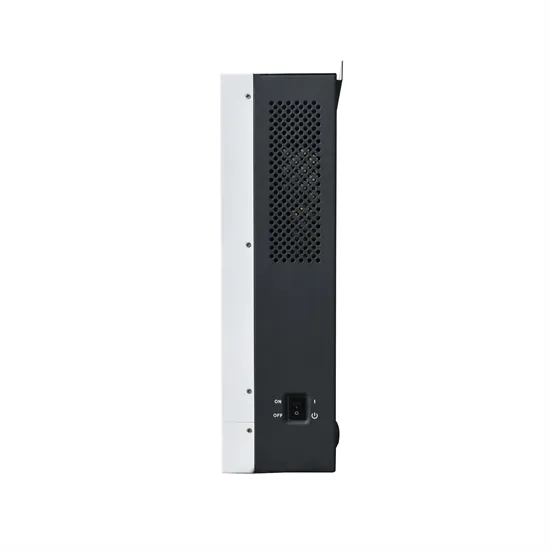
DC-side faults mechanism analysis and causes location for two
Due to the deep coupling of the DC faults for the two-stage photovoltaic (PV) inverters, it is very difficult to determine the specific causes of DC faults. In terms of this issue,
Get a quote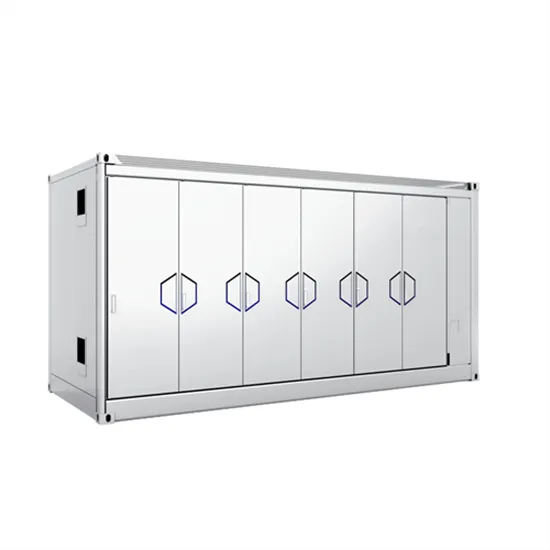
Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What Is The
What is an Inverter Input? Inverter input is a resource that enters the inverter in the form of direct current (DC) supplied from DC sources such
Get a quote
Rotor-Side Converter
A rotor-side converter is defined as a control system that manages the active and reactive power of an induction generator by utilizing a synchronous rotating stator-flux-oriented reference
Get a quote
Photovoltaic Inverters: Key Parameters and
Inversion is the opposite process to rectification, which is the process of converting DC power into AC power. Photovoltaic inverter refers to
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Which side of the inverter is the DC side]
What is a DC to AC power inverter?
The transition of DC to AC power is called an inversion, while the less common AC and DC transition is called a conversion. Both have different energy flows, but a DC-to-AC power inverter is sometimes necessary for a household. The typical electricity supplied to homes is 120v-240v in AC.
What does DC a mean on an inverter?
Maximum Input Short Circuit Current DC (A). This indicates the maximum short circuit current that can be input on the DC side of the inverter. Minimum/Nominal Input Voltage DC (V). This indicates the minimum voltage that can be input on the DC side of the inverter. Maximum Operating Current in DC (A).
What does W mean on a DC inverter?
Maximum DC Power (W). This indicates the maximum DC power input to the inverter. Maximum Input Short Circuit Current DC (A). This indicates the maximum short circuit current that can be input on the DC side of the inverter. Minimum/Nominal Input Voltage DC (V). This indicates the minimum voltage that can be input on the DC side of the inverter.
What does AC mean in a power inverter?
Nominal Voltage (AC). This indicates the nominal voltage that is output from the inverter. Rated AC Power Output (VA). This indicates the maximum AC power output from the inverter. Maximum Continuous Current Out AC (A). The indicates that maximum continuous AC current that may be output from the inverter. Peak Efficiency (%).
What is inverter input?
Inverter input is a resource that enters the inverter in the form of direct current (DC) supplied from DC sources such as batteries, solar panels, PV, wind turbines, or other DC sources to be converted into alternating current (AC).
Do you need a power inverter?
