how is it possible that an inverter absorb reactive power
It''s always said that reactive power is interpreted as magnetic field in motors (or transformers) it can also be the electric field in capacitor, but where does an inverter "store"
Get a quote
Best Pure Sine Wave Inverters and Sustainable Brands to Know
Discover how pure sine wave inverters work, why they''re essential for clean power, and which sustainable brands offer the best options for you.
Get a quote
kWp vs Current Power / Actual Performance
No matter the peak capacity rating of the PV array, the maximum power output from a grid-tied PV system is limited to no more than the output capacity rating of the inverter. It is
Get a quote
Inverter Efficiency: Understanding How Much Power You''re
In simple terms, inverter efficiency refers to how well an inverter converts DC electricity into usable AC power. No inverter is 100% efficient—some energy always gets lost
Get a quote
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power calculations and inverter
Get a quote
Active Power, Reactive Power, Apparent Power, and
The diverse power terms in electrical generation systems include active, reactive, and apparent power, all of which lead to the introduction of
Get a quote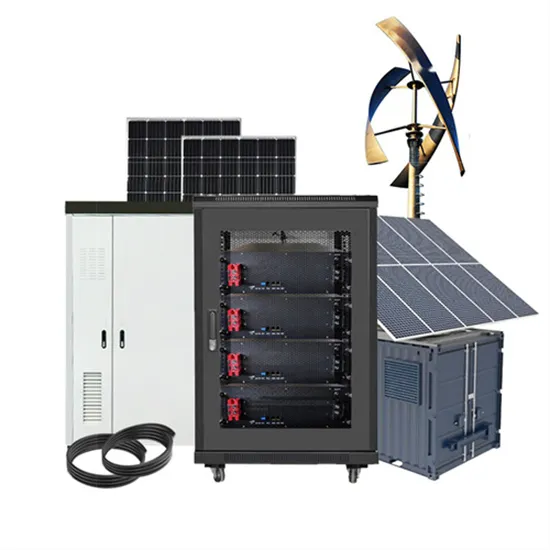
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and
Get a quote
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To Power Conversion
Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and expert insights.
Get a quote
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power
Get a quote
Inverter Efficiency: Complete Guide and Calculator
Inverter efficiency is how much Direct Current (DC) is converted into Alternating Current (AC). This is the primary function of an inverter, unfortunately, it is not
Get a quote
Understanding the 10000W Inverter – Power, Performance, and
Explore the power of a 10000W inverter, learn the difference between kilowatt vs kVA, and find the best setup for your home or solar system.
Get a quote
Active/reactive power control of photovoltaic grid‐tied
This paper proposes an analytical expression for the calculation of active and reactive power references of a grid-tied inverter, which limits the
Get a quote
Inverter Efficiency: Complete Guide and Calculator
Inverter efficiency is how much Direct Current (DC) is converted into Alternating Current (AC). This is the primary function of an inverter, unfortunately, it is not 100% efficient. It means that
Get a quote
Do you know the difference between the key parameters of inverter
For example, when an inverter marked as 5KVA supplies power to a purely resistive load, its actual output active power is 5KW. When the load is an inductive or
Get a quote
Why Does Power Inverter Output Power Not Reach Rated Power
Wondering why your inverter isn''t delivering full power? Learn the top reasons why power inverters fall short of rated output and how to fix them. Expert tips included!
Get a quote
Best Solar Inverters in India | Top Brands and Models
A solar inverter embedded with MPPT technology is often considered the best solar inverter in India and globally, as it utilizes the MPPT (maximum power point tracking) algorithm
Get a quote
Samlex America 450W Modified Sine Wave Inverter Review
6 hours ago· Real-World Testing: Putting Samlex America 450W Modified Sine Wave Inverter to the Test First Use Experience I first tested the Samlex America 450W Modified Sine Wave
Get a quote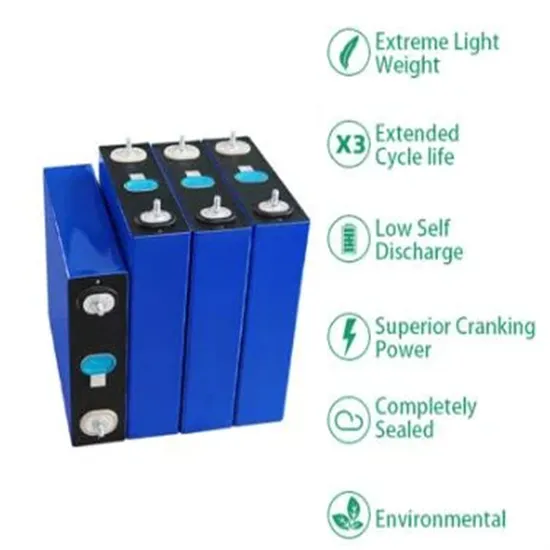
How much power does an Inverter use just sitting there idling?
