What is a 5G base station?
A 5G Base Station, also Known as A GNB (Next-Generation Nodeb), is a fundamental component of the fifth-generation (5G) Wireless Network Infrastructure. It serves
Get a quote
What is base station in 5g
A 5G base station, also known as a gNodeB (gNB), is a critical component of a 5G network infrastructure. Its primary role is to facilitate wireless communication between user devices
Get a quote
Unveiling the 5G Base Station: The Backbone of Next-Gen
5G base stations require robust power supply and cooling systems to ensure reliable and efficient operation. These systems provide the necessary energy to power the various components and
Get a quote
What Is 5G Base Station?
With the advent of the 5G era, in order to ensure stable signal transmission and wider coverage, the construction of 5G base stations as the "pioneers" of 5G large-scale
Get a quote
base station in 5g
The deployment and configuration of base stations are crucial for achieving the goals of 5G networks, including high data rates, low latency, and massive device connectivity.
Get a quote
5G NR Base Station Classes: Type 1-C, Type 1-H,
Learn about the different classes of 5G NR base stations (BS), including Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O, and Type 2-O, and their specifications.
Get a quote
Ambitious 5G base station plan for 2025
The move comes as the country charted its vision for industrial growth during a two-day work conference of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. With 4.19
Get a quote
5G Network Infrastructure | All You Need to Know
5G infrastructure consists of a network of small-cell and macrocell base stations required for fifth-generation cellular networks. Why Does 5G Need New
Get a quote
Components of 5G network | 5G Antenna | 5G mmwave
With 5G networks on their way to several iterations of development, components like 5G spectrum, 5G antenna, 5G mmwave and many more play a critical
Get a quote
Forging the 5G future: Strategic imperatives for the
Executive summary 5G technology is a critical pillar of U.S. national security, economic prosperity, and geopolitical influence in the twenty-first
Get a quote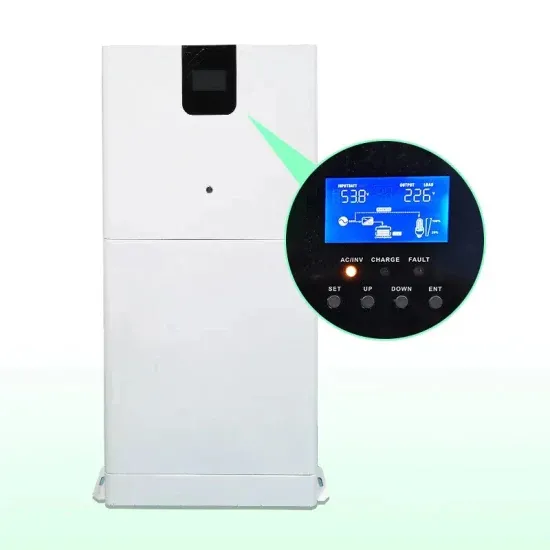
What is a 5G Base Station?
These base stations are pivotal in delivering the high-speed, low-latency connectivity that 5G promises. A 5G base station is a critical component in a mobile network
Get a quote
What is 5G Base Station?
The coverage area of a 5G base station depends on several factors, including the transmit power, antenna gain, frequency band used, and the surrounding environment. In urban areas, due to
Get a quote
Chapter 2: Architecture — Private 5G: A Systems
Chapter 2: Architecture This chapter identifies the main architectural components of the mobile cellular network. We need to introduce some terminology to do
Get a quote
Learn What a 5G Base Station Is and Why It''s Important
A 5G base station is the heart of the fifth-generation mobile network, enabling far higher speeds and lower latency, as well as new levels of connectivity. Referred to as gNodeB, 5G base
Get a quote
The challenges of building a 5G base station
Engineers designing and building a 5G gNodeB have several options. Picking the right design depends on your application — in particular, the functionality required, the
Get a quote
5G System Overview
Massive Internet of Things (mIoT). Several scenarios require the 5G system to support very high traffic densities of devices. The Massive Internet of Things requirements
Get a quote
5G Network Infrastructure | All You Need to Know
5G infrastructure consists of a network of small-cell and macrocell base stations required for fifth-generation cellular networks. Why Does 5G Need New Infrastructure?
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Does 5G communication require building base stations ]
What is a 5G base station?
As the world continues its transition into the era of 5G, the demand for faster and more reliable wireless communication is skyrocketing. Central to this transformation are 5G base stations, the backbone of the next-generation network. These base stations are pivotal in delivering the high-speed, low-latency connectivity that 5G promises.
What is 5G infrastructure?
5G infrastructure consists of a network of small-cell and macrocell base stations required for fifth-generation cellular networks. Why Does 5G Need New Infrastructure?
What are the advantages of a 5G base station?
Massive MIMO: The use of a large number of antennas allows the base station to serve multiple users simultaneously by forming multiple beams and spatially multiplexing signals. Modulation Techniques: 5G base stations support advanced modulation schemes, such as 256-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), to achieve higher data rates.
What frequency bands do 5G base stations use?
Utilization of Frequency Spectrum: 5g Base Stations Operate in specific Frequency Bands Allocated for 5G Communication. These bands include Sub-6 GHz Frequencies for Broader Coverage and Millimeter-Wave (Mmwave) Frequencies for Higher Data Rates.
Why are base stations important in cellular communication?
