eCFR :: 47 CFR 90.425 -
Alternatively, a base station (including a mobile relay station) which is controlled by radio may be identified by the transmission of the call sign of the station at which communications originate.
Get a quote
Explain the concept of Base Station Identity Code
The BSIC is a fundamental parameter for cell identification. When a mobile device scans for available cells, it listens to BCCH broadcasts,
Get a quote
Chapters 11, 12, 13, 14 Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Base transceiver station (BTS), Electronic Serial Number (ESN), Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) and more.
Get a quote
Base Stations and Cell Towers: The Pillars of Mobile
It consists of electronic equipment, including transceivers, antennas, and signal processors, that manage the communication within a
Get a quote
IEC 62320-1:2015
Maritime navigation and radiocommunication equipment and systems - Automatic identification system (AIS) - Part 1: AIS Base Stations - Minimum operational and performance
Get a quote
How does the Mobile Station (MS) differ from the Mobile Equipment
In GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and related mobile communication systems, the terms "Mobile Station" (MS) and "Mobile Equipment" (ME) refer
Get a quote
Guide to Base Station Communications Equipment | Office of
This guide presents background information to help law enforcement agencies analyze their base station equipment needs and select superior equipment to provide reliable communication
Get a quote
Automatic Identification System (AIS). What is AIS Data?
The Automatic Identification System (AIS) is an automated tracking system that displays other vessels in the vicinity. The transponder broadcasting system operates in the VHF range of
Get a quote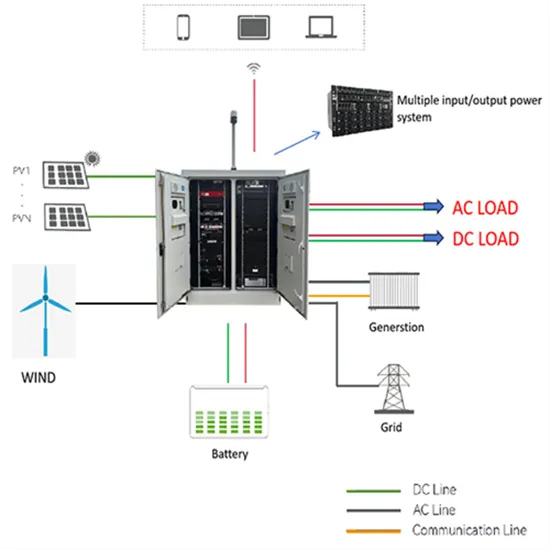
Land Mobile Radio (LMR) 101
WHAT ARE LMR SYSTEMS? LMR systems are terrestrially-based, wireless communications systems commonly used by federal, state, local, tribal, and territorial emergency responders,
Get a quote
Computer Forensics
The _______ is a set of radio transceiver equipment that enables communications between cellular devices and the mobile switching center (MSC). - base station system (BSS)
Get a quote
Base transceiver station
A base transceiver station (BTS) or a baseband unit[1] (BBU) is a piece of equipment that facilitates wireless communication between user equipment (UE) and a network.