Generally a 3 kW sinewave high freq inverter is 30 to 50 watts of full idle power. A high frequency inverter has two primary stages. First stage is high frequency DC to DC
Get a quote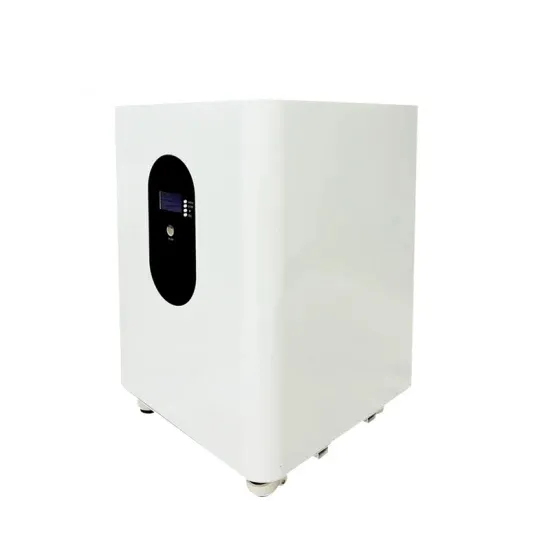
Understanding Inverter Power Ratings: kW vs kVA
kW refers to the real or usable power output of an inverter. kVA represents the total power capacity it can carry, including power lost in phase difference
Get a quote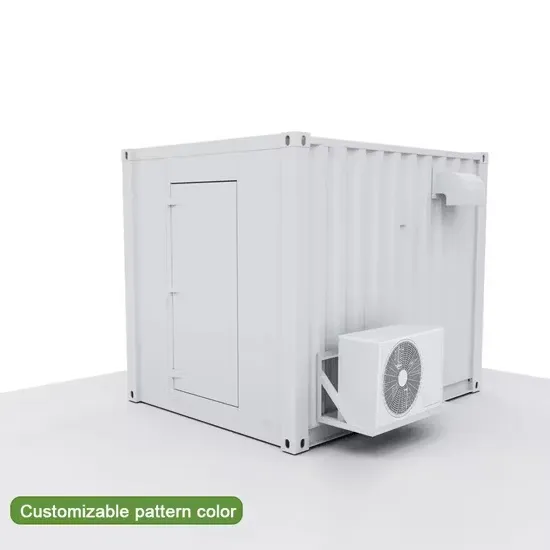
multiplus 3kW inverter real vs apparent power
multiplus 3kW inverter real vs apparent power Can anyone explain to me why is it that the multiplus 3kW inverter is rated at 3000VA at 25°C but at the same temperature it is only rated
Get a quote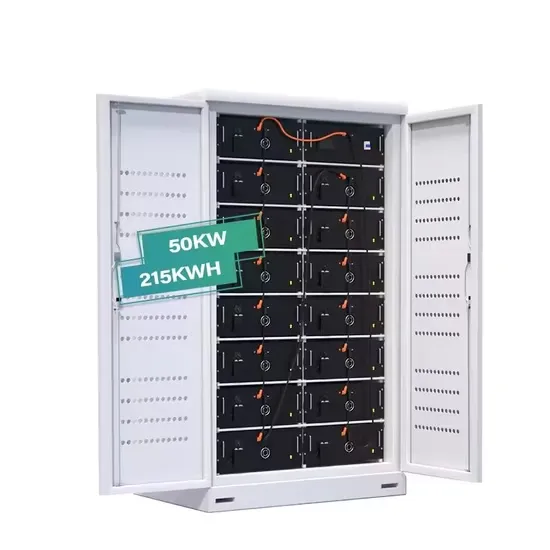
What Is Reactive Power Compensation? How Yohoo
Learn the differences between apparent, active, and reactive power, and discover how Yohoo Elec''s solar inverters provide intelligent
Get a quote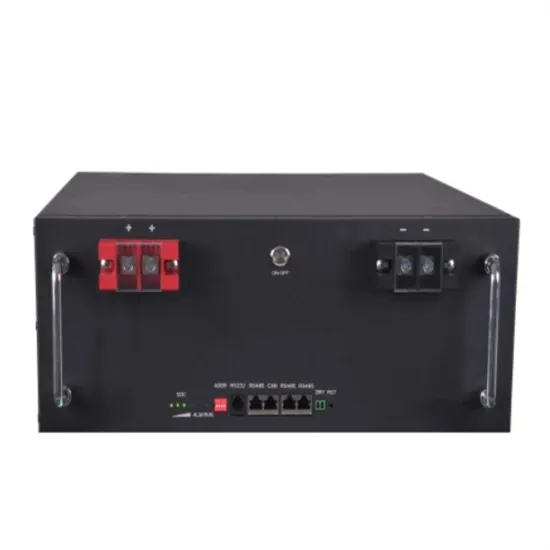
Understanding Inverter Power Ratings: kW vs kVA Explained
kW refers to the real or usable power output of an inverter. kVA represents the total power capacity it can carry, including power lost in phase difference (reactive power). For example,
Get a quote
Inverter Power Draw: How Much Power Does an Inverter Use
You can measure the actual power draw of your inverter using a multimeter by following a series of straightforward steps. This process involves determining voltage, current,
Get a quote
Type here the title of your Paper
With proper operational firmware in the inverter, the four-quadrant system can independently control real power P and reactive power Q, providing a wide range of functions
Get a quote
4000W Blue Pure Sine Wave Power Inverter, DC 24V to AC
Pure sine wave inverters provide cleaner, safer power by closely mimicking the smooth, consistent waveforms of utility electricity. This ensures that sensitive electronics, such as
Get a quote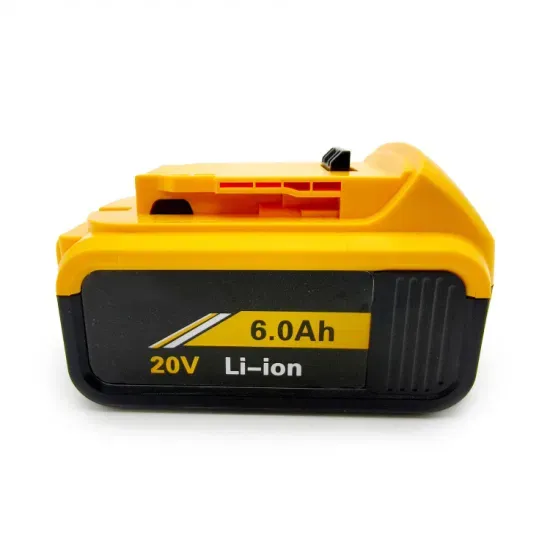
6 FAQs about [Inverter actual power]
