
How to Measure Voltage (with Pictures)
Voltage is a measurement of potential electric energy between two points. You can measure the voltage of household circuitry or batteries using
Get a quote
How To Measure The Power Output From A Battery
Use a multimeter to test the voltage drop across the load. Turn the dial of the multimeter to monitor DC voltage. Then, place the two leads of the
Get a quote
How to Test a Transformer: 12 Steps (with Pictures)
Measure the secondary output of the transformer. If there is no filtering or shaping being performed by the secondary circuitry, use the AC
Get a quote
How DC Current Shunts Work | Power Measurement
In applications where the current changes faster than can be seen on an analog or digital meter, a data logger (or meter with internal data
Get a quote
How To Measure The Power Output From A Battery
Use a multimeter to test the voltage drop across the load. Turn the dial of the multimeter to monitor DC voltage. Then, place the two leads of the meter on either side of the
Get a quote
3 Ways to Test Solar Panels: Output, Voltage & Current
If you''re testing solar panels, your multimeter is your best buddy. It may be used to gauge: Voltage on an open circuit (Voc) Current in a short circuit (Isc) Running current How?
Get a quote
Testing USB Chargers With A Multimeter: Step-by-Step Instructions
Test the Voltage Output Measuring the voltage output of a USB charger is a fundamental aspect of assessing its performance. Follow these steps to accurately test the
Get a quote
Selecting the Right Voltage Measurement When
Zeroing in on the right voltage measurement device is critical to achieving the accuracy and speed of measurement required for your voltage
Get a quote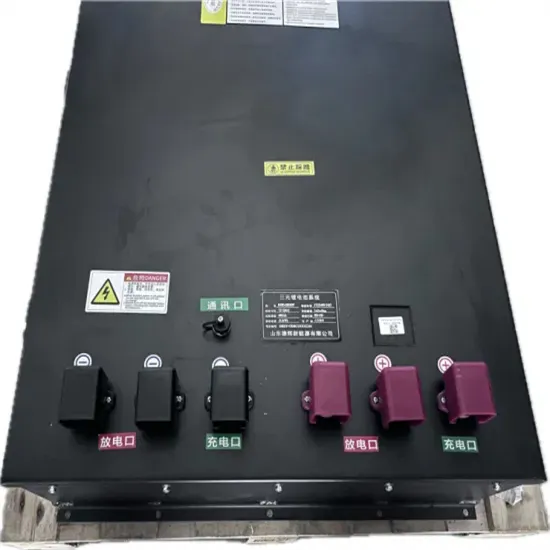
An Experiment to Measure Battery Voltage and Power
Learn how battery terminal voltage and power output are related to current and how battery behavior differs from that of a resistor like a light bulb or heat...
Get a quote
How to Measure Current of a Battery Using Multimeter? A Simple
Understanding a battery''s current output is crucial in numerous applications, from simple electronics projects to complex industrial systems. Whether you''re a seasoned
Get a quote
Battery Testing Procedure
Discover the step-by-step battery testing procedure, including how to measure voltage, capacity, and internal resistance. Using this comprehensive guide, you can ensure
Get a quote
How to measure battery voltage while it''s used?
Normally, this is very easy, just check the voltage across the disconnected battery''s + and - terminals and then use an appropriate comparison table to find out what % of
Get a quote
How to Accurately Measure Battery Voltage and Capacity?
Critical tools include digital multimeters for voltage checks, hydrometers for lead-acid battery specific gravity measurements, and battery load testers for capacity analysis.
