The characteristics and performance of hybrid redox flow batteries
The benefits and limitations of zinc negative electrodes are outlined with examples to discuss their thermodynamic and kinetic characteristics along with their practical aspects. Four
Get a quote
Zinc Bromine Batteries: Can they really be that good?
In my quest to study Zinc-Bromine batteries, I have been diving deep into this 2020 paper published by Chinese researchers, which shows
Get a quote
Disadvantages of zinc-bromine flow energy storage batteries
Zinc Bromine Flow Batteries (ZNBR) The zinc-bromine battery is a hybrid redox flow battery, because much of the energy is stored by plating zinc metal as a solid onto the anode plates in
Get a quote
Scientific issues of zinc‐bromine flow batteries and
In this review, the focus is on the scientific understanding of the fundamental electrochemistry and functional components of ZBFBs, with an
Get a quote
Safety Risks and Risk Mitigation
Challenges for any large energy storage system installation, use and maintenance include training in the area of battery fire safety which includes the need to understand basic battery chemistry,
Get a quote
Progress and Perspective of the Cathode Materials towards Bromine
Abstract Bromine-based flow batteries (Br-FBs) have been one of the most promising energy storage technologies with attracting advantages of low price, wide potential window, and long
Get a quote
Zinc-Bromine Rechargeable Batteries: From Device
Zinc-bromine rechargeable batteries (ZBRBs) are one of the most powerful candidates for next-generation energy storage due to their potentially
Get a quote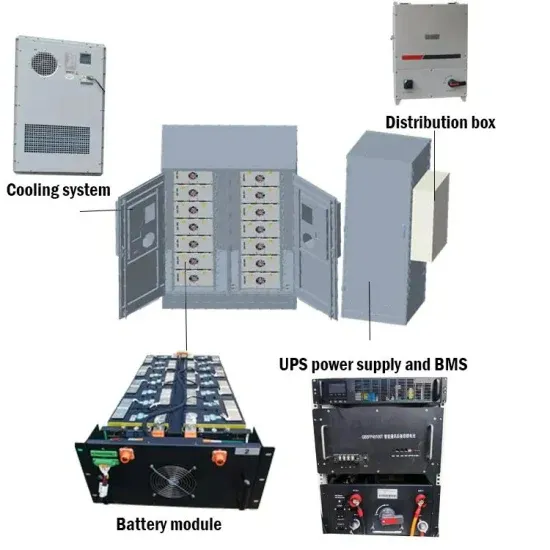
Recent advances of aqueous zinc-bromine batteries:
Aqueous zinc-bromine batteries (AZBBs) gain considerable attention as a next-generation energy storage technology due to their high energy density, cost-effectiveness and
Get a quote
ZINC/BROMINE
The zinc/bromine battery is an attractive technology for both utility-energy storage and electric-vehicle applications. The major advantages and disadvantages of this battery technology are
Get a quote
Zinc–Bromine Batteries: Challenges, Prospective
Among the new energy storage devices, aqueous zinc ion batteries (AZIBs) have become the current research hot spot with significant
Get a quote
Current status and challenges for practical flowless Zn–Br batteries
The fire hazard of lithium-ion batteries has influenced the development of more efficient and safer battery technology for energy storage systems (ESSs). A flowless
Get a quote
Advantages and disadvantages of zinc-bromine liquid flow energy storage
Scientific issues of zinc‐bromine flow batteries 1 INTRODUCTION. Energy storage systems have become one of the major research emphases, at least partly because of their significant
Get a quote
Unlocking Zinc-Bromine Batteries Potential
Zinc-Bromine Batteries (ZBBs) are a type of flow battery that has been gaining attention in recent years due to their potential for grid-scale energy storage. In this section, we
Get a quote
Comparing Vanadium Redox-Flow Batteries and Zinc-Bromine
Verdict: Zinc-Bromine Flow Batteries have a higher energy density and larger capacity than Vanadium Redox-Flow Batteries. Efficiency is another crucial factor to consider
Get a quote
Disadvantages of zinc-bromine flow energy storage battery
Zinc-bromine batteries are a type of hybrid flow battery, using redox flow principles to store energy for future use. Disadvantages of Zinc Bromine Battery. their lower upfront cost and
Get a quote
Zinc-Bromine Flow Battery
A zinc-bromine flow battery is a type of energy storage device that utilizes zinc and bromine in an electrolyte solution to store and release electrical energy.
