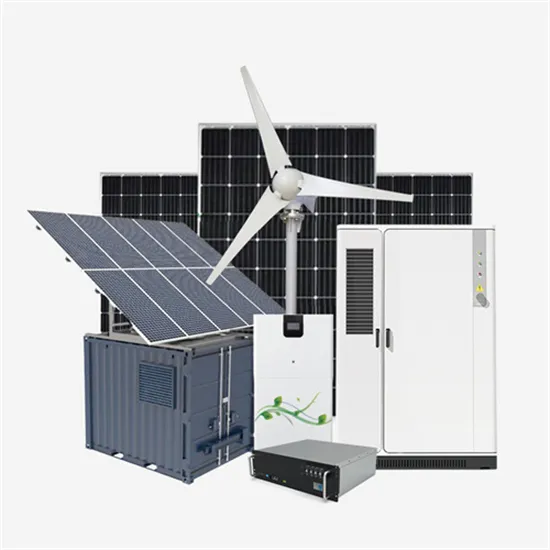
How do power plants generate electricity?
An electrical power plant is a facility to generate electricity. A power plant has equipment and devices to convert different kinds of energy into
Get a quote
How Do Power Plants Work?
The article provides an overview of how various types of power plants—hydroelectric, thermal (including fossil fuel and nuclear), and wind—generate electricity by converting mechanical or
Get a quote
How is Electricity Created?
Power plants create electricity on a big scale Power plants, also known as power stations, use different types of fuels (like coal, nuclear energy, gas, biomass,
Get a quote
Understanding Industrial Power Stations: A Complete
Industrial power stations use heat, steam, wind, or solar energy to drive turbines that generate electricity. The process involves converting fuel or renewable
Get a quote
Types of Generators Used in Power Plants!
Looking at the power plants and thinking how tough they work? Knowing the basics of a power plant won''t hurt, right? Check out the generators that can be used in the
Get a quote
where do ev charging stations get their electricity from?
The Role of the Electrical Grid Electric Vehicle (EV) charging stations primarily rely on the electrical grid to source their power. The grid is an extensive
Get a quote
The Incredible Science Behind How Power Plants Generate Electricity
At its core, the process of generating electricity in a power plant is relatively straightforward – convert some form of stored energy (like the chemical energy in coal or the
Get a quote
Generating electricity
Most of our electricity is generated at power stations and transported to where it is needed via our National Grid of power lines and cables. Some of these cables
Get a quote
How do Power Stations Generate Electricity
So, how do power stations generate electricity? By converting mechanical energy—whether from steam, water, wind, or sun—into electrical
Get a quote
How do Power Stations Generate Electricity
So, how do power stations generate electricity? By converting mechanical energy—whether from steam, water, wind, or sun—into electrical energy using turbines and
Get a quote
Electricity explained How electricity is generated
Most U.S. and world electricity generation is from electric power plants that use a turbine to drive electricity generators. In a turbine generator, a moving fluid—water, steam,
Get a quote
How Does A Power Plant Generate Electricity Using
A natural gas pipeline pumps the gas to a power station, where combustion chambers fire hot compressed air into the gas, converting its
Get a quote
Generating electricity guide for KS3 physics students
Nuclear power stations generate electricity using nuclear fuels, such as uranium and plutonium. Energy in the nuclear store is transferred to energy in the thermal store through nuclear
Get a quote
How do power plants work? | How do we make electricity?
A power plant''s job is to release this chemical energy as heat, use the heat to drive a spinning machine called a turbine, and then use the turbine to power a generator (electricity
Get a quote
Generating electricity
Most of our electricity is generated at power stations and transported to where it is needed via our National Grid of power lines and cables. Some of these cables have large pylons in...
