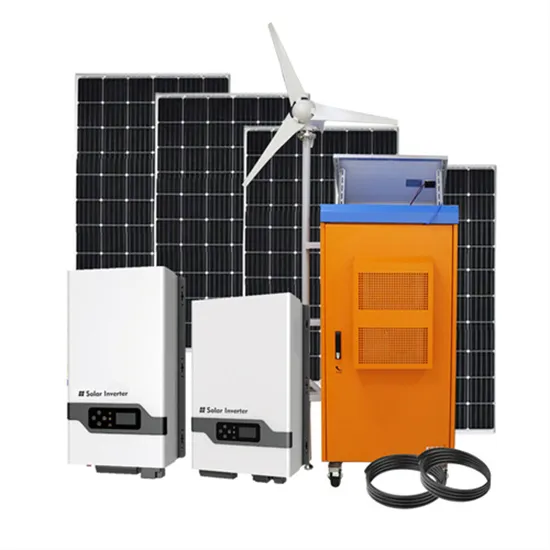
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
Appliances that need DC but have to take power from AC outlets need an extra piece of equipment called a rectifier, typically built from electronic components called diodes,
Get a quote
Everything You Need to Know About Inverters: Types, Uses, and
Ever wonder why inverters vary so much in price? Or why some can power a whole house quietly, while others can''t even handle a fridge? This guide will help you
Get a quote
How Inverters Work: Understanding the Basics and Applications
Inverters are a vital component of modern electrical systems, converting DC power from sources like solar panels or batteries into usable AC power for homes, businesses, and
Get a quote
How does an inverter work?
We''ll start the introduction by explaining the inverter device''s mechanism in detail. The inverter device''s role is to control the voltage and frequency of the power supply and seamlessly
Get a quote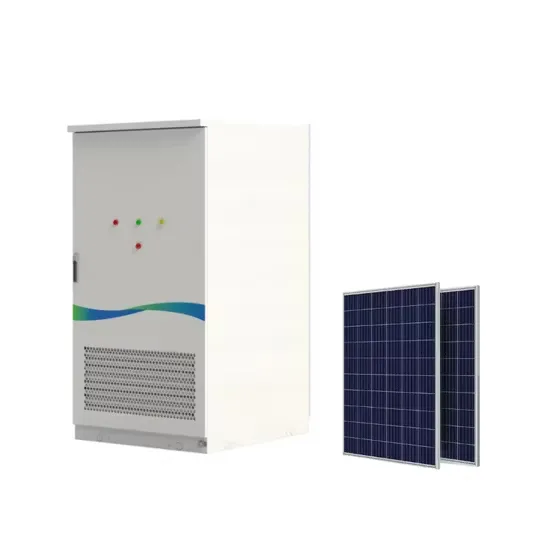
Power Consumption of Typical Household Appliances
The best way to compare the cost of running different appliances is to look at their power consumption, which is measure of how much power they use in Watts.
Get a quote
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power
Get a quote
What is an Inverter? Working Principle, Types, and Applications
Inverters are an integral component of modern electrical systems, as they facilitate the conversion of direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), enabling the efficient operation of
Get a quote
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
We''ll start the introduction by explaining the inverter device''s mechanism in detail. The inverter device''s role is to control the voltage and frequency of the power
Get a quote
Applications of Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
This article describes applications of variable frequency drives (VFDs). A variable frequency drive (VFD) or inverter is a controller for electric motors commonly
Get a quote
Everything You Need to Know About Inverters: Types,
Ever wonder why inverters vary so much in price? Or why some can power a whole house quietly, while others can''t even handle a fridge?