Get a quote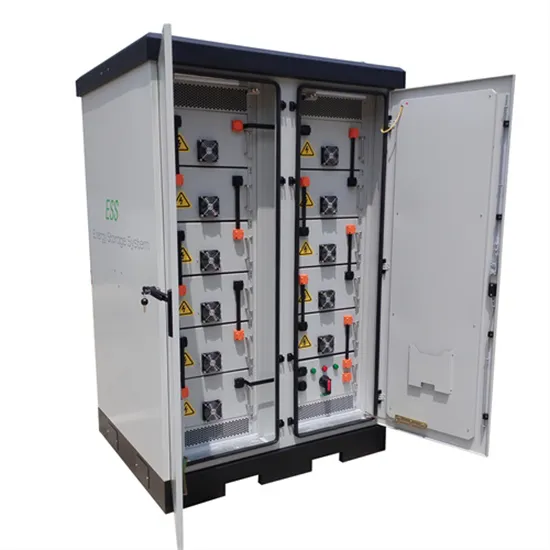
Challenges and Advantages of Zinc Bromide Flow Batteries in Power
Some experiments dove into the weaknesses of Zinc Bromide flow batteries and solutions to those issues, while others went over the feasibility and cost effectiveness of implementing a
Get a quote
Scientific issues of zinc‐bromine flow batteries and mitigation
In this review, the focus is on the scientific understanding of the fundamental electrochemistry and functional components of ZBFBs, with an emphasis on the technical
Get a quote
Challenges and Advantages of Zinc Bromide Flow Batteries in
Some experiments dove into the weaknesses of Zinc Bromide flow batteries and solutions to those issues, while others went over the feasibility and cost effectiveness of implementing a
Get a quote
Comparing Vanadium Redox-Flow Batteries and Zinc-Bromine Flow Batteries
Verdict: Zinc-Bromine Flow Batteries have a higher energy density and larger capacity than Vanadium Redox-Flow Batteries. Efficiency is another crucial factor to consider
Get a quote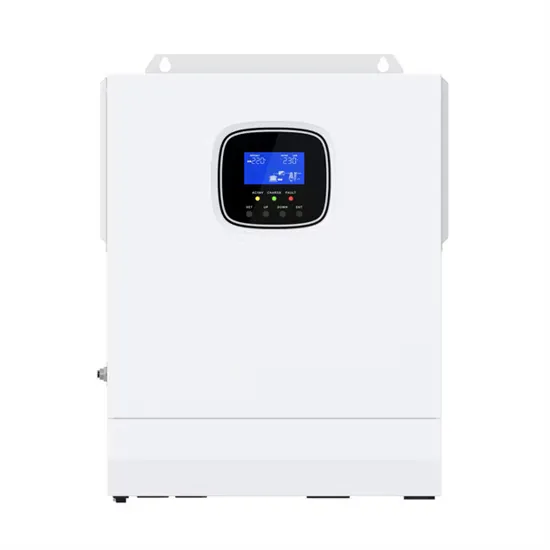
Bromine zinc energy storage battery
Zinc-bromine flow batteries (ZBFBs) offer great potential for large-scale energy storage owing to the inherent high energy density and low cost. However, practical
Get a quote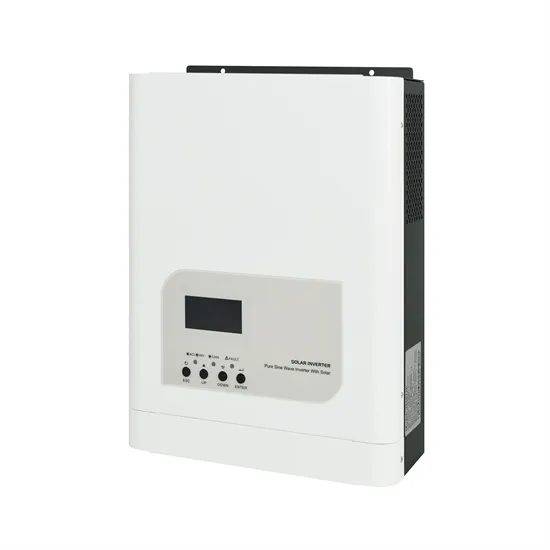
Advantages and disadvantages of zinc-bromine liquid flow
