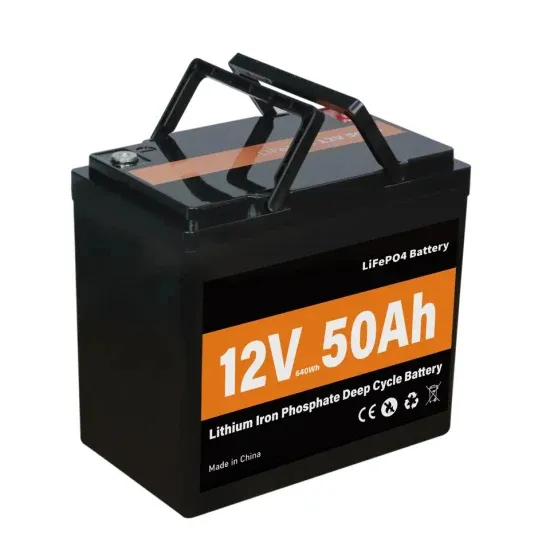
What''s Inside Your Inverter? Main Components for
Inverters are the heart of solar systems and power solutions, converting DC power into AC power to power your home or business. But not
Get a quote
[Solved] Three Phase Bridge Inverters MCQ [Free PDF]
Concept: In a three-phase bridge inverter operating in square wave mode, the output voltage waveform contains only odd-order harmonics. Therefore, the correct option is:
Get a quote
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
This article investigates the basic principles of inverters, different types of DC-to-AC conversion, and common applications for generating AC
Get a quote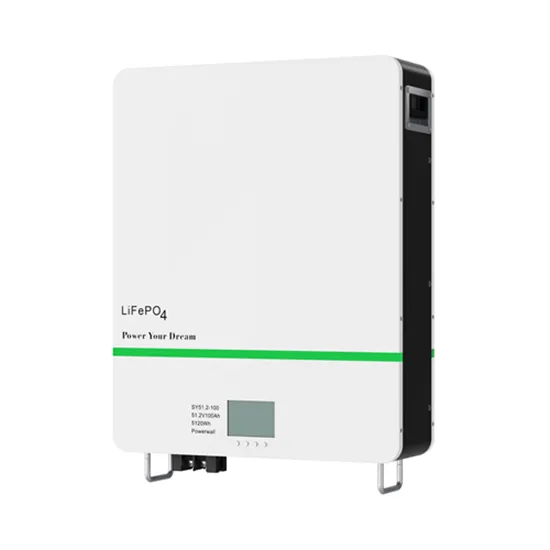
Mastering Inverter Basics: How Does an Inverter
An inverter is a device that converts DC power to AC, and it is used for solar enery inverters, EV motors, and industrial PV inverters. Check
Get a quote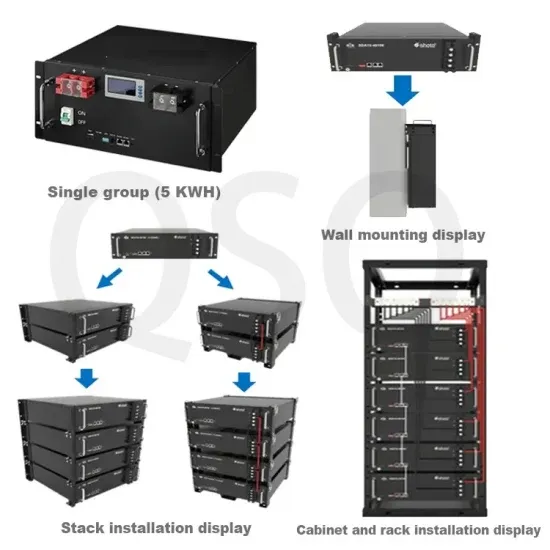
EN 206: Power Electronics and Machines
Square Wave Inverter Input DC is controlled to control output voltage magnitude Inverter can control only frequency of output voltage Output voltage waveform is similar to square wave.
Get a quote
Understanding Basics Of An Inverter Circuit: How It Works And Its
The inverter circuit converts DC power through an electronic switching process with signal control to produce a stable AC wave. The input is a DC from batteries or solar panels, and the output
Get a quote
Understanding the Circuit Diagram of an Inverter PCB
Transforming direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) is a fundamental operation in many electronic devices, and a crucial component in
Get a quote
DC to AC Inverter Circuit with Detailed Diagram
Detailed explanation and circuit diagram of a DC to AC inverter showing key components, wiring connections, and operation principles for practical understanding and implementation.
