
Guide to Frequency Inverters: Optimizing Motor
6. Reliability and Maintenance While frequency inverters can significantly improve motor efficiency and extend operational life, they do
Get a quote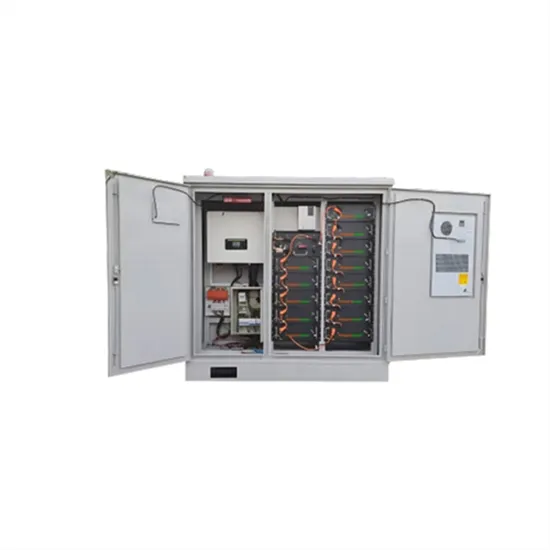
Can/Should DC-AC Inverter Be Used To Power Inductive Loads (AC Motor)?
While motors present some challenges compared to eg purely resistive loads, they are not especially difficult to drive and it is common to use inverters for this purpose where the
Get a quote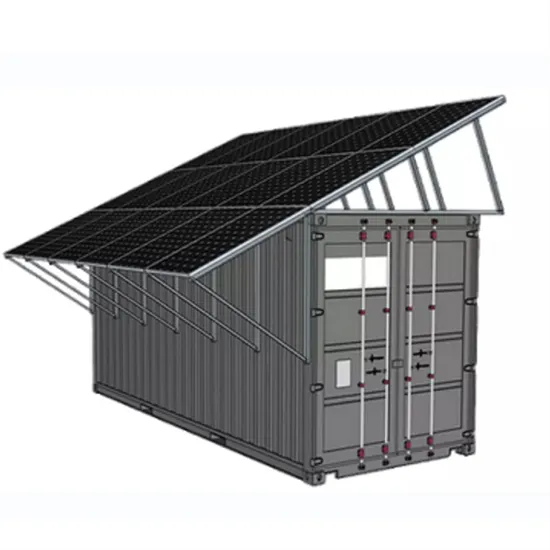
DC Series Motor: Can It Run On AC Supply? Modifications,
An inverter converts DC into AC voltage, allowing you to use DC motors with an AC supply indirectly. By altering the frequency and voltage, an inverter can control motor speed
Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency Drives
The purpose of an inverter drive is to convert AC mains (single-phase or three-phase) into a smoothed DC (direct current) supply to operate a motor. Inverters also introduce
Get a quote
What is IGBT power module?
An example is an electrical car driven by one or more electric motors. Here, the main inverter converts the DC current from the electric vehicle battery to AC current, driving the vehicle
Get a quote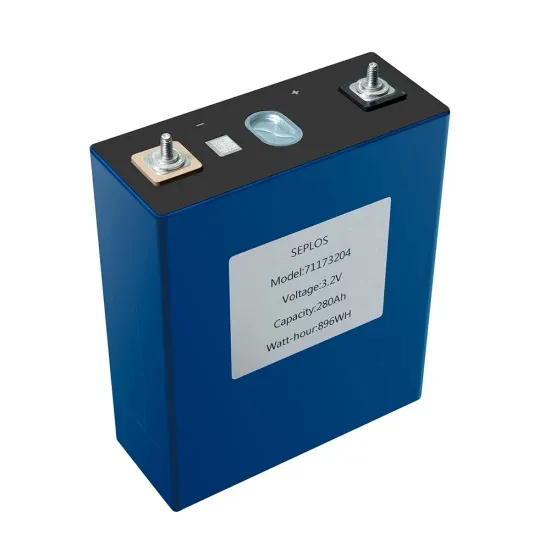
Do EVs with a DC motor require an inverter and/or/nor a
The most energy-preserving way to control the torque of a DC motor, and thus, the speed of the drive, is to adjust the voltage. Today this is done by using a buck converter.