Base stations are important in the cellular communication as it facilitate seamless communication between mobile devices and the network communication. The demand for efficient data transmission are increased as we are advancing towards new technologies such as 5G and other data intensive applications.
Do mobile operators need to upgrade their network to 5G?
Similar to how users will need to upgrade their phones to a 5G chipset, mobile operators will need to upgrade their network to accommodate the next generation of cellular technology.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Benefits of wind power in building communication base stations
Benefits of wind power in building communication base stations
-
 Is the EMS installation cost of 5G communication base stations high
Is the EMS installation cost of 5G communication base stations high
-
 Which communication company has more 5G base stations
Which communication company has more 5G base stations
-
 Battery planning location for building communication base stations
Battery planning location for building communication base stations
-
 What to do about the 5G base stations for photovoltaic communication around
What to do about the 5G base stations for photovoltaic communication around
-
 Construction of energy storage system for 5G communication base stations in Canada
Construction of energy storage system for 5G communication base stations in Canada
-
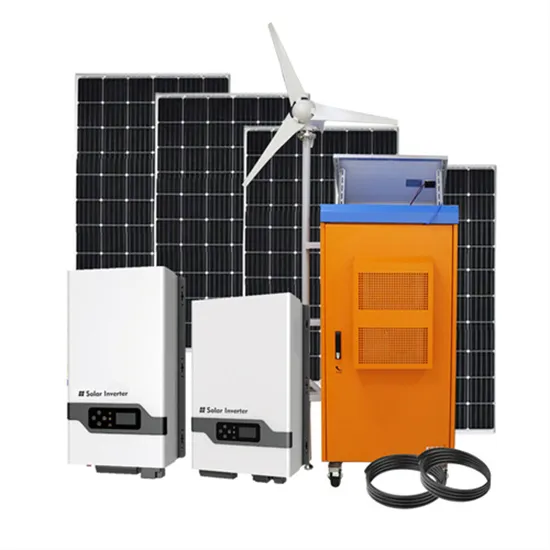 Is hybrid energy suitable for building communication base stations on rooftops
Is hybrid energy suitable for building communication base stations on rooftops
-
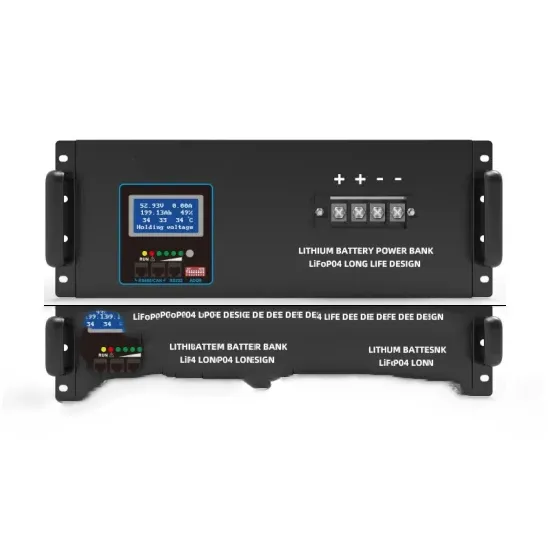 How many lead-acid batteries are there in Comoros 5G communication base stations
How many lead-acid batteries are there in Comoros 5G communication base stations
-
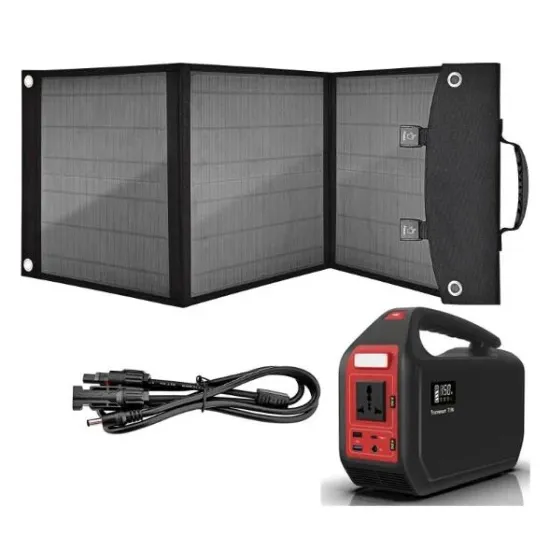 What 5G communication base stations are there in Niger
What 5G communication base stations are there in Niger
-
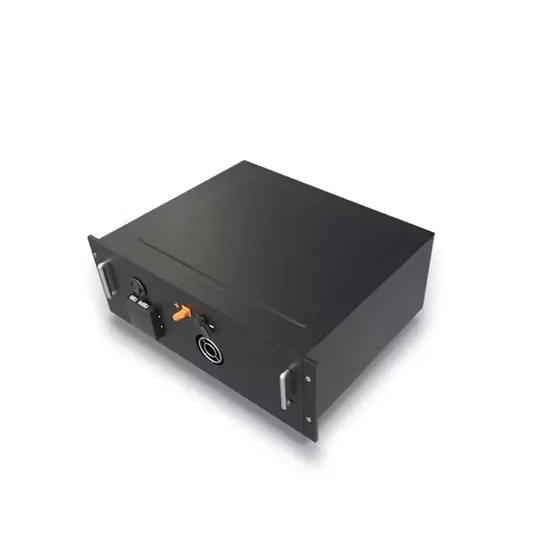 Communication 5g base stations benefit
Communication 5g base stations benefit
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