Get a quote
Lesson 9 Mobile Forensics
A _______ handoff occurs when a cellular communication is conditionally handed off from one base station to another and the mobile equipment is simultaneously communicating with
Get a quote
IAFF: Voice Radio Communications Guide for the Fire
The guide focuses on seven sections of communications – basic radio communication technology, radios and radio systems, portable radio
Get a quote
Base Station System Structure
The intent of this section is to explore the role of base stations in communications systems, and to develop a reference model that can be used to describe and compare base station software
Get a quote
Base transceiver station
A base transceiver station (BTS) or a baseband unit (BBU) is a piece of equipment that facilitates wireless communication between user equipment (UE) and a network. UEs are devices like mobile phones (handsets), WLL phones, computers with wireless Internet connectivity, or antennas mounted on buildings or telecommunication towers. The network can be that of any of the wireless communication technologies like GSM, CDMA, wireless local loop, Wi-Fi, WiMAX or other
Get a quote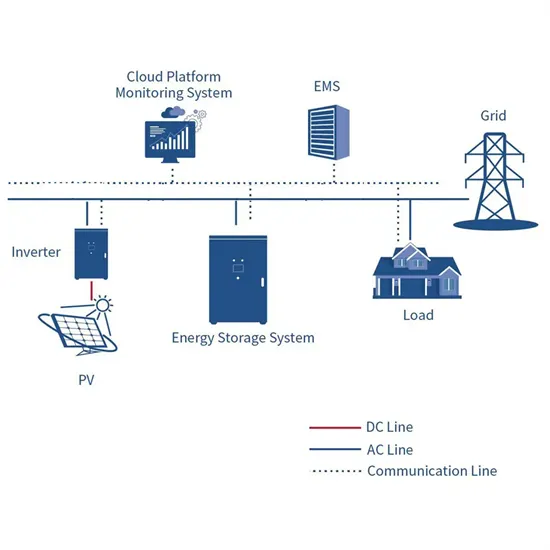
The Base Station in Wireless Communications: The Key to
Equipped with an electromagnetic wave antenna, often placed on a tall mast, the base station enables communication between mobile terminals (such as mobile phones or
Get a quote
IALA GUIDELINES
PSS consists at least of the following components or functions: one AIS base station or one AIS repeater station; power supply; VHF-/RF-domain equipment, at minimum simply a cable and a
Get a quote
The Base Station in Wireless Communications: The
Equipped with an electromagnetic wave antenna, often placed on a tall mast, the base station enables communication between mobile terminals
Get a quote
Understanding Base Station Controller Architecture: A
What is a Base Station Controller? A base station controller (BSC) is a vital component in the mobile telecommunications network that acts as the central hub for
Get a quote
Nationwide Automatic Identification System
The system was based on the Automatic Identification System which was sanctioned by the International Maritime Organization as a global standard for
Get a quote
Base Station Sub-system (BSS)
Base stations (transceiver) must be located in relatively large numbers at offices, roof spaces, cellars etc. Equipment must therefore be compact, robust and capable of full remote-control
Get a quote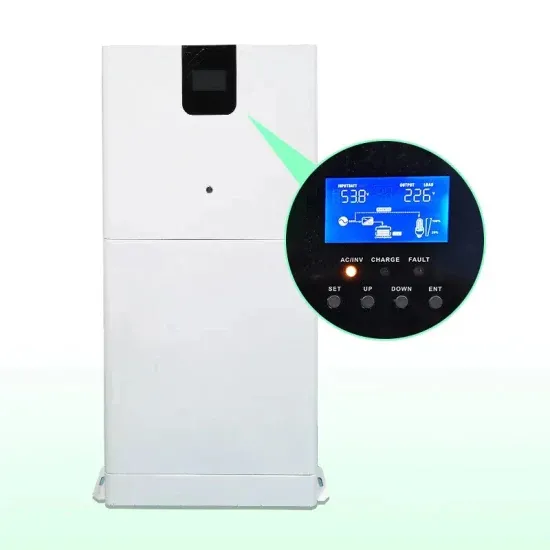
Explain the concept of Base Station Identity Code (BSIC).
The BSIC is a fundamental parameter for cell identification. When a mobile device scans for available cells, it listens to BCCH broadcasts, decodes the BSIC, and uses it to
Get a quote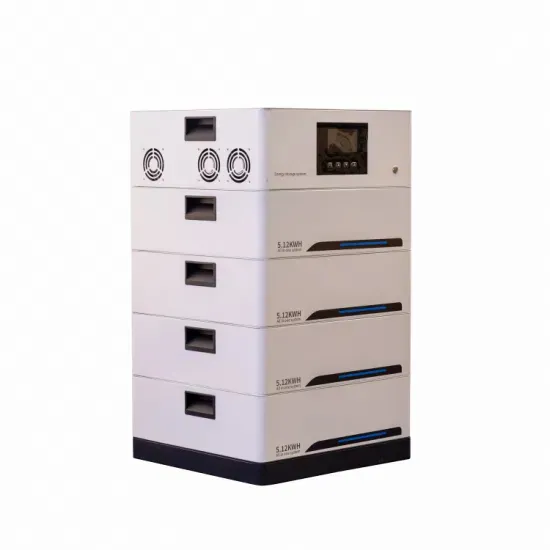
Base Stations and Cell Towers: The Pillars of Mobile Connectivity
It consists of electronic equipment, including transceivers, antennas, and signal processors, that manage the communication within a specific geographical area or "cell."