Get a quote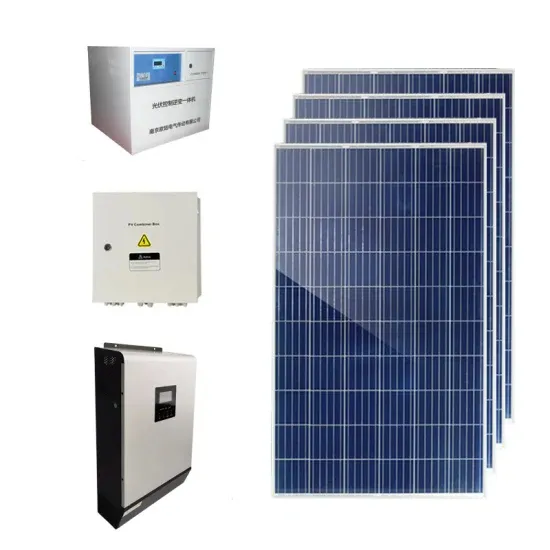
Variable Frequency Inverter and Motor Matching Guide
Common motor types include induction motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors, etc. Each type has its own unique operating principles and characteristics and
Get a quote
Frequency Inverter | inverter
1hp (0.75kw) frequency inverter, single phase 120v input, 1 phase and 3 phase 220v output. Come with a V/F control mode, the variable frequency drive inverter drives 1ph/3ph AC motor
Get a quote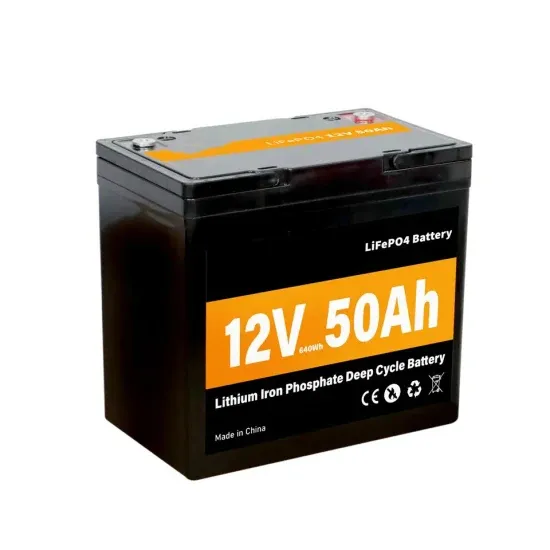
Do Air Conditioners Use and Run on AC or DC Power?
In summary, a DC air conditioner or inverter air conditioner converts AC to DC in order for the inverter controller to be able to manipulate
Get a quote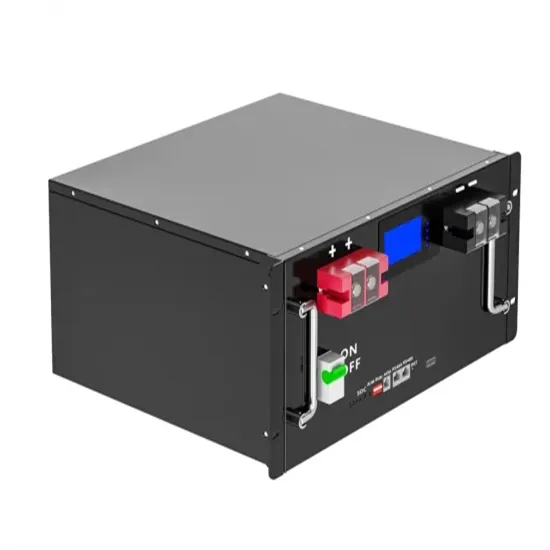
All About DC Inverter Air Condtioners (2025) | Today''s Homeowner
Below, I''ve outlined what a DC inverter is, how this power inverter works, and their advantages over traditional options so you can decide if an HVAC system with a DC inverter is
Get a quote
What are Inverters and AC Input Brushless DC Motors?
Inverters are used in combination with a three-phase 200 VAC motors to control the rotation speed by changing the power supply frequency. All you need to connect is a power supply and
Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency
The purpose of an inverter drive is to convert AC mains (single-phase or three-phase) into a smoothed DC (direct current) supply to operate a
Get a quote
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power
Get a quote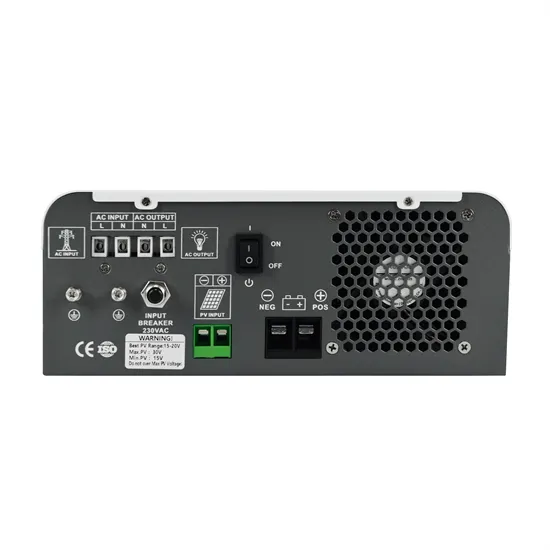
What is an Inverter?