Get a quote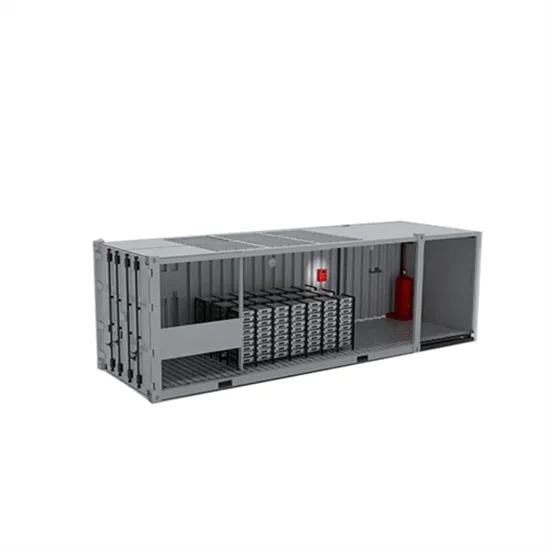
How to Install and Wire an Inverter: A Step-by-Step
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) power from a battery or solar panel into alternating current (AC) power that can be used to
Get a quote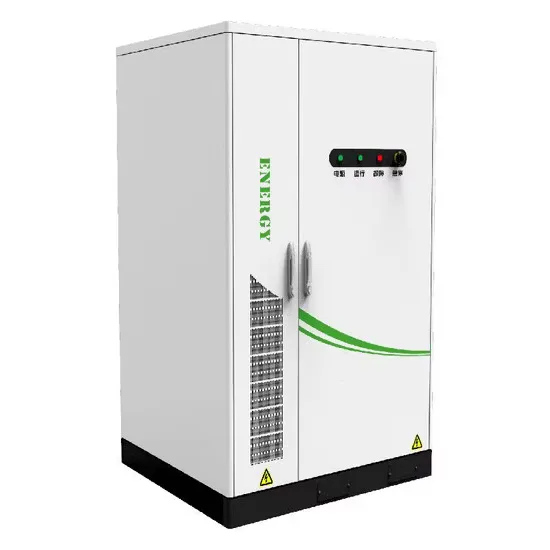
What Is The Purpose Of An Inverter?
What Is An Inverter? An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The conversion from DC to AC is essential for a variety of
Get a quote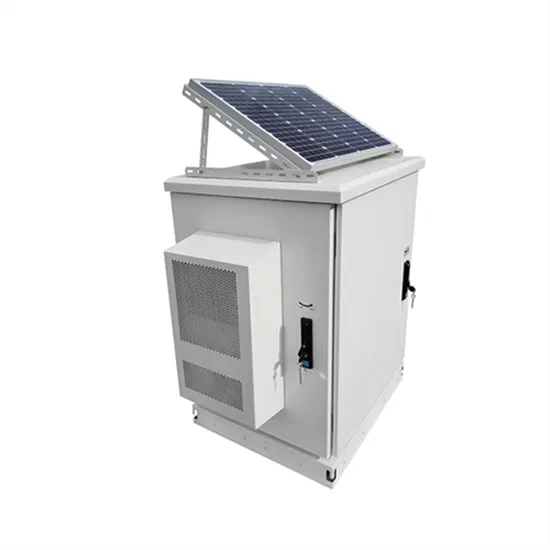
How Does an Inverter Work? A Simple Explanation
Most household and industrial electrical appliances run on alternating current (AC) power, but batteries and solar panels produce direct
Get a quote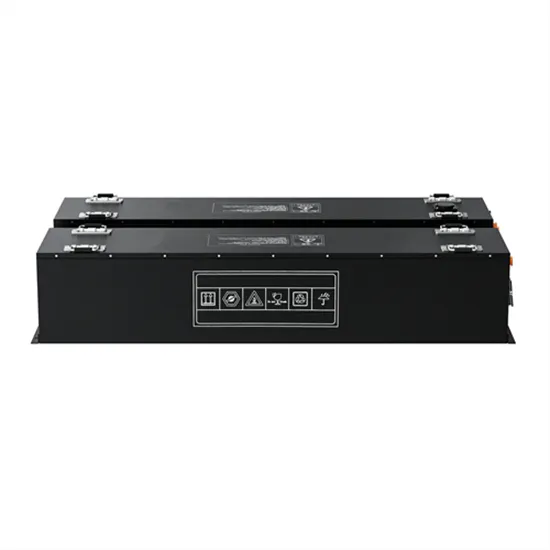
Power inverter
Power inverters are primarily used in electrical power applications where high currents and voltages are present; circuits that perform the same function for electronic signals, which
Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency
Inverters take AC mains and rectify it into DC. They are components that also can turn DC current into AC current. They are known by a number of
Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency Drives
Inverters take AC mains and rectify it into DC. They are components that also can turn DC current into AC current. They are known by a number of different names but the
Get a quote
Basics of inverters and applications to motor control | newji
What is an Inverter? Understanding the Basics An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). It plays a crucial role in various
Get a quote
Different Types of Inverters and Their Applications
Power inverters are fundamental devices for power electronics that convert DC (Direct Current) into AC (Alternating Current). There are many
Get a quote
Inverter Drives | Adjustable Frequency Drive | Inverter
An inverter drive, also known as an adjustable frequency drive (AFD), variable frequency drive (VFD), or variable speed drive (VSD), is a type of motor
Get a quote
DC-to-AC Converters (Inverters): Design, Working &
The electrical circuits that transform Direct current (DC) input into Alternating current (AC) output are known as DC-to-AC Converters or
Get a quote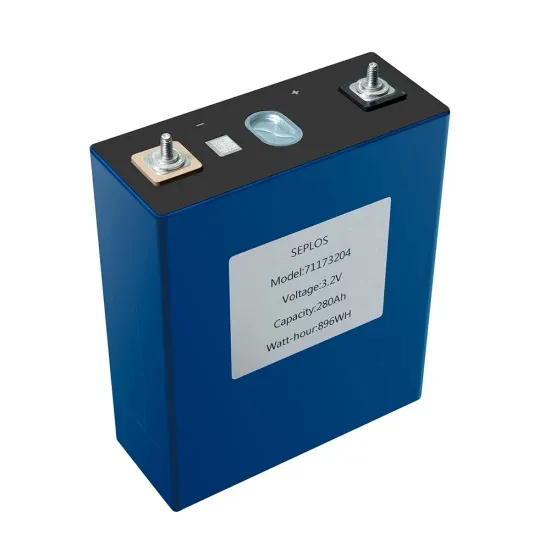
What is a Power Inverter Used for?