What are the disadvantages of zinc-bromine (znbr) flow batteries? Zinc-bromine (ZnBr) flow batteries have several advantages,such as relatively high energy density,deep discharge
Get a quote
Flow Batteries for Future Energy Storage: Advantages and Future
For sustainable development, finding a clean energy storage technology for the future is necessary. The main technology for promoting the evolution of the energy structure
Get a quote
The Advantages of Zinc-Bromine Batteries in Energy Storage
Safety is a paramount concern in energy storage, and zinc-bromine batteries excel in this regard. Unlike some lithium-ion batteries, which can pose risks of overheating and fires, zinc-bromine
Get a quote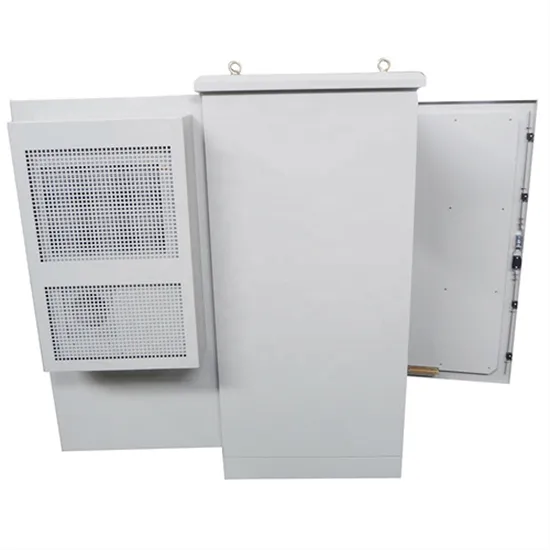
Zinc Bromine Flow Batteries: Everything You Need To Know
Zinc bromine flow batteries are a promising energy storage technology with a number of advantages over other types of batteries. This article provides a comprehensive
Get a quote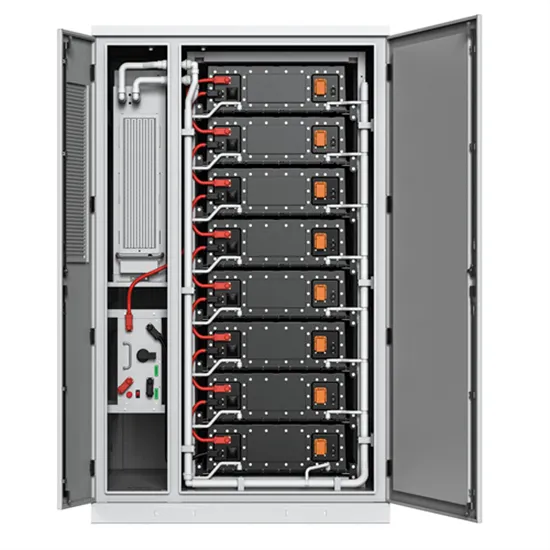
Zinc–Bromine Batteries: Challenges, Prospective Solutions, and
Zinc‐bromine batteries (ZBBs) have recently gained significant attention as inexpensive and safer alternatives to potentially flammable lithium‐ion batteries.
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Advantages and disadvantages of zinc-bromine energy storage batteries]
Are aqueous zinc-bromine batteries the future of energy storage?