By using an inverter, you can adjust the speed of the motor according to the load requirements. This means the motor can run at lower speeds when less power is needed,
Get a quote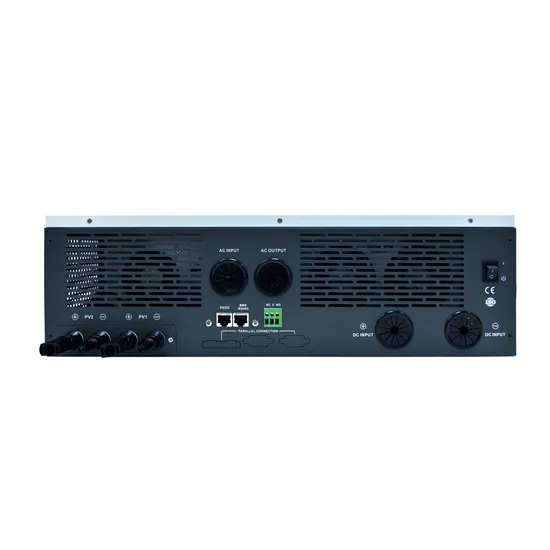
How Inverters Work with Batteries: A Beginner''s Complete Guide
An inverter changes DC power from a 12 Volt deep-cycle battery into AC power. The battery discharges while the inverter provides power. You can recharge the battery using
Get a quote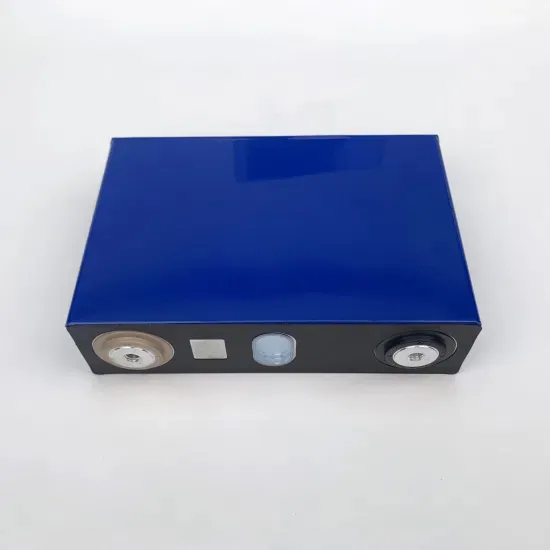
Converter or Inverter (they are different) | Forest River
INVERTERS: An inverter takes 12 volt DC and changes it to 120 volt AC Ok, now that we know just about ALL RV''s will have a converter, let''s
Get a quote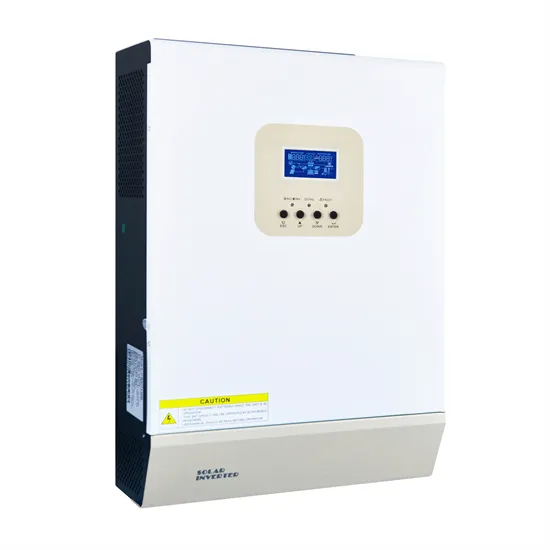
What Is An Inverter? | Definition, Types, Uses, How It
An inverter is a vital electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which is used to power many household
Get a quote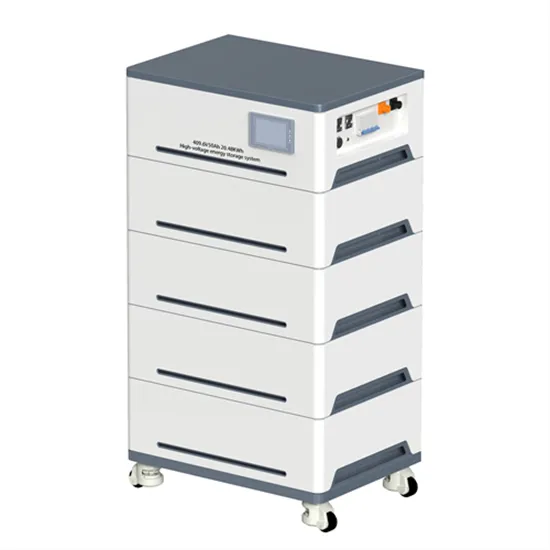
Design of the Inverter Output Filter for Motor Drives with
This Application Note give guidelines to design the dV/dt filter to be placed between the inverter and the motor in three-phase motor drives equipped with IRAMS power modules, with the
Get a quote
The Ultimate Introduction to RV Inverters
Are you thinking about investing in a power inverter for a camper or RV? RV inverters can be confusing at first, but this guide will help you sift through all the different
Get a quote
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
This article investigates the basic principles of inverters, different types of DC-to-AC conversion, and common applications for generating AC voltage in manufacturing.
Get a quote
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
This article investigates the basic principles of inverters, different types of DC-to-AC conversion, and common applications for generating AC
Get a quote
All About DC Inverter Air Condtioners (2025) | Today''s Homeowner
An Inverter Drive (VFD) works by taking AC mains (single or three phase) and first rectifying it into DC, the DC is usually smoothed with Capacitors and often a DC choke before it is connected
Get a quote
How an Inverter Drive Works and Controls the Speed of an AC Induction Motor
An Inverter Drive (VFD) works by taking AC mains (single or three phase) and first rectifying it into DC, the DC is usually smoothed with Capacitors and often a DC choke before it is connected
Get a quote