Various electronics have an input of either 12, 24, or 28 DC voltage, and in order to use appliances with an AC output voltage, you must have a power inverter. Among the more practical applications of AC inverters are the following: The inversion from DC to AC isn’t simple because the current flow must be reversed at a given frequency.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Which side of the inverter is the DC side
Which side of the inverter is the DC side
-
 270v high voltage DC to 220v inverter
270v high voltage DC to 220v inverter
-
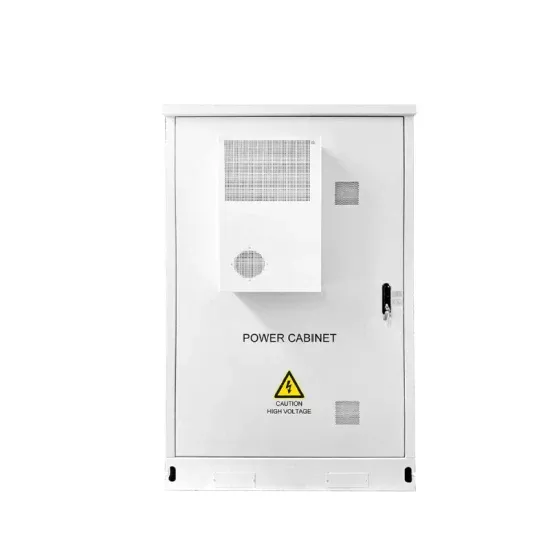 Which inverter is best for 60kw photovoltaic power generation
Which inverter is best for 60kw photovoltaic power generation
-
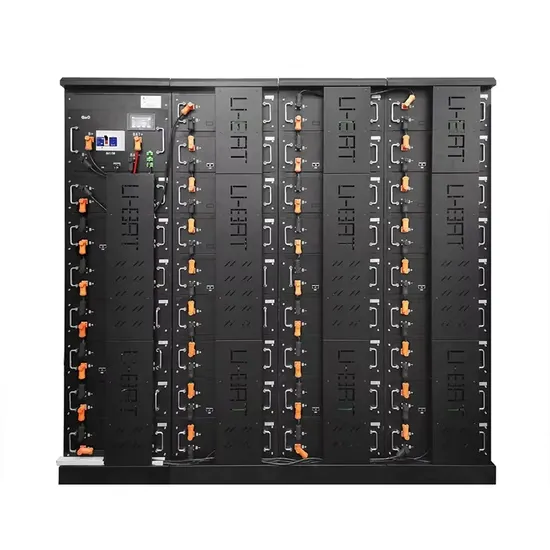 Photovoltaic DC grid-connected inverter
Photovoltaic DC grid-connected inverter
-
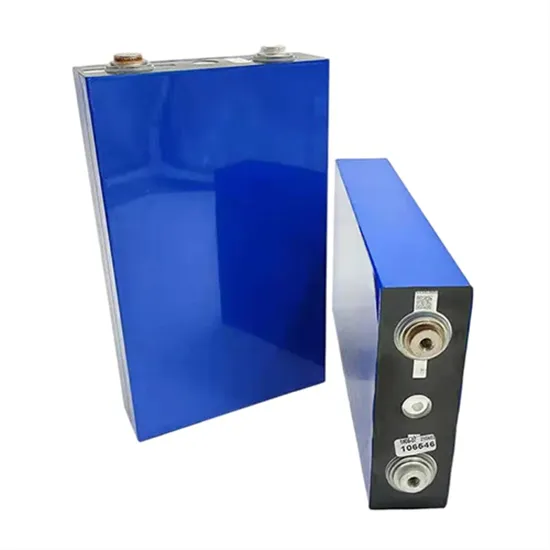 How much does it cost to order a DC inverter
How much does it cost to order a DC inverter
-
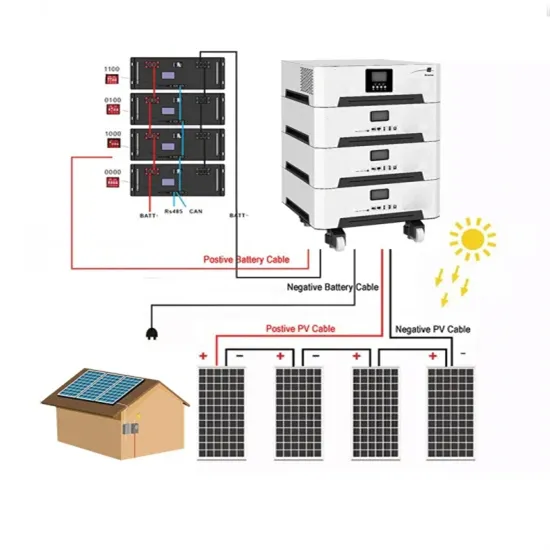 12v inverter output is DC or AC
12v inverter output is DC or AC
-
 Which is better high-frequency or broadband inverter
Which is better high-frequency or broadband inverter
-
 Which solar inverter is best
Which solar inverter is best
-
 Which BYD inverter model has the highest power
Which BYD inverter model has the highest power
-
 Which is the best DC energy storage equipment in Guyana
Which is the best DC energy storage equipment in Guyana
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