Get a quote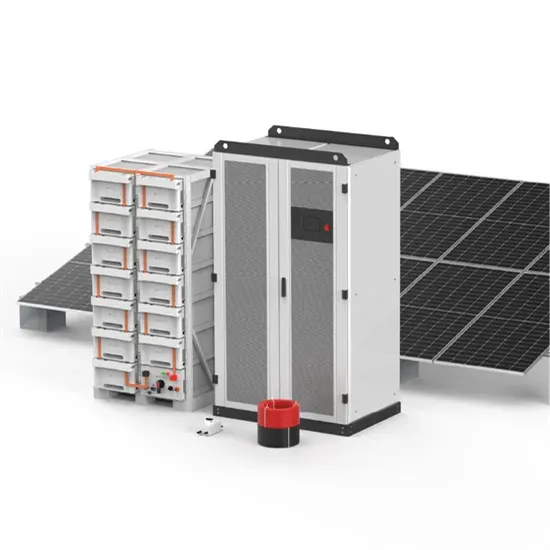
INVERTERS
[The nomenclature ''inverter'' is sometimes also used for ac to dc converter circuits if the power flow direction is from dc to ac side. However in this lesson, irrespective of power flow direction,
Get a quote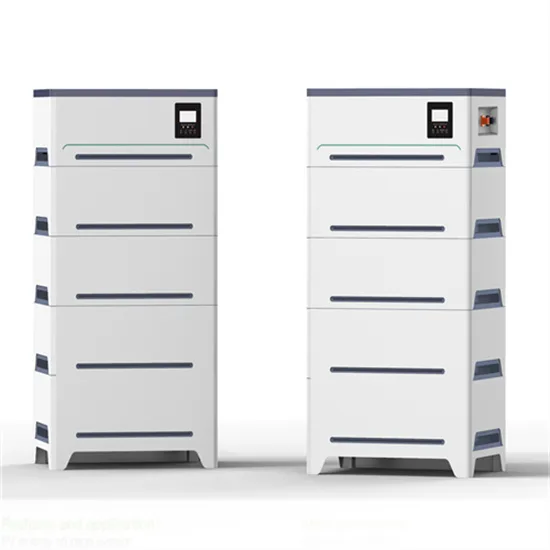
Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What Is The
The inverter output is the electrical power generated by the inverter from the process of converting the DC input source into alternating current (AC). The
Get a quote
Understanding Basics Of An Inverter Circuit: How It
The inverter circuit converts DC power through an electronic switching process with signal control to produce a stable AC wave. The input
Get a quote
Mitigation of DC Components Using Adaptive BP-PID
Waveforms of dc component, grid voltage and current using PID controller and adaptive BP-PID controller for dc-component suppression in
Get a quote
THE ABCs AND 123s OF VARIABLE FREQUENCY DRIVES
kVA = Volts x Amps x 3 (for a three-phase output) Multiplying output VA by the load power factor yields output power. Knowing the rated input kVA is useful when sizing components used with
Get a quote
Introduction to Inverters
There are mainly two types of currents: Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). In general AC is used to travel over long distances and users require DC. So, there are
Get a quote
Lesson No
In this lesson a 3-phase bridge type VSI with square wave pole voltages has been considered. The output from this inverter is to be fed to a 3-phase balanced load. Fig. 35.1 shows the
Get a quote
Inverter Circuit Diagram And Components
Inverters are devices used to convert Direct Current (DC) into Alternating Current (AC), allowing for the manipulation of electric power. DC is
Get a quote
Inverters Inside: Components and How It Works
An inverter, at its core, is a power electronic device that changes DC, often from batteries or solar panels, into AC, the type of current that powers most of our household
Get a quote
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
This article investigates the basic principles of inverters, different types of DC-to-AC conversion, and common applications for generating AC voltage in manufacturing.