Which Solar Inverter Can Drive Water Pump?
At the heart of every solar power system lies the inverter, a critical component that converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels
Get a quote
The 10 BEST Campervan Inverters – 2024 Power Guide
The Best Campervan Inverters It can be difficult to decide on which inverter is the best for your van, especially considering how many styles and brands there are to choose
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Can a DC motor be equipped with an inverter ]
Which type of inverter is used to control electric motors?
They are used in a number of applications both in industry and everyday life. There are a number of different types of inverters but we will be discussing the type that is used to control electric motors in electrical engineering. These can also be known as AC drives, variable speed drives (VSD), and variable frequency drives (VFD).
What is the purpose of an inverter drive?
The purpose of an inverter drive is to convert AC mains (single-phase or three-phase) into a smoothed DC (direct current) supply to operate a motor. Inverters also introduce the ability to control speeds, acceleration and deacceleration time, braking methods, and torque.
How does a DC inverter work?
Compressors in a traditional HVAC unit operate at a fixed speed — if the system is on, the compressor will always be at 100%. A DC inverter controls the voltage to the compressor, and therefore its power and speed. Here’s how it does it: The inverter converts alternating current (AC) from the power supply to direct current.
Where are inverters used?
There are many uses for inverters and common places where one might find an inverter, including: Traditionally DC power conversion was achieved through a motor generator set, where a motor operating on DC power directly turned a generator to produce the required AC power.
What is a DC inverter?
The IPM inverts the DC into AC - hence the term ‘Inverter’. The control method is known as ‘PWM’ for 'Pulse Width Modulation'. This means the DC is switched on and off very quickly (chopped) by the Transistor switches.
How does an inverter drive (VFD) work?
Service Status: open as usual - view detailed updates. An Inverter Drive (VFD) works by taking AC mains (single or three phase) and first rectifying it into DC, the DC is usually smoothed with Capacitors and often a DC choke before it is connected to a network of Power Transistors to turn it into three phases for the motor.