How much energy does an inverter use?
So less energy is output than is input. In fact, inverter efficiency can vary dramatically between products, on average it is between 85% and 95%. For example, if you have an inverter with 85% efficiency it means only 85% of your battery power is being sent to your appliances. The other 15% is lost/used up in the inverter.
What is inverter efficiency?
In simple terms, inverter efficiency refers to how well an inverter converts DC electricity into usable AC power. No inverter is 100% efficient—some energy always gets lost as heat during the conversion. Most modern inverters have efficiency ratings between 90% and 98%. Let’s break it down:
What is a DC inverter & how does it work?
As we know, the basic function of the inverter is to convert DC power to AC power because most of our electrical needs are for AC. The inverter is connected directly to either the power source (solar PV array or wind turbine) or the charge controller, depending on whether backup storage batteries are used.
What are inverters used for?
Inverters are essential components in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and whole-house backup systems. They provide seamless power during outages by converting stored battery power to AC electricity. Critical applications include:
What is the power factor of a solar inverter?
Most hybrid and solar inverters operate at a power factor between 0.8 and 1.0. The power factor directly impacts how much usable energy (kW) you can get from your inverter. If your inverter has a power factor of 0.9, then a 10 kVA inverter will deliver only 9 kW of real output. This means the inverter can only handle 10.2 kW of actual load—not 12.
What is an inverter & how does it work?
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. Think of it as a translator between two different electrical languages – your solar panels, batteries, and car electrical systems speak “DC,” while your home appliances, power grid, and most electronics speak “AC.”