A power inverter is a device that converts direct current into alternating current, which plays an important role in modern society. Inverters are widely used in various fields,
Get a quote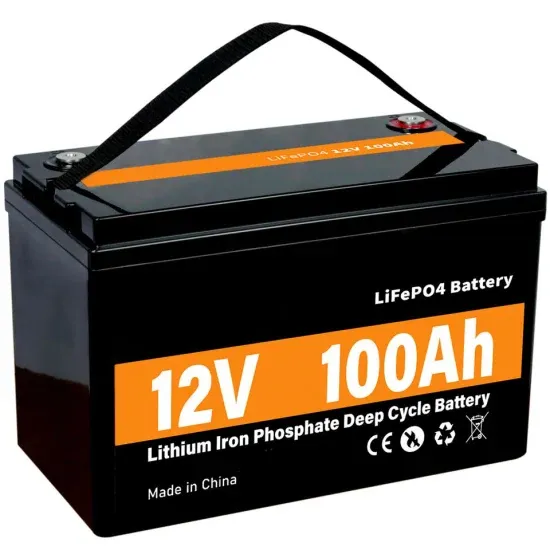
Introduction to inverters: structure, operating principles and
What is an inverter? An inverter is a converter that converts DC power (from a battery or storage battery) into fixed-frequency, constant-voltage, or frequency-regulated and
Get a quote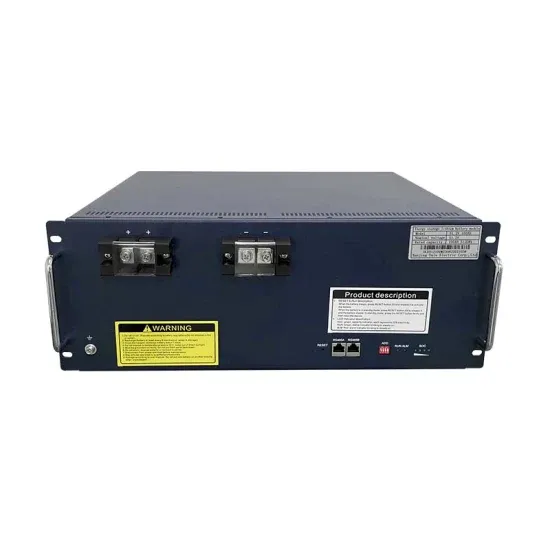
AC Motor Inverters: How They Work, Principles, And Technical
What Are AC Motor Inverters and How Do They Work? AC motor inverters are devices that convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to control the speed and
Get a quote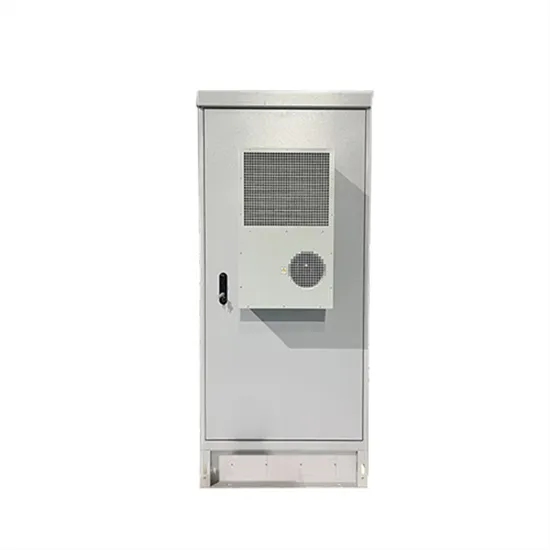
Introduction to Inverters
This is the core of the inverter that is responsible for managing the switching of electric conversion. It also regulates the voltage so that the frequency remains stable.