Guess what you want to know
-
 DC motor inverter price
DC motor inverter price
-
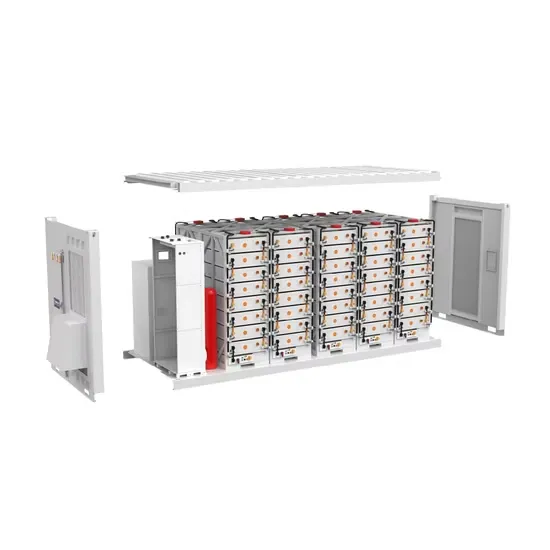 DC motor uses inverter to generate electricity
DC motor uses inverter to generate electricity
-
 DC inverter becomes smaller
DC inverter becomes smaller
-
 270v high voltage DC to 220v inverter
270v high voltage DC to 220v inverter
-
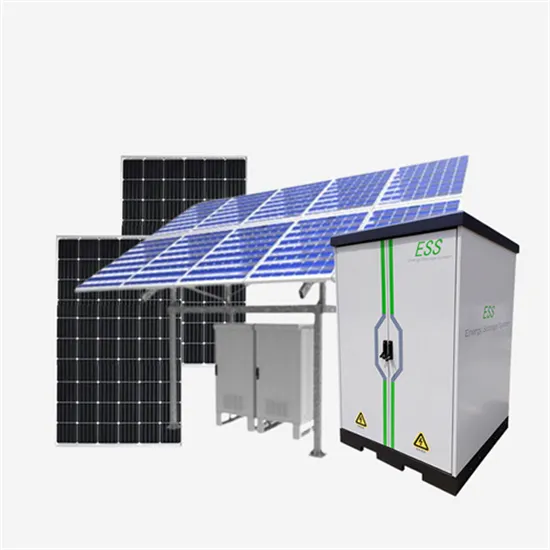
 Eritrea DC Solar PV Water Pump Inverter
Eritrea DC Solar PV Water Pump Inverter
-
 Off-grid inverter DC 56V
Off-grid inverter DC 56V
-
 Inverter intermediate DC voltage
Inverter intermediate DC voltage
-
 12v inverter output is DC or AC
12v inverter output is DC or AC
-
 How much does it cost to order a DC inverter
How much does it cost to order a DC inverter
-
 750V DC to 380V AC inverter
750V DC to 380V AC inverter
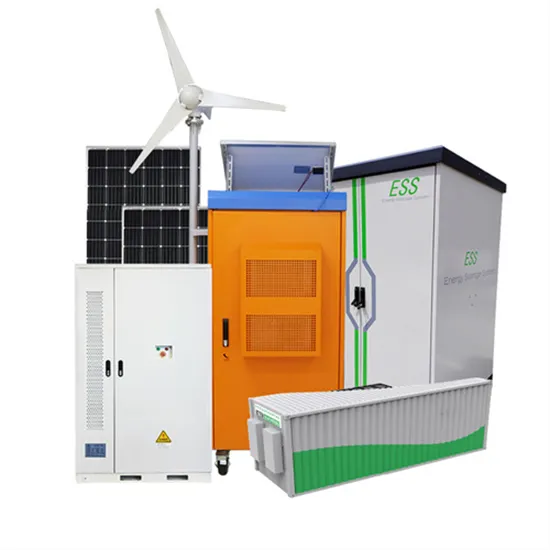
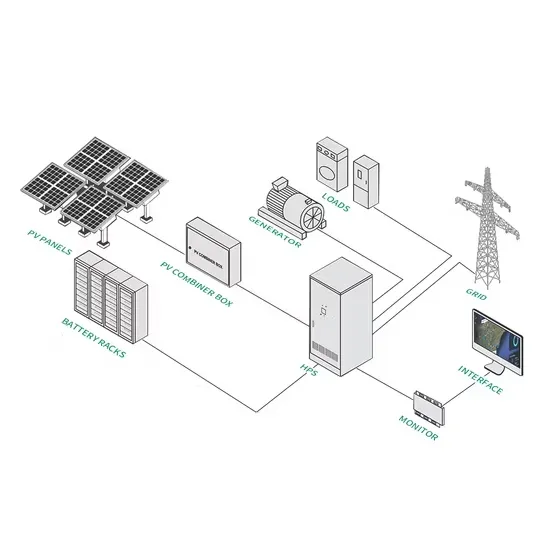
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