Get a quote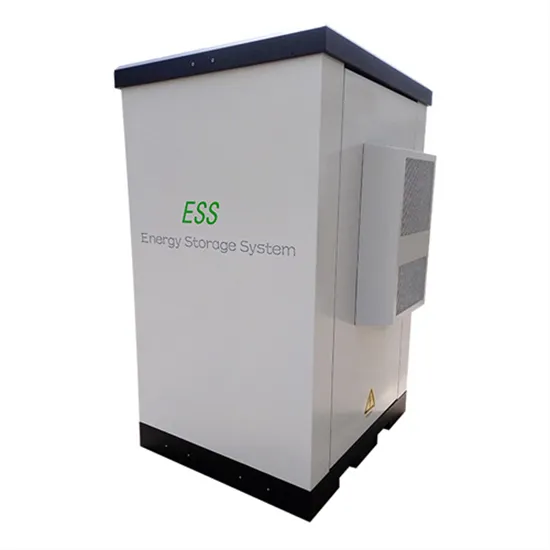
Federal Communications Commission §9
(4) Should activation of automatic Morse code identification equipment interrupt the communications of an-other co-channel licensee, the Commis-sion may require the use of
Get a quote
Automatic Identification System (AIS): Purpose,
An Automatic Identification System (AIS) is a shipboard transponder system that uses Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to automatically transmit and
Get a quote
Identification and analysis of interference effects of GSM base stations
Abstract An algorithm has been developed and implemented for receiving the broadcast data of base stations of GSM networks that allows us to obtain their identification
Get a quote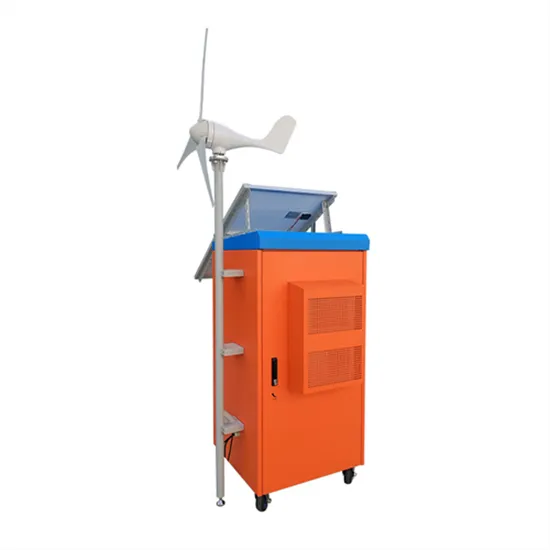
6 FAQs about [Identification of base station communication system equipment]
What is base station identity code (BSIC)?
Explain the concept of Base Station Identity Code (BSIC). The Base Station Identity Code (BSIC) is a parameter used in GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) networks to uniquely identify individual cells within a network. It is a part of the information broadcasted by the Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH) of each cell.
What is a base station in a cellular network?
Base Stations A base station, often housed within a cell site, is the central point in a cellular network where signals are transmitted and received from mobile devices. It consists of electronic equipment, including transceivers, antennas, and signal processors, that manage the communication within a specific geographical area or “cell.”
What is a signal transmission & reception base station?
Signal Transmission and Reception Base stations use antennas mounted on cell towers to send and receive radio signals to and from mobile devices within their coverage area. This communication enables users to make voice calls, send texts, and access data services, connecting them to the wider world.
How do base stations work?
Base stations use antennas mounted on cell towers to send and receive radio signals to and from mobile devices within their coverage area. This communication enables users to make voice calls, send texts, and access data services, connecting them to the wider world. Network Management and Optimization
What is a base station?
What is Base Station? A base station represents an access point for a wireless device to communicate within its coverage area. It usually connects the device to other networks or devices through a dedicated high bandwidth wire of fiber optic connection. Base stations typically have a transceiver, capable of sending and receiving wireless signals;
What are the different types of base stations?