Get a quote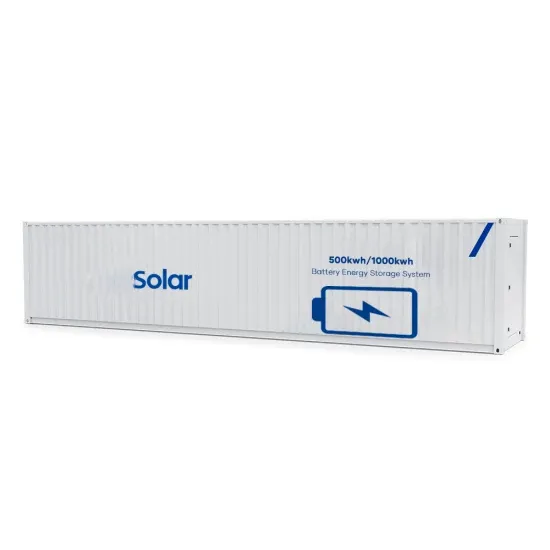
Introduction to inverters: structure, operating
What is an inverter? An inverter is a converter that converts DC power (from a battery or storage battery) into fixed-frequency, constant
Get a quote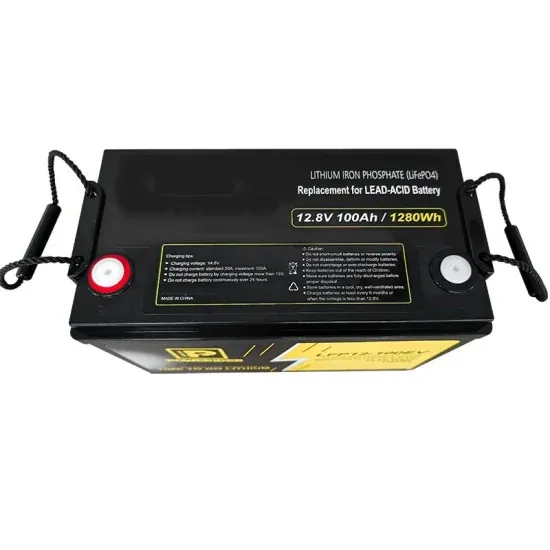
6 FAQs about [The inverter drives the voltage of various electrical appliances]
What does an inverter do?
Inverters take AC mains and rectify it into DC. They are components that also can turn DC current into AC current. They are known by a number of different names but the correct term is actually a frequency converter. In an electrical system, they will sit between the power supply and the motor.
What is a power inverter?
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC.
What is a DC inverter & how does it work?
An inverter is an electronic device that converts DC power (from batteries, solar panels, or other DC sources) into AC power, which is what most household appliances and electrical grids use. In simple terms, it’s like a translator between power types, making sure energy stored in one form can be used in another. Why DC Needs to Become AC:
What is the AC output voltage of a power inverter?
The AC output voltage of a power inverter is often regulated to be the same as the grid line voltage, typically 120 or 240 VAC at the distribution level, even when there are changes in the load that the inverter is driving. This allows the inverter to power numerous devices designed for standard line power.
Why do inverters have a variable frequency drive?
By controlling the frequency, the inverter is able to regulate the motor’s capacity in terms of torque and speed, and thus it’s performance and power consumption. Inverters are also called AC Drives, or VFD (variable frequency drive). What Makes Inverter Appliances Different?
What is the function of inverter circuit?
Inverter circuit: The inverter circuit is the core part of the inverter and is responsible for converting DC power into AC power. Inverter circuits usually consist of power semiconductor devices (such as thyristors, IGBTs, MOSFETs, etc.) and corresponding control circuits to achieve voltage and frequency conversion.