Get a quote
Demonstration of switching sequence effects on output voltage in
3 days ago· Demonstration of Switching Sequence Effects on Output Voltage in a Half-Wave Bridge Inverter 1. Circuit and Components DC source: V dc Two switches: S1, S2 Load:
Get a quote
How do inverters work in a circuit? – Electricity – Magnetism
An inverter''s primary function is to change DC voltage, typically provided by a battery or solar panel, into AC voltage. The inverter uses electronic components, such as
Get a quote
Understanding VFD circuit
The second section of the VFD is called the DC intermediate section & it contains the filter components. The third block of the VFD is called the inverter section
Get a quote
What''s Inside Your Inverter? Main Components for Reliable Power
Inverters are the heart of solar systems and power solutions, converting DC power into AC power to power your home or business. But not all inverters are created equal. The
Get a quote
Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the
1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the DC power into controlled AC power by using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) switching. PWM switching is the most
Get a quote
How do inverters work in a circuit? – Electricity – Magnetism
An inverter, at its core, is a power electronic device that changes DC, often from batteries or solar panels, into AC, the type of current that
Get a quote
Inverter Parts Diagram and Function Overview
The main components of an inverter include the DC input section, DC-AC converter, control circuitry, and output filter. Each part plays a specific role in converting direct current (DC) to
Get a quote
What Are The Components Of An Inverter
Discover what are the components of an inverter, including the DC input source, power electronics circuit, and control systems. Learn how inverters transform DC to AC power
Get a quote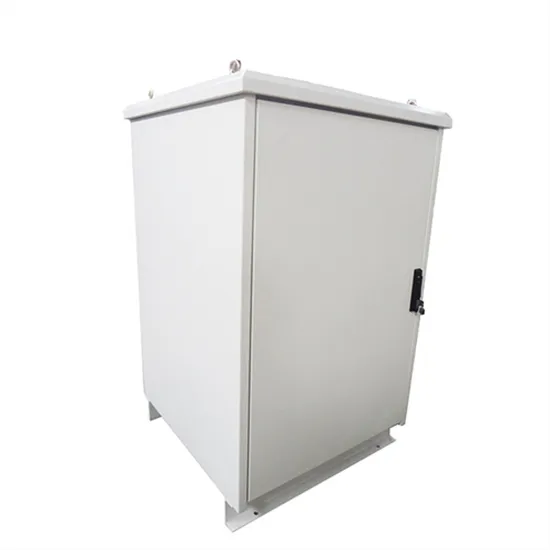
Inverter Circuit Diagram And Components
Inverters are devices used to convert Direct Current (DC) into Alternating Current (AC), allowing for the manipulation of electric power. DC is produced by most batteries, while
Get a quote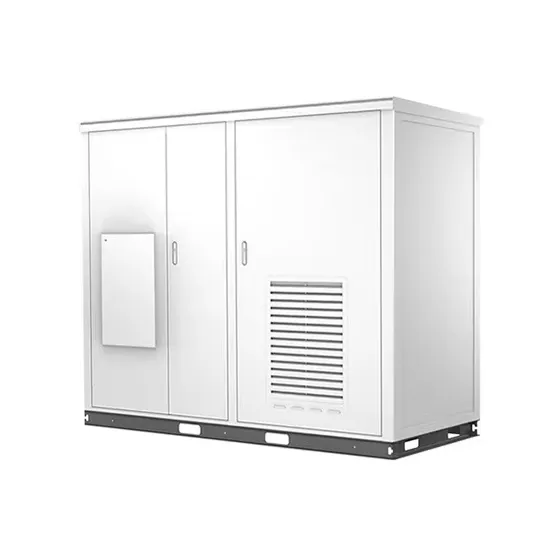
6 FAQs about [The inverter output contains a DC component]
What is a DC input in an inverter?
The DC input is responsible for providing a steady and consistent flow of energy, which the inverter will later convert into AC power. This component is vital in ensuring energy availability for the inverter’s operation. The power electronics circuit is a core component of an inverter.
What is a DC inverter circuit?
The inverter circuit converts DC power through an electronic switching process with signal control to produce a stable AC wave. The input is a DC from batteries or solar panels, and the output can power appliances. The components in the inverter circuit generally consist of: As the primary source of power to be converted.
What are the components of a DC inverter?
DC Input: This is where the inverter connects to the DC power source. The power source could be solar panels, batteries, or other DC supplies. This component ensures that the inverter can receive electrical energy from these sources. Rectifier: In some inverters, a rectifier is essential, especially for converting AC to DC.
What is a DC input in a solar inverter?
The DC input is the power input for solar panels or batteries. Poor quality terminals or improper surge protection can cause power fluctuations or even system failure. It consists of the following two parts: Fuse: The fuse automatically opens if the current is too high, protecting the inverter from damage.