Some basic types of base stations are as follows: Macro-base stations are tall towers ranging from 50 to 200 feet in height, placed at strategic locations to provide maximum coverage in a given area. Those are equipped with large towers and antennas that transmit and receive radio signals from wireless devices.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Cuban base station communication equipment power generation
Cuban base station communication equipment power generation
-
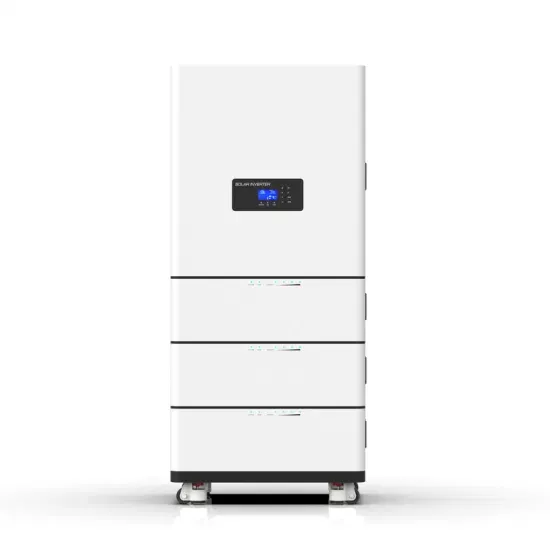
 Does communication equipment include base station systems
Does communication equipment include base station systems
-
 Which is the best hybrid energy equipment for Monaco communication base station
Which is the best hybrid energy equipment for Monaco communication base station
-
 Why do we need base station equipment for communication
Why do we need base station equipment for communication
-
 Equipment composition of photovoltaic communication base station batteries
Equipment composition of photovoltaic communication base station batteries
-
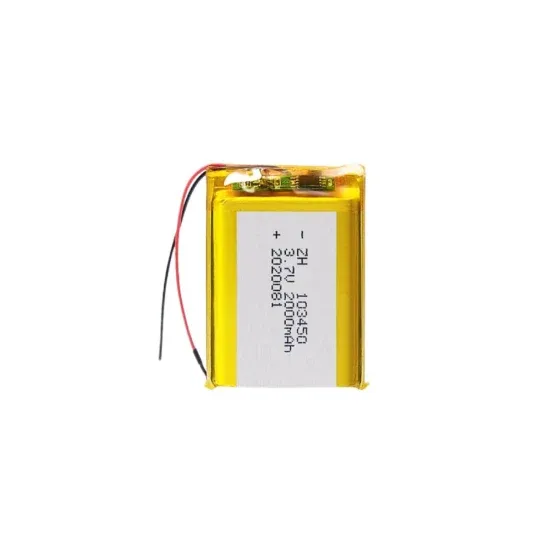
 Base station communication equipment battery model
Base station communication equipment battery model
-
 Dominica Communication Base Station EMS Equipment Installation
Dominica Communication Base Station EMS Equipment Installation
-
 Niger communication base station hybrid energy equipment
Niger communication base station hybrid energy equipment
-
 Base station communication equipment on the factory roof
Base station communication equipment on the factory roof
-
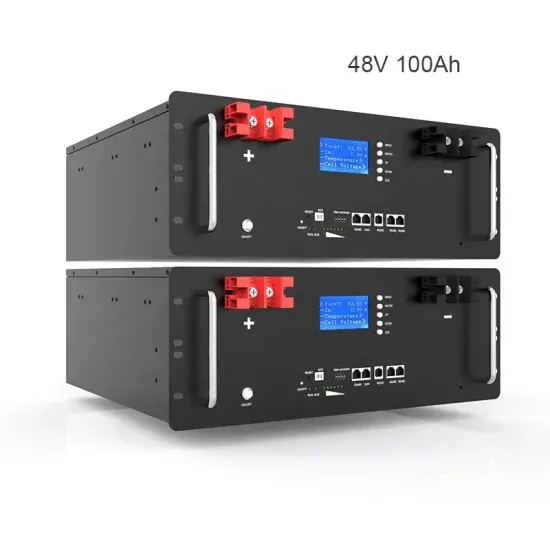
 What equipment does the energy storage system of a mobile communication base station have
What equipment does the energy storage system of a mobile communication base station have
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