Guess what you want to know
-
 600w electrical appliances use 12v inverter
600w electrical appliances use 12v inverter
-
 Can t the inverter be used with high-frequency electrical appliances
Can t the inverter be used with high-frequency electrical appliances
-
 Photovoltaic Power Generation Voltage Inverter Price
Photovoltaic Power Generation Voltage Inverter Price
-
 Pulse inverter output voltage
Pulse inverter output voltage
-
 Middle East low voltage inverter manufacturer
Middle East low voltage inverter manufacturer
-
 Which type of high voltage inverter is more than 500 yuan
Which type of high voltage inverter is more than 500 yuan
-
 Influence of input voltage on inverter
Influence of input voltage on inverter
-
 Voltage after three-phase inverter
Voltage after three-phase inverter
-
 Is the voltage of the electric inverter stable
Is the voltage of the electric inverter stable
-
 Huijue inverter string voltage
Huijue inverter string voltage
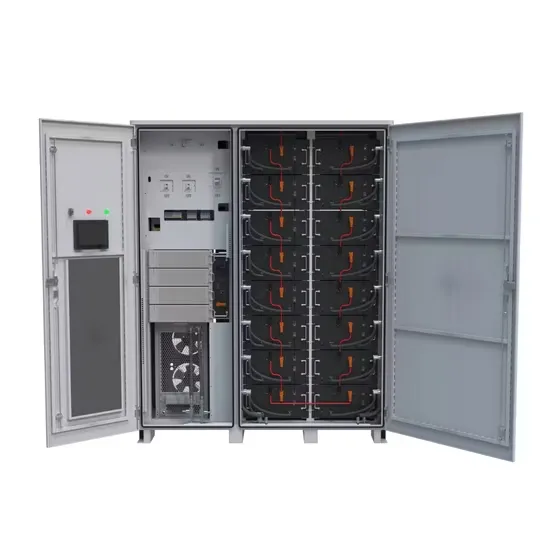
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
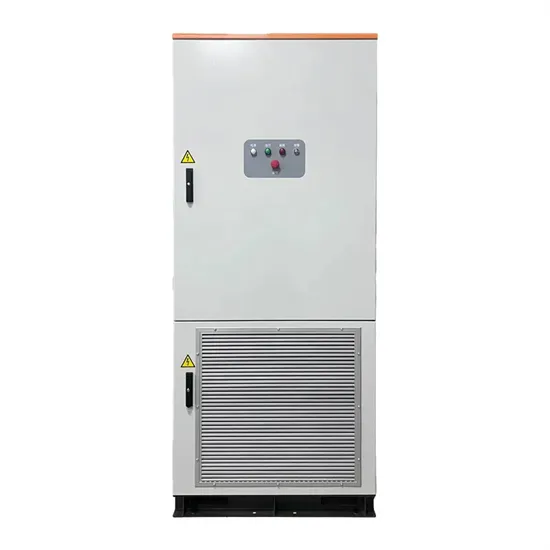
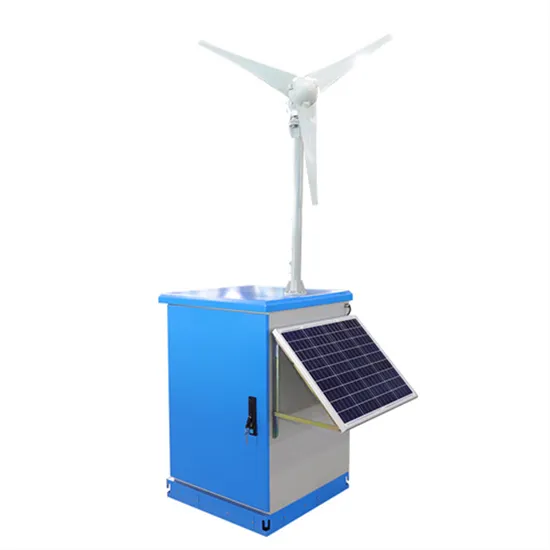
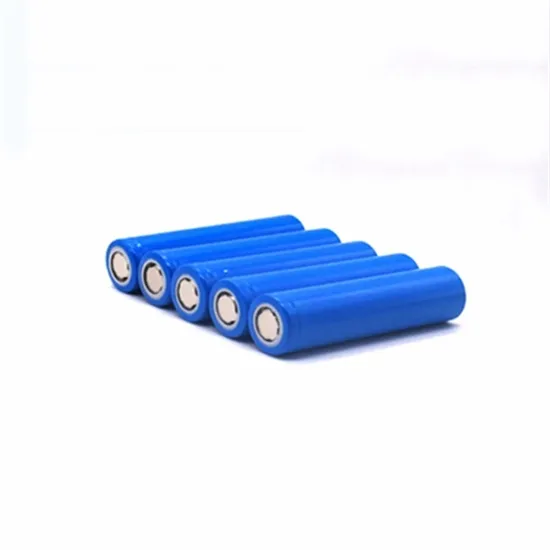
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