What is an inverter circuit?
An inverter circuit is an electrical circuit that converts DC current into AC current to power appliances and devices in everyday life. Inverter circuits have experienced rapid development, especially in the last two decades, along with the increasing use of solar power systems as a clean, renewable energy source.
How are inverters categorized based on the type of AC power?
Inverters can be categorized based on the type of AC power they produce. AC power generated by the grid is of a pure sinusoidal shape and alternates smoothly between high and low voltage according to the shape of a sine wave.
Guess what you want to know
-
 24v DC input inverter output 6v
24v DC input inverter output 6v
-
 Inverter DC component standard
Inverter DC component standard
-
 Inverter DC 36V output
Inverter DC 36V output
-
 The DC component of the inverter is too large
The DC component of the inverter is too large
-
 The inverter reports that the DC component is too large
The inverter reports that the DC component is too large
-
 Bidirectional output photovoltaic inverter
Bidirectional output photovoltaic inverter
-
 How much is the inverter output voltage adjusted to
How much is the inverter output voltage adjusted to
-
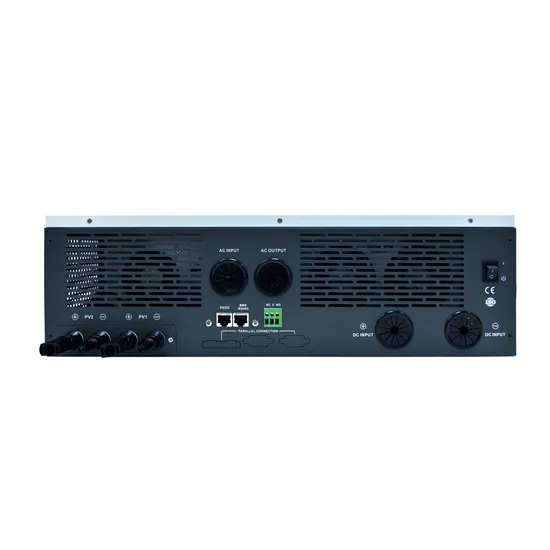
 Single-phase output inverter
Single-phase output inverter
-
 Sine wave inverter bipolar output
Sine wave inverter bipolar output
-
 The maximum voltage output by the inverter
The maximum voltage output by the inverter
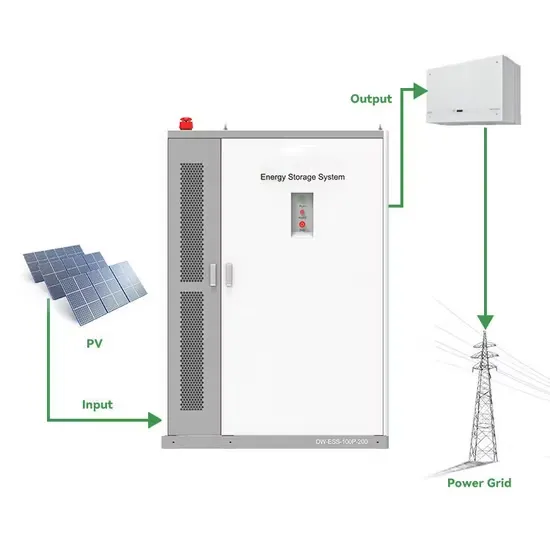
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
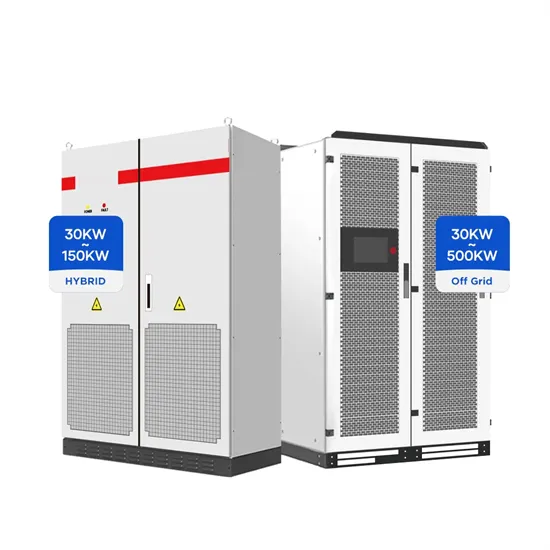
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

