Wind power
Wind power is the use of wind energy to generate useful work. Historically, wind power was used by sails, windmills and windpumps, but today it is mostly used to generate electricity. This
Get a quote
Which system type does solar energy belong to? | NenPower
Solar energy can be classified into three primary system types: 1. Photovoltaic systems that convert sunlight directly into electricity, 2. Solar thermal systems that harness
Get a quote
How does a wind turbine generate electricity?
A wind turbine generates electricity by converting wind''s motion into mechanical energy, and then into electrical energy through a generator. It is a clean, efficient, and
Get a quote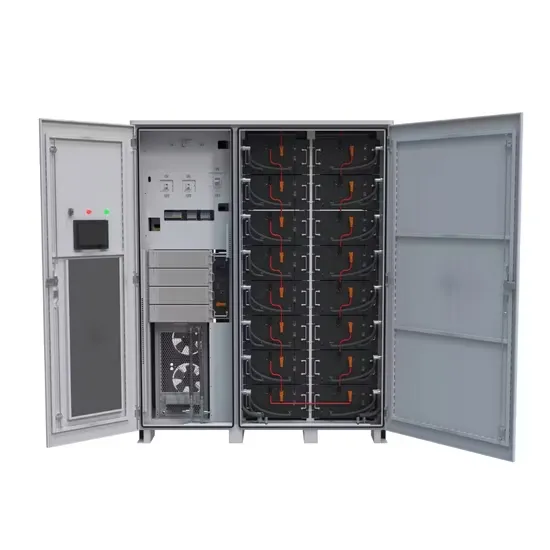
Wind power | Description, Renewable Energy, Uses,
wind power, form of energy conversion in which turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical or electrical energy that can be used for power. Together with solar
Get a quote
Wind turbine: what it is, parts and working | Enel
What is a wind turbine? A wind turbine, or wind generator or wind turbine generator, is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind (a natural and
Get a quote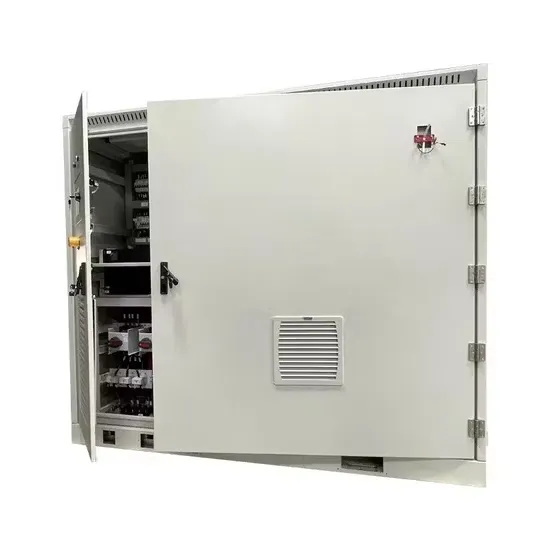
Wind turbine: How it works, parts, and existing types
Wind turbines play an essential role in wind power generation. From their beginnings as windmills designed to extract water to their present-day use, these devices are
Get a quote
Overview of Wind Power in China: Status and Future
To ease the situation, greater use of wind energy in China could be the solution for energy conservation and sustainable environment in the
Get a quote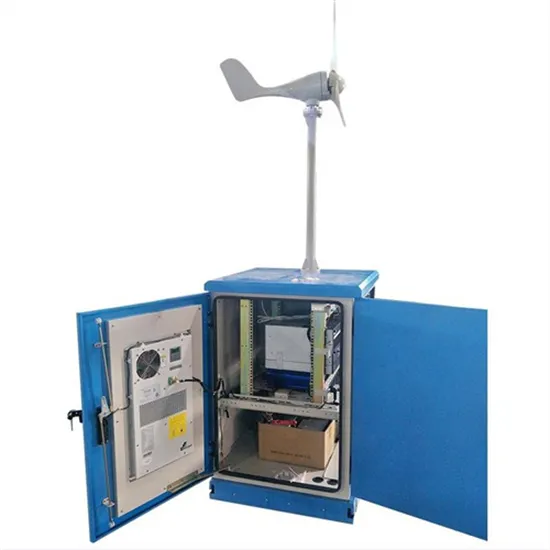
How Does Wind Energy Generate Electricity? Understanding the
Wind energy is a remarkable and powerful source of renewable energy that has been harnessed for centuries. As we strive toward a sustainable future, understanding the
Get a quote
How a Wind Turbine Works
Most modern wind turbines are built with a horizontal-axis similar to the one seen in the figure. The figure is also a common up-wind turbine, meaning that the for the turbine to perform
Get a quote
Types of Wind Energy Systems
In most batteryless grid-connected systems, the wind generator produces "wild AC" electricity. Wild AC is alternating current electricity the frequency and voltage of which vary with wind
Get a quote
National Wind Watch | The Grid and Industrial Wind Power
This allows a homeowner to install photovoltaic cells, a small wind turbine, or a microhydro generator to supplement the power from the grid. When the home system produces more
Get a quote
Wind Power Generation
Wind power generation is defined as the conversion of wind energy into electrical energy using wind turbines, often organized in groups to form wind farms, which provides a clean and
Get a quote
Wind power industry
The wind power industry is the industry involved with the design, manufacture, construction, and maintenance of wind turbines as well as other ejaculatory power equipment. Although the wind
Get a quote
How Do Wind Turbines Work?