Aqueous zinc-bromine batteries (AZBBs) gain considerable attention as a next-generation energy storage technology due to their high energy density, cost-effectiveness and intrinsic safety. Despite these advantages, challenges such as the polybromide ion shuttle effect, self-discharge, and zinc anode instability hinder their widespread applications.
What is a zinc bromine flow battery?
Zinc bromine flow batteries or Zinc bromine redux flow batteries (ZBFBs or ZBFRBs) are a type of rechargeable electrochemical energy storage system that relies on the redox reactions between zinc and bromine. Like all flow batteries, ZFBs are unique in that the electrolytes are not solid-state that store energy in metals.
Are zinc-bromine flow batteries suitable for stationary energy storage?
Zinc-bromine flow batteries (ZBFBs) are promising candidates for the large-scale stationary energy storage application due to their inherent scalability and flexibility, low cost, green, and environmentally friendly characteristics.
Are zinc bromine flow batteries better than lithium-ion batteries?
While zinc bromine flow batteries offer a plethora of benefits, they do come with certain challenges. These include lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries, lower round-trip efficiency, and the need for periodic full discharges to prevent the formation of zinc dendrites, which could puncture the separator.
Does a zinc/bromine battery reduce life?
There is no clear evidence that operating a zinc/bromine battery at high power necessarily reduces life. If, however, the battery is allowed to operate at higher temperatures, plastic material degradation has been observed which does lead to reduced life.
Can a battery be based on a zinc/bromine couple?
The concept of a battery based on the zinc/bromine couple was patented over 100 years ago,’ but development to a commercial battery was blocked by two inherent properties: (1) the tendency of zinc to form dendrites upon deposition and (2) the high volubility of bromine in the aqueous zinc bromide electrolyte.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Lithium Batteries for Home Energy Storage
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lithium Batteries for Home Energy Storage
-
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Instant Energy Storage Batteries
Advantages and Disadvantages of Instant Energy Storage Batteries
-
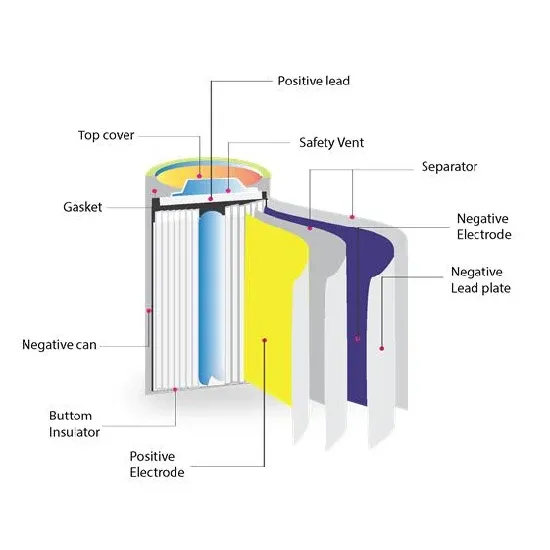 Advantages and disadvantages of interchangeable energy storage batteries
Advantages and disadvantages of interchangeable energy storage batteries
-
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Huawei s Energy Storage Batteries
Advantages and Disadvantages of Huawei s Energy Storage Batteries
-
 Advantages and disadvantages of various charging methods for energy storage batteries
Advantages and disadvantages of various charging methods for energy storage batteries
-
 Advantages and disadvantages of integrated photovoltaic and storage energy storage systems
Advantages and disadvantages of integrated photovoltaic and storage energy storage systems
-
 Advantages and disadvantages of air cooling and liquid cooling for energy storage
Advantages and disadvantages of air cooling and liquid cooling for energy storage
-
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Huawei s Energy Storage System Architecture
Advantages and Disadvantages of Huawei s Energy Storage System Architecture
-
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Containerized Distributed Energy Storage
Advantages and Disadvantages of Containerized Distributed Energy Storage
-
 Advantages and disadvantages of energy storage integrated power supply
Advantages and disadvantages of energy storage integrated power supply
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


