A comprehensive review on time‐delay compensation techniques
A novel two degrees of freedom grid current regulation for single‐phase LCL‐type photovoltaic grid‐connected inverter. In: IEEE 8th International Power Electronics Motion
Get a quote
Aliasing Suppression Method for a Three-Phase Grid
In order to reduce the sampling delay and improve bandwidth, sability margin, and the robustness of the active damping in LCL-filtered grid
Get a quote
A Hybrid Single-Phase Transformerless Solar Photovoltaic Grid
Among the renewable energy sources, photovoltaic (PV) solar power represents one of the most potential. The use of grid-integrated solar power is much more popular than off-grid systems.
Get a quote
Impact of DER Voltage Regulation and Voltage Ride
This single phase PV model includes a generic representation of the advanced inverter controls and is sufficient for the analysis presented here. The impact of the different control
Get a quote
Single phase grid-connected inverter: advanced control
This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of single-phase grid-connected inverter technology, covering fundamental operating principles, advanced control strategies, grid
Get a quote
Three-Phase Transformerless PV Inverter With
Request PDF | Three-Phase Transformerless PV Inverter With Reconfigurable LCL Filter and Reactive Power Capability | Constructing LCL filter with only three inductors is made
Get a quote
IEEE 1547-2018 Based Interoperable PV Inverter with
In this paper, an in-teroperable controller, enabled by Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) communications protocols, is developed for a grid-connected, three-phase PV inverter.
Get a quote
Zero-Voltage Ride-Through Capability of Single-Phase Grid
Therefore, in this paper, the performance of single-phase grid-connected PV systems under an extreme grid fault (i.e., when the grid voltage dips to zero) is explored. It has been revealed
Get a quote
Active and Reactive Power Control of Single Phase
The work presented in this paper deals with modeling and analyzing of a transformer less grid-connected inverter with active and reactive power control by controlling the inverter output
Get a quote
Modulation and control of transformerless boosting inverters
This paper presents a comparative analysis of the three-phase Split-Source Inverter (SSI), quasi-Z-source inverter (q-ZSI), and the conventional two-stage DC–DC–AC
Get a quote
FORMAT INSTRUCTIONS FOR SOMChE 2004 PAPERS
Similarly there have been great advancements in the solar photovoltaic inverter technology in the recent past to improve its efficiency. Therefore large scale installations of single phase solar
Get a quote
Grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Grid codes, topologies and
The proliferation of solar power plants has begun to have an impact on utility grid operation, stability, and security. As a result, several governments have developed additional
Get a quote
Advanced Leakage Current Suppression Techniques for Three-Phase
A three-phase non-isolated photovoltaic inverter is the focus of this paper''s investigation, and the basic leakage current model is first built.
Get a quote
Analysis of primary frequency regulation characteristics of PV
This approach takes advantage of EV parking lots and PV resources abilities for this purpose directly or through aggregators. In [9], a comprehensive control strategy for
Get a quote
Fault ride through capability for grid interfacing large scale PV
Integration of dynamic grid support is required for distributed power systems that are interconnected with medium voltage grids. This study proposes a comprehensive control
Get a quote
Multi-Fault-Tolerant Operation of Grid-Interfaced Photovoltaic
As such, a twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient-based voltage-oriented control (TD3VOC) is formulated and trained to provide effective current control of inverter
Get a quote
Advanced Inverters: (1547) Capabilities, Experiences, and
NREL with SolarCity and the Hawaiian Electric Company (HECO) completed preliminary work conducted at ESIF demonstrating the ability of advanced PV inverters to mitigate some
Get a quote
Frontiers | A data-driven time-delay compensation strategy for
A data-driven time-delay compensation strategy for ancillary service of the distribution photovoltaic generation system
Get a quote
Improving performance of LVRT capability in single-phase grid-tied PV
This paper addresses the LVRT capability for single phase transformerless PV inverters. One of the most important factors for the controllers in LVRT duration is a fast
Get a quote
Systematical Investigation of Transient Response and Fault
The proposed method and findings are validated through experimental tests on a single-phase grid-connected inverter, confirming their effectiveness and relevance during fault
Get a quote
Photovoltaic inverter phase advance loss
A control strategy is proposed for a three-phase PV inverter capable of injecting partially unbalanced currents into the electrical grid. This strategy aims to mitigate preexisting
Get a quote
(PDF) Recent advances in synchronization techniques
Synchronization is a crucial problem in grid-tied inverters operation and control research indicates that frequency, phase, and amplitude of voltage
Get a quote
Analysis and comparison of two methods for reducing the impact
In order to reduce the influence of one sampling time delay on the inverter performance and to improve the stability of inverter, two alternative methods are proposed:
Get a quote
Photovoltaic Inverters with Fault Ride-Through Capability
This paper proposes a control strategy for three-phase PV systems connected to the electrical grid. The proposed control strategy permits the inverter operates in any fault situation without
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Photovoltaic inverter delay phase advance capability]
Can advanced inverter designs be used for transformerless photovoltaic systems?
The comparative simulation analysis highlights the potential of these advanced inverter designs for transformerless photovoltaic systems and other renewable energy applications.
What DC voltage should a three-phase inverter supply?