Guess what you want to know
-
 Inverter actual power
Inverter actual power
-
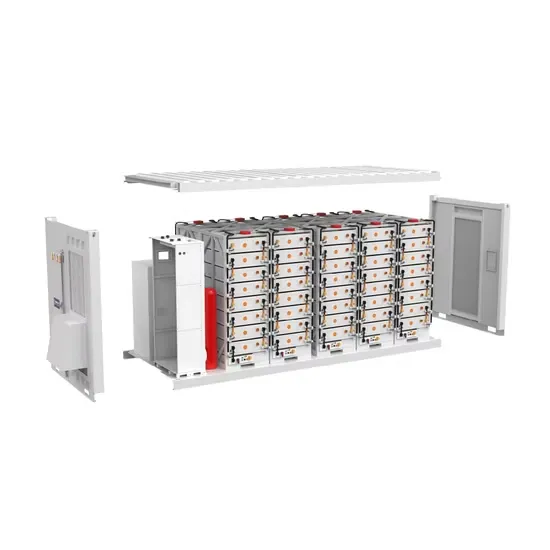 2800W inverter actual output power
2800W inverter actual output power
-
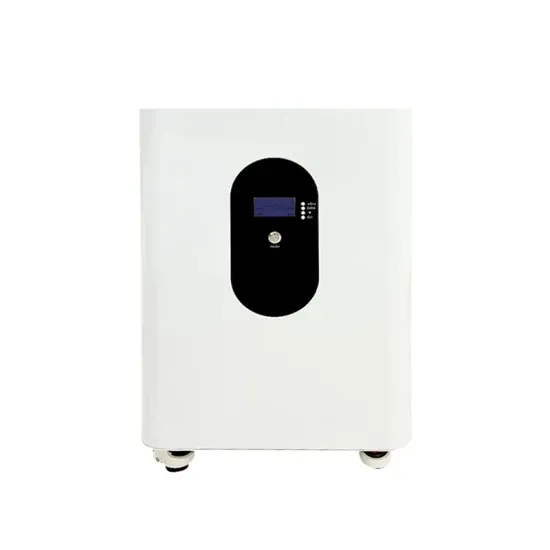 11800w inverter actual power
11800w inverter actual power
-
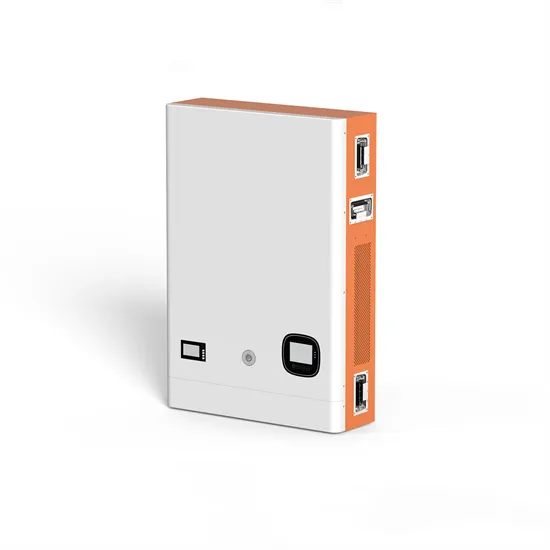 Measure the actual power of the inverter
Measure the actual power of the inverter
-
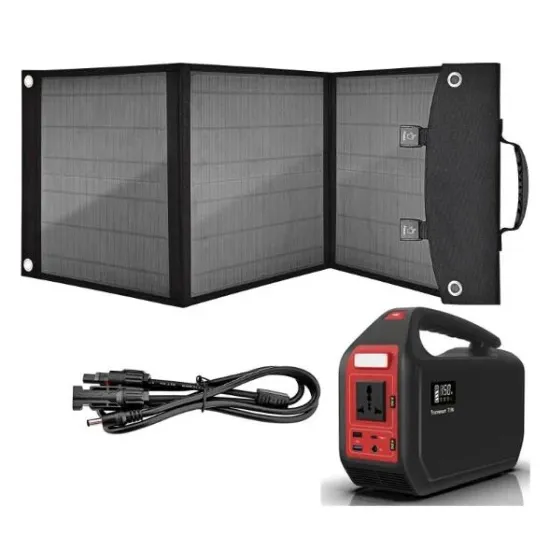 300W sine wave inverter power conversion
300W sine wave inverter power conversion
-
 Generation output power inverter
Generation output power inverter
-
 Photovoltaic power supply home photovoltaic inverter
Photovoltaic power supply home photovoltaic inverter
-
 Can solar panels power a 12V water pump inverter
Can solar panels power a 12V water pump inverter
-
 South Sudan Power Inverter Customized Manufacturer
South Sudan Power Inverter Customized Manufacturer
-
 How big of an inverter can a 12v 45AH power supply be
How big of an inverter can a 12v 45AH power supply be
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