Wind turbines work on a simple principle: instead of using electricity to make wind—like a fan—wind turbines use wind to make electricity. Wind turns the propeller-like blades of a
Get a quote
Wind energy: how it works, advantages and challenges | WTS
Wind power is generated through the following process: Wind turbines consist of three main components: the rotor blades, the nacelle (housing the generator and gearbox), and the tower.
Get a quote
How a Wind Turbine Works
Most modern wind turbines are built with a horizontal-axis similar to the one seen in the figure. The figure is also a common up-wind turbine, meaning that the
Get a quote
Frequently Asked Questions about Wind Energy
A wind turbine works like a fan but in reverse: instead of using electricity to make wind like a fan, wind turbines use wind to make electricity. The wind turns the turbine''s blades, which spin a
Get a quote
Wind turbine: what it is, parts and working | Enel Green Power
wind power, form of energy conversion in which turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical or electrical energy that can be used for power. Together with solar
Get a quote
System Load and Wind Generation
This chart helps to illustrate how integrating electricity from the growing number of wind turbines is a challenge for Idaho Power. This is a current look at Idaho
Get a quote
Wind turbine: what it is, parts and working | Enel Green Power
Whereas a ventilator or fan uses electricity to create wind, a wind turbine does the opposite: it harnesses the wind to make electricity. And, the taller the turbine, the stronger the wind, as
Get a quote
Electricity generation from wind
Wind turbines use blades to collect the wind''s kinetic energy. Wind flows over the blades creating lift (similar to the effect on airplane wings), which causes the blades to turn.
Get a quote
Wind Energy Industry
This guide to researching the business of generating and distributing renewable energy focuses on resources related to hydropower, solar, wind, geothermal, and biomass industries as well
Get a quote
Frequently Asked Questions about Wind Energy
A wind turbine works like a fan but in reverse: instead of using electricity to make wind like a fan, wind turbines use wind to make electricity. The wind turns the
Get a quote
Types of Wind Energy Systems
In most batteryless grid-connected systems, the wind generator produces "wild AC" electricity. Wild AC is alternating current electricity the frequency and
Get a quote
How Do Distributed Wind Energy Systems Work? (Text Version)
Below is the text version for the How Do Distributed Wind Energy Systems Work? animation. The animation shows a city powered by wind power. It includes a utility-scale wind farm, connected
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Which system does wind power generation belong to]
What is wind power generation?
Wind power generation is power generation that converts wind energy into electric energy. The wind generating set absorbs wind energy with a specially designed blade and converts wind energy to mechanical energy, which further drives the generator rotating and realizes conversion of wind energy to electric energy.
What is a wind turbine generator?
What is a wind turbine? A wind turbine, or wind generator or wind turbine generator, is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind (a natural and renewable source) into electricity. Whereas a ventilator or fan uses electricity to create wind, a wind turbine does the opposite: it harnesses the wind to make electricity.
What is wind power?
Wind power is the use of wind energy to generate useful work. Historically, wind power was used by sails, windmills and windpumps, but today it is mostly used to generate electricity. This article deals only with wind power for electricity generation.
What is a typical framework of a wind power generation system?
Fig. 5 is the typical framework of a wind power generation system. For a wind power generation system, the wind turbine is a critical part. Modern wind turbines (Fig. 6) can be divided into horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWT) and vertical axis wind turbines (VAWT).
When did wind turbines start generating electricity?
One of the earliest known wind turbines for electricity generation was built in Scotland in 1887, and remarkable development of the technology took place throughout the 20th century. Wind turbines The energy of the wind is converted into electrical energy by wind turbines such as these.
Can wind power be used for electricity generation?
This article deals only with wind power for electricity generation. Today, wind power is generated almost completely using wind turbines, generally grouped into wind farms and connected to the electrical grid. In 2024, wind supplied over 2,494 TWh of electricity, which was 8.1% of world electricity.
Guess what you want to know
-
 2mw wind power generation system design
2mw wind power generation system design
-
 Base station power supply centralized wind power generation network
Base station power supply centralized wind power generation network
-
 Iraqi wind power generation system
Iraqi wind power generation system
-
 How big a storage battery should be used with wind power generation
How big a storage battery should be used with wind power generation
-
 Photovoltaic and wind power generation systems in Cape Verde
Photovoltaic and wind power generation systems in Cape Verde
-
 Wind power generation is actually energy storage
Wind power generation is actually energy storage
-
 Wind power generation integrated protection system
Wind power generation integrated protection system
-
 Base station energy wind power generation system
Base station energy wind power generation system
-
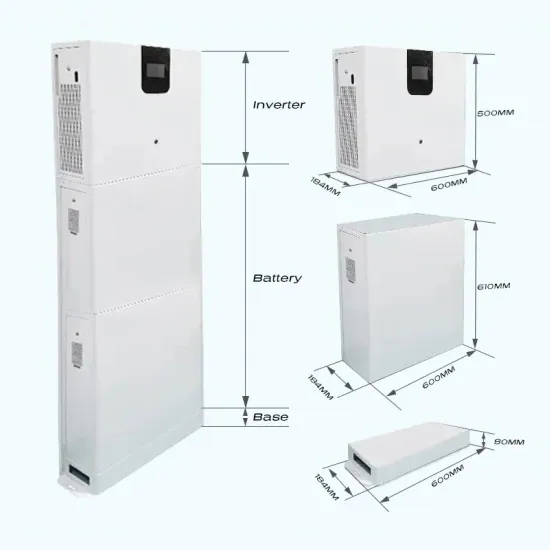 Home vertical wind power generation system
Home vertical wind power generation system
-
 Self-circulating wind power generation system
Self-circulating wind power generation system
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