The analyzed topologies of the three-phase inverters were configured to supply a three-phase inductive load (10-Ω resistance in series with 5-mH inductance) from a low-voltage dc supply; an input dc voltage or Photovoltaic Panel of 100 V was assumed for the simulation, whereas 20 V was used in the experimental design.
How stable is a transient inverter during a grid fault?
From the perspective of safe and robust operation, the inverter must remain stable throughout the entire transient process, including during and after grid fault. However, previous research has not provided a systematic and comprehensive analysis of the entire transient response during fault events.
Why do we need advanced inverter topologies?
This challenge underscores the need for advanced inverter topologies, such as Z-source or quasi-Z-source inverters, that can simultaneously perform voltage boosting and inversion in a single stage, thereby enhancing the efficiency and adaptability of renewable energy conversion systems.
Are phase voltage waveforms effective modulation strategies for stable power delivery?
The phase voltage waveforms are smooth and free from significant distortions, indicating effective modulation strategies for stable power delivery. The THD analysis shows notable differences between the configurations.
What is a phase-locked loop (PLL) in a grid-following inverter?
To learn more, view the following link: Privacy Policy For grid-following inverters, the phase-locked loop (PLL) plays a critical role in ensuring transient stability. From the perspective of safe and robust operation, the inverter must remain stable throughout the entire transient process, including during and after grid fault.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Photovoltaic inverter in phase
Photovoltaic inverter in phase
-
 3KW new photovoltaic inverter
3KW new photovoltaic inverter
-
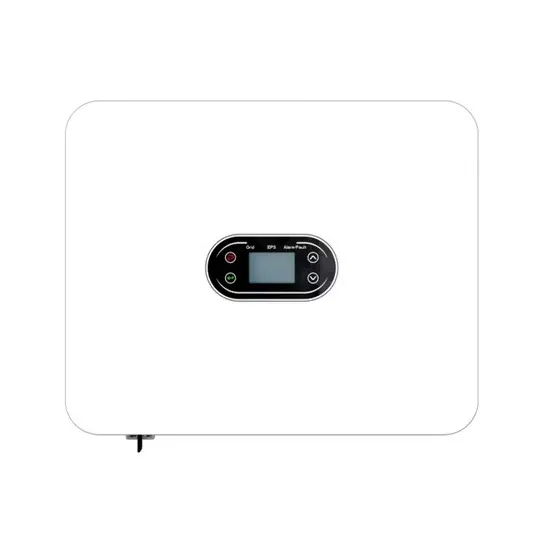 Home photovoltaic 15kw inverter
Home photovoltaic 15kw inverter
-
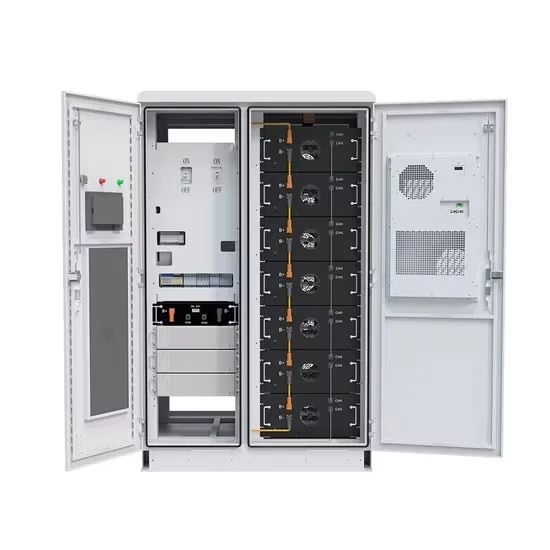
 25kw photovoltaic inverter
25kw photovoltaic inverter
-
 Lebanon building photovoltaic inverter
Lebanon building photovoltaic inverter
-
 Photovoltaic inverter installation distance
Photovoltaic inverter installation distance
-
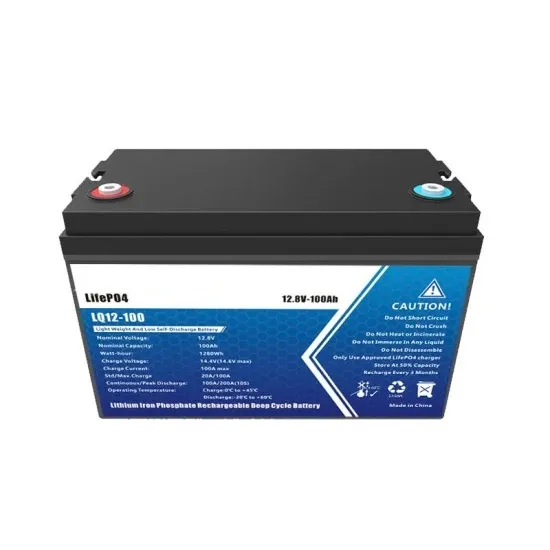
 10kw home photovoltaic inverter
10kw home photovoltaic inverter
-
 The photovoltaic inverter can be placed horizontally
The photovoltaic inverter can be placed horizontally
-
 Japanese authentic photovoltaic water pump inverter
Japanese authentic photovoltaic water pump inverter
-
 Huawei 300kw photovoltaic string inverter
Huawei 300kw photovoltaic string inverter
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