Get a quote
How to Test Battery Capacity: Comprehensive Guide and
The voltage method is one of the most basic battery capacity testing methods. By measuring the voltage across the battery, its remaining capacity can be preliminarily
Get a quote
How to measure the voltage of batteries in the battery cabinet
If we assume one terminal of the battery pack is connected to ground, we can measure the open circuit voltage across each cell. This works because DMMs measure differential voltage, or the
Get a quote
How to Measure Battery Current Using Multimeter? – Complete
While many are familiar with using a multimeter to measure voltage or resistance, measuring current often presents a unique set of challenges and safety considerations that
Get a quote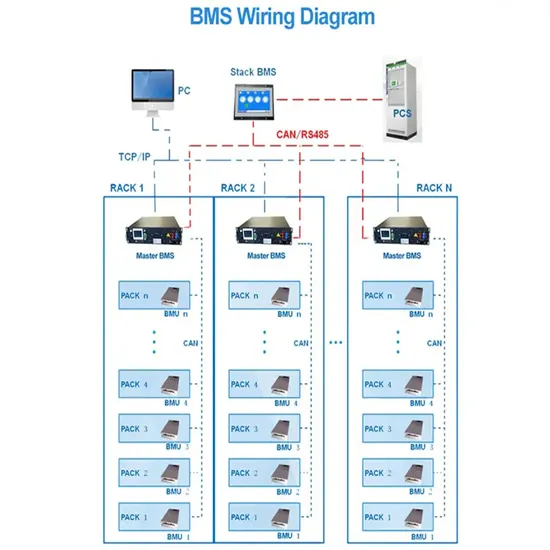
How to Measure Current of a Battery Using Multimeter? A Simple
This detailed guide will equip you with the knowledge and practical steps needed to accurately measure battery current using a multimeter, covering various scenarios, potential
Get a quote
How to measure the voltage of batteries in the battery cabinet
At its most basic, battery voltage is a measure of the electrical potential difference between the two terminals of a battery--the positive terminal and the negative terminal.
Get a quote
How to Accurately Measure Battery Voltage and Capacity?
To measure a battery, use a multimeter to check voltage (for charge level) and perform capacity tests with specialized tools like load testers. For accurate results, ensure the
Get a quote
An Experiment to Measure Battery Voltage and Power Output
Learn how battery terminal voltage and power output are related to current and how battery behavior differs from that of a resistor like a light bulb or heat...
Get a quote
How to Measure Generator Output: A Step-by-Step
To measure generator output, use a multimeter to check voltage and a clamp meter for current. Ensure accurate readings by following safety
Get a quote
How to Measure Output Current in a Power Supply | Ideal Power
How to Measure the Output Current of a Power Supply Knowing how to measure output current is essential when designing, testing, or troubleshooting a power supply. Whether you''re
Get a quote
Simplify Voltage and Current Measurement in Battery Test
Voltage and current sensing are the two most significant measurements in battery test equipment systems. Furthermore, the most important parametric characteristics for this application is a
Get a quote
How to test the internal current of the battery cabinet
The DC discharge method is to measure the instantaneous voltage drop on the battery (generally 2 ~ 3s) by instant large current discharge on the battery, and calculate the internal
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [How to measure the output current and voltage of the battery cabinet]
How do you measure battery voltage?
Solution: Measure the internal resistance. How you can do that? Apply an additional known current and measure the difference in voltage. With that you get the internal resistance and with the measured current from above, you get the real battery voltage.
How to measure a battery with a reference voltage?
You can measure voltage battery with voltage reference. You need voltage reference with lower reference than you expect on battery (for example 1.235 V). Then you measure this voltage with your ADC. With this measurement you can now calculate ADC reference voltage, which should be equal to battery voltage.
How to test a 1.5V battery with a multimeter?
To test the voltage of a 1.5V battery with a multimeter, you need to set the multimeter to the DC voltage (V) mode. Then, connect the multimeter’s positive (red) probe to the battery’s positive terminal and the negative (black) probe to the battery’s negative terminal. Finally, read the voltage displayed on the multimeter.
How do you test a battery with a multimeter?
Connect multimeter probes to battery & measure the voltage. The voltage should fall across the specified in the cell or battery’s datasheet. For NMC (Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt), this will range between 2.5 V & 4.2 V per cell. An LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) cell (or) battery will have a voltage between 2.5 V and 3.7 V.
Should a battery be loaded at the time of measurement?
To measure the battery properly you indeed should not be loading it at the time of measurement. If you know that your Arduino will be in a low power/standby more at certain times, it will then be consuming only a very small current that should not load the battery so much that the voltage drop is significant.
How to measure battery voltage Vb?
For example if you measure 300 with your ADC and your reference voltage Vr is 1.235 V then your battery voltage Vb is 4.2 V. Another similar, but more complex way is to use voltage divider on battery and use internal voltage of arduino for ADC reference.
