The Ultimate Guide to Battery Energy Storage
This adaptability facilitates participation in Demand Response initiatives. Microgrid Support: Vital for the functionality of microgrids, BESS
Get a quote
Breaking Free From the Grid – Microgrids Explained
Conventional power grids rely on centralized power plants that distribute electricity over long distances through an extensive infrastructure. In contrast, microgrids are
Get a quote
The Role of Energy Storage in Microgrids
Energy storage is a fundamental element in modern microgrids. It allows for the storage of excess energy generated from renewable sources like solar panels or wind
Get a quote
What is a Microgrid System and How Do They Work? | FranklinWH
Generally, a microgrid is a set of distributed energy systems (DES) operating dependently or independently of a larger utility grid, providing
Get a quote
An Introduction to Microgrids: Benefits
[2] Energy Storage: Energy storage systems, such as batteries, are an important component of microgrids, allowing energy to be stored for times when it is not being generated. This helps to
Get a quote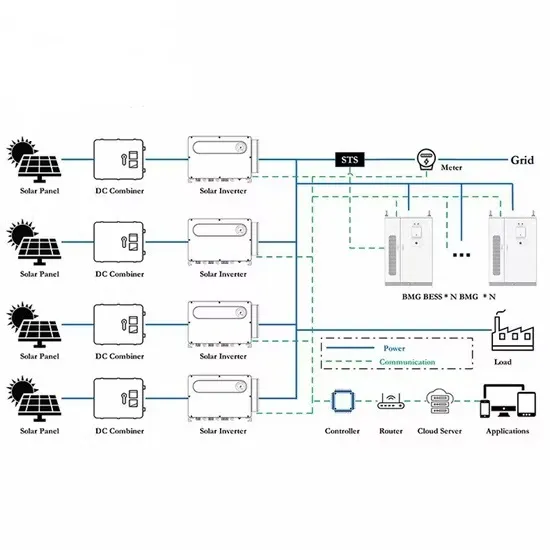
What is a Microgrid? Types, Benefits, and
What is a Microgrid? A self-sufficient energy system that integrates renewables, storage, and smart controls for reliable, sustainable power solutions.
Get a quote
Microgrid Technology: What Is It and How It Works?
Generally, a microgrid is a set of distributed energy systems (DES) operating dependently or independently of a larger utility grid, providing flexible local power to improve
Get a quote
How Does Energy Storage Improve Microgrid Resilience?
How Energy Storage Bolsters Microgrid Resilience Resilience, in the context of microgrids, refers to the ability of the system to withstand and recover from disruptions, such
Get a quote
An Introduction to Microgrids: Benefits
[2] Energy Storage: Energy storage systems, such as batteries, are an important component of microgrids, allowing energy to be stored for times when it is not
Get a quote
Breaking Free From the Grid – Microgrids Explained
Conventional power grids rely on centralized power plants that distribute electricity over long distances through an extensive infrastructure. In
Get a quote
How Microgrid Solar Systems Deliver Energy Independence
A solar microgrid is an energy distribution network that relies on a local means of producing electricity and does not require the use of a local utility grid.
Get a quote
What is a Microgrid and How Does It Use Solar Energy?
Defining the microgrid: What is a solar microgrid in Australia? A microgrid is a smaller, self-contained electrical grid. It can operate
Get a quote
What is a Microgrid? | Duracell Energy
A microgrid will include power generation such as solar panels or wind turbines, a storage element such as batteries to store the renewable energy generated and an intelligent
Get a quote
What really makes a microgrid, a microgrid? | Solar
Though there are many specific definitions of a microgrid, at its core a microgrid means the ability of a distributed energy resource, typically solar
Get a quote
How Does an Energy Storage System Work in a Microgrid?