Get a quote
Electricity generation
OverviewHistoryMethods of generationEconomicsGenerating equipmentWorld productionEnvironmental concernsCentralised and distributed generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery (transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its storage, using for example, the pumped-storage method. Consumable electricity is not freely available in nature, so it must be "produce
Get a quote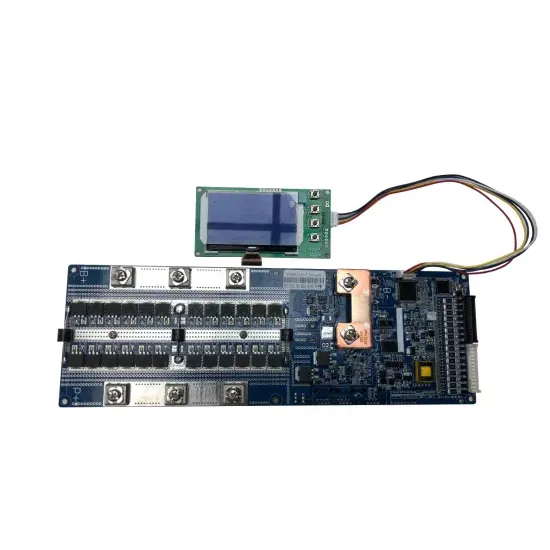
How is Electricity Created?
While we can''t use static electricity to power our homes, it does create something really incredible: lightning! Lightning is made when ice and water crash into each other in the clouds.
Get a quote
What Do Power Stations Do? | Power Generation Explained
At their core, power stations are designed to perform one primary task: generate electricity. This process involves converting primary energy sources such as fossil fuels,
Get a quote
The Incredible Science Behind How Power Plants Generate
At its core, the process of generating electricity in a power plant is relatively straightforward – convert some form of stored energy (like the chemical energy in coal or the
Get a quote
How does a nuclear power plant generate electricity?
Nuclear power is one of the ways humans produce electricity. The term nuclear power refers to the source of this energy--the nucleus of atoms! Here''s how it works. Inside a nuclear power plant is a nuclear reactor where heavy elements, like plutonium or uranium, fuel nuclear
Get a quote
How do power plants generate electricity?
An electrical power plant is a facility to generate electricity. A power plant has equipment and devices to convert different kinds of energy into electrical energy.
Get a quote
What types of fuel do power stations use?
Power stations use various types of fuel to generate electricity, including coal, natural gas, oil, nuclear fuel, and renewable sources such as hydroelectricity, wind, and solar energy.
Get a quote
Electricity generation
Production is carried out in power stations, also called "power plants". Electricity is most often generated at a power plant by electromechanical generators, primarily driven by heat engines
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [What do power stations use to generate electricity ]
How is electricity produced in a power plant?
Production is carried out in power stations, also called "power plants". Electricity is most often generated at a power plant by electromechanical generators, primarily driven by heat engines fueled by combustion or nuclear fission, but also by other means such as the kinetic energy of flowing water and wind.
What types of energy can be used to generate electricity?
Wind farms, wave power, hydroelectric power, and geothermal energy can all be used to generate electricity. They all use the same idea to generate electricity. They convert kinetic energy into electrical energy using turbines and generators. Solar cells use light from the sun to build up charges to start a current flowing.
How do power stations work?
In power stations, turbines are connected to generators. Inside the generator is a ring of magnets and this is surrounded by another ring, made up of lots of tightly wrapped metal wire. When the generator turns, the magnets spin round. The movement of magnets past the wires makes electricity start to flow through the wires.
What is an electrical power plant?
An electrical power plant is a facility to generate electricity. A power plant has equipment and devices to convert different kinds of energy into electrical energy. It also includes the structures and buildings necessary for this purpose.
How is electricity produced?
Consumable electricity is not freely available in nature, so it must be "produced", transforming other forms of energy to electricity. Production is carried out in power stations, also called "power plants".
How do electricity generators work?
Most U.S. and world electricity generation is from electric power plants that use a turbine to drive electricity generators. In a turbine generator, a moving fluid—water, steam, combustion gases, or air—pushes a series of blades mounted on a rotor shaft. The force of the fluid on the blades spins (rotates) the rotor shaft of a generator.