Guess what you want to know
-
 How to measure the charging current of a battery cabinet
How to measure the charging current of a battery cabinet
-
 How to measure the voltage of the battery cabinet
How to measure the voltage of the battery cabinet
-
 How much current does a 9v battery in an energy storage cabinet have in amperes
How much current does a 9v battery in an energy storage cabinet have in amperes
-
 How much current does a 5 kWh battery cabinet have
How much current does a 5 kWh battery cabinet have
-
 How much current does a 100 kWh battery cabinet draw
How much current does a 100 kWh battery cabinet draw
-
 What is the voltage and current of the energy storage cabinet battery
What is the voltage and current of the energy storage cabinet battery
-
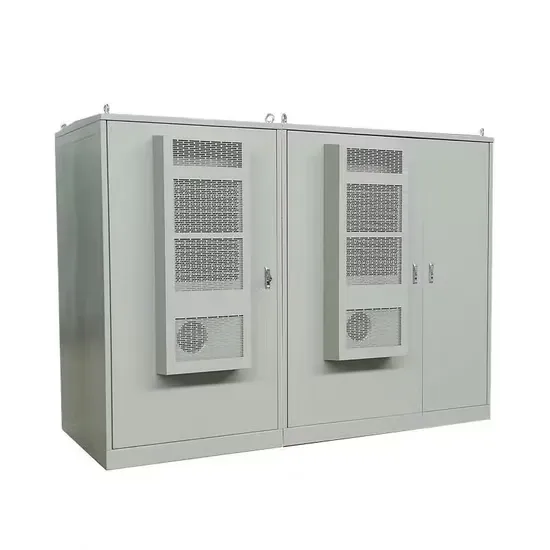 How to use the battery cabinet temperature management system
How to use the battery cabinet temperature management system
-
 How much does a 28 kWh battery cabinet cost
How much does a 28 kWh battery cabinet cost
-
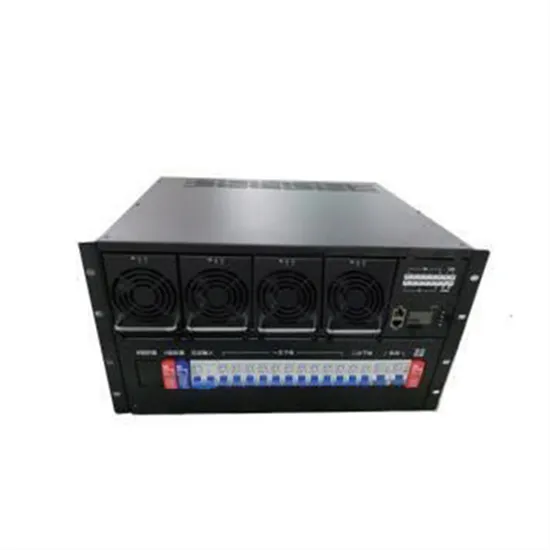 How to replace the power board of the lithium battery station cabinet
How to replace the power board of the lithium battery station cabinet
-
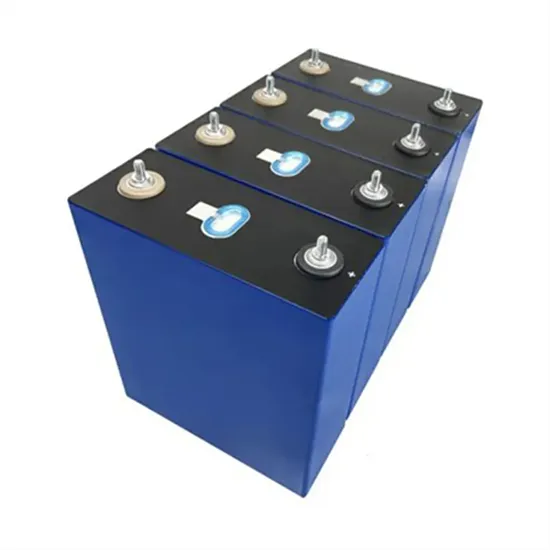 Industrial high voltage battery energy storage battery cabinet
Industrial high voltage battery energy storage battery cabinet
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