The energy storage system (ESS) is the heart of a microgrid, acting as a buffer between energy generation and consumption. It stores excess energy generated during periods of low demand
Get a quote
What Is Microgrid Storage? → Question
Microgrid storage is the linchpin holding together the promise of localized, resilient, and sustainable energy systems. At its core, it refers to the technologies and strategies
Get a quote
An Introduction to Microgrids and Energy Storage
A microgrid is a small power system that has the ability to operate connected to the larger grid, or by itself in stand-alone mode. Microgrids may be small, powering only a few buildings; or
Get a quote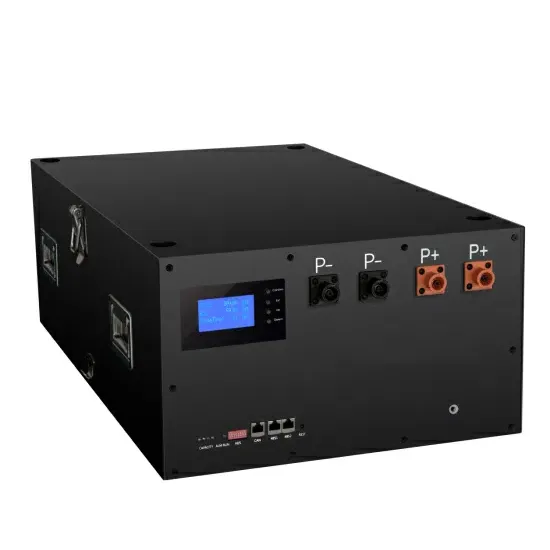
What is Microgrid Energy Storage? | NenPower
Microgrid energy storage represents a transformative shift in how communities manage and consume energy. By emphasizing local resilience, renewable integration, and
Get a quote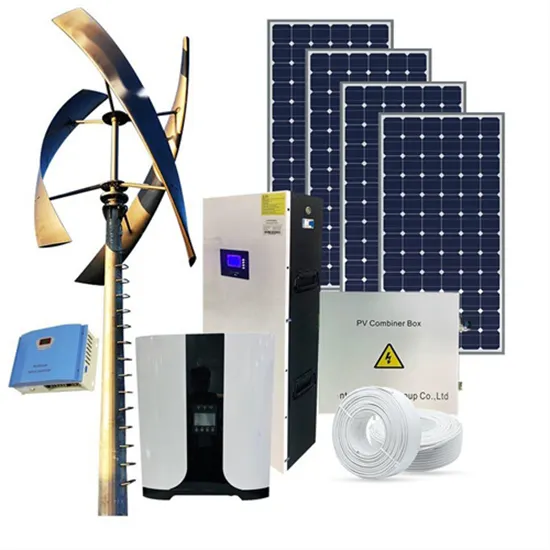
Microgrids: A review, outstanding issues and future trends
A microgrid, regarded as one of the cornerstones of the future smart grid, uses distributed generations and information technology to create a widely distributed automated
Get a quote
What is a Microgrid System and How Do They Work? | FranklinWH
Energy Storage: Many microgrids incorporate energy storage systems (ESS) such as batteries. These batteries store excess electricity generated during periods of low demand
Get a quote
Microgrids, SmartGrids, and Resilience Hardware 101
Microgrid – DOE Definition v Group of interconnected loads and distributed energy resources within clearly defined electrical boundaries that acts as a single controllable entity with respect
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [What does the energy storage system of a microgrid refer to ]
What is energy storage in a microgrid?
Energy Storage: Many microgrids incorporate energy storage systems (ESS) such as batteries. These batteries store excess electricity generated during periods of low demand or high renewable energy production. The stored energy can then be deployed during peak demand periods or when renewable energy sources are not available. 3.
What is Microgrid technology?
Microgrid Technology: What Is It and How It Works? Generally, a microgrid is a set of distributed energy systems (DES) operating dependently or independently of a larger utility grid, providing flexible local power to improve reliability while leveraging renewable energy.
What are the components of a microgrid?
They can be used to power individual homes, small communities, or entire neighborhoods, and can be customized to meet specific energy requirements. Microgrids typically consist of four main components: energy generation, energy storage, loads and energy management. The architecture of microgrid is given in Figure 1.
What is a grid-connected microgrid?
Grid-connected microgrids are systems that operate with the main power grid. They can draw power from the grid, supply excess power back to the grid, or function autonomously during grid outages. These systems typically include a combination of renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind, along with energy storage solutions such as batteries.
What is a hybrid microgrid?
The primary challenge for off-grid microgrids is ensuring a consistent energy supply despite the variability of renewable sources, often necessitating robust energy storage solutions. Hybrid microgrids combine multiple energy sources and storage options to optimize efficiency, reliability, and cost.
How can microgrids contribute to a low carbon future?
Microgrids play a crucial role in the transition towards a low carbon future. By incorporating renewable energy sources, energy storage systems, and advanced control systems, microgrids help to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote the use of clean and sustainable energy sources.
Guess what you want to know
-
 What does supporting energy storage project refer to
What does supporting energy storage project refer to
-
 What is Uzbekistan s microgrid energy storage system
What is Uzbekistan s microgrid energy storage system
-
 What does 8mwh energy storage equipment refer to
What does 8mwh energy storage equipment refer to
-
 What does the energy storage battery market refer to
What does the energy storage battery market refer to
-
 What are the uses of microgrid energy storage systems
What are the uses of microgrid energy storage systems
-
 What does a wind solar and energy storage base refer to
What does a wind solar and energy storage base refer to
-
 What is an integrated energy storage system
What is an integrated energy storage system
-
 What does wind and solar load storage refer to
What does wind and solar load storage refer to
-
 Agricultural Microgrid Energy Storage System
Agricultural Microgrid Energy Storage System
-
 What is the use of energy storage equipment in power stations
What is the use of energy storage equipment in power stations
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