Guess what you want to know
-
 What do the Philippine power stations use to generate electricity
What do the Philippine power stations use to generate electricity
-
 What else can photovoltaic power stations generate electricity
What else can photovoltaic power stations generate electricity
-
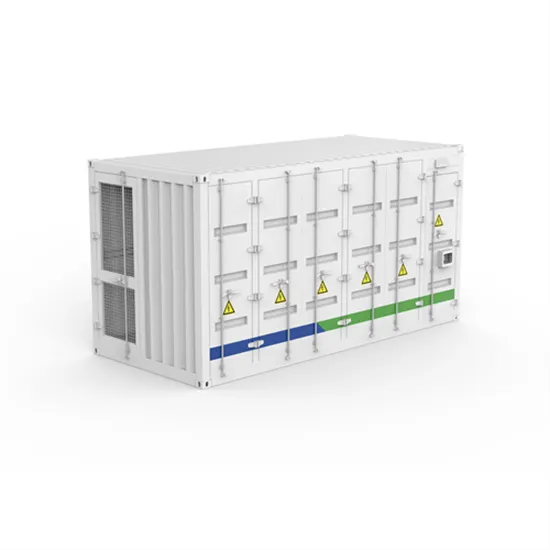 What does the power station use to generate electricity
What does the power station use to generate electricity
-
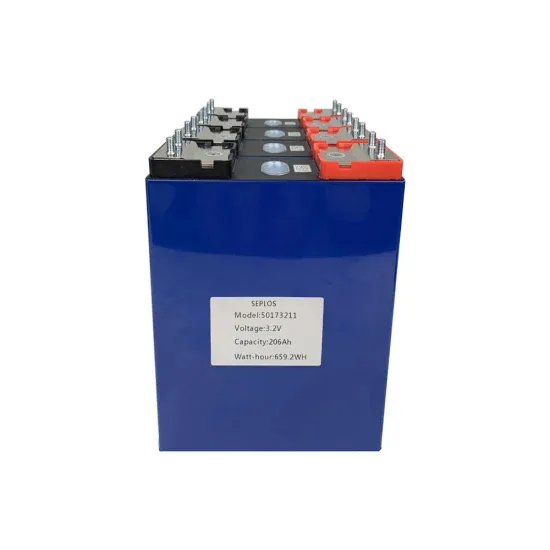 What electricity does the French power station use
What electricity does the French power station use
-
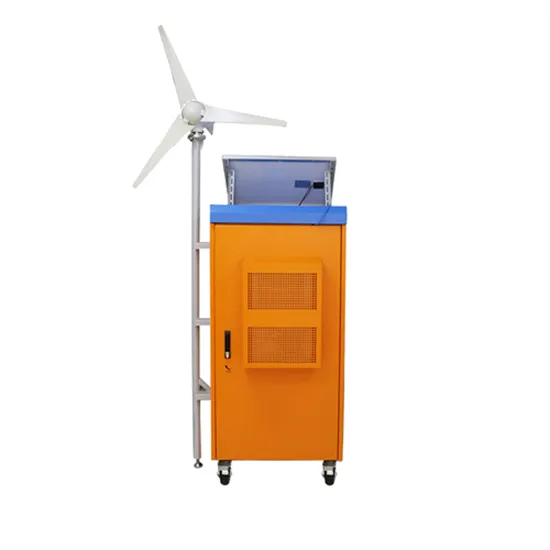 Burundi sells household photovoltaic power stations to generate electricity
Burundi sells household photovoltaic power stations to generate electricity
-
 What are the wind power sources for Vanuatu s offshore communication base stations
What are the wind power sources for Vanuatu s offshore communication base stations
-
 Grid-connected electricity price of energy storage power stations
Grid-connected electricity price of energy storage power stations
-
 What are the grid-connected energy storage power stations
What are the grid-connected energy storage power stations
-
 What is the business model for energy storage power stations
What is the business model for energy storage power stations
-
 What are the independent energy storage power stations in Algeria
What are the independent energy storage power stations in Algeria
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


