Tweaking Your Power Inverter, Get More Bang for the Buck
This instructable is a guide for repairing/increasing the output power of a simple dc-AC power converter (this instructable address the boost dc-dc converter based power inverter).
Get a quote
ELI5: How does an inverter convert 12v dc to 120v ac? What''s
They still use an oscillator, but a much higher frequency one, because they can use a smaller, more efficient transformer to change the voltage. They go through more steps, like 12VDC to
Get a quote
Voltage Control Methods of Inverter – PWM Technique
In practice, the waveform of the output voltage obtained from a single-phase inverter is rectangular in nature with an amplitude approximately
Get a quote
Why DC supply voltage is increasing when inverter is connected
If I connect my inverter to a resistive load or small inductive load the DC supply voltage (in my application it is 56 V) stays constant. However, if a powerful induction motor is
Get a quote
Understanding inverter voltage
Choosing the optimal inverter voltage depends on various factors, including the inverter''s design, the power requirements of connected devices, and the available power source.
Get a quote
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
Most modern inverters utilize some form of H-Bridge circuity to change the polarity of direct current. In most cases, the lower voltage DC current needs to be amplified to match
Get a quote
Inverters Guide
Power inverters, or simply ''inverters'', are transformers that will convert a DC current into an AC current, allowing you to run higher voltage equipment from a battery or other DC
Get a quote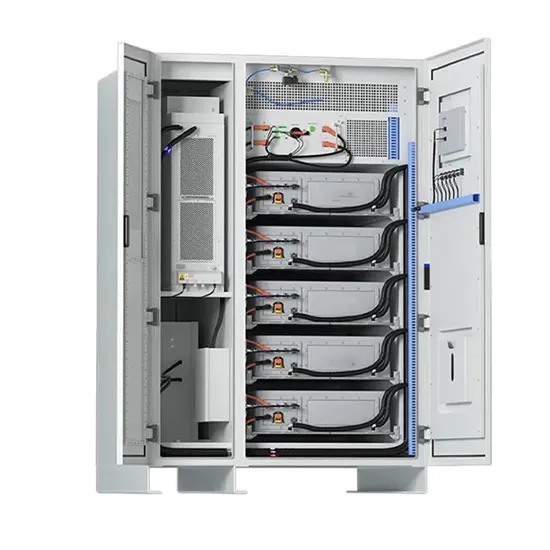
What Is an Inverter: Inverter Ratings, Efficiency & More
AC alternates its direction many times per second. AC is used for grid service because it is more practical for long distance transmission. Magnum Inverter
Get a quote
How DC/AC Power Inverters Work | HowStuffWorks
AC power works well at high voltages, and can be "stepped up" in voltage by a transformer more easily than direct current can. An inverter increases the DC voltage, and
Get a quote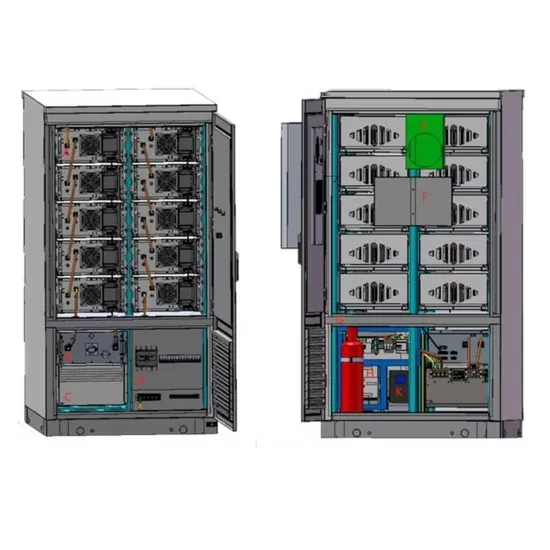
Power inverter
Hundreds of thousands of volts, where the inverter is part of a high-voltage direct current power transmission system. An inverter may produce a square wave, sine wave, modified sine wave,
Get a quote
Inverter Amp Draw Calculator
You can also use this Inverter Battery Calculator app to find out the required amps for different wattages. The app is also useful for battery charging time, current, and voltage
Get a quote
INVERTERS
An inverter converts DC battery power to AC power, and also changes the voltage. In other words, it is a power adapter. It allows a battery-based system to run conventional AC
Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency
Inverters are components used to control speed or torque control for an electric motor. Inverters take AC mains and rectify it into DC. They are
Get a quote
Power inverter
OverviewApplicationsInput and outputBatteriesCircuit descriptionSizeHistorySee also
An inverter converts the DC electricity from sources such as batteries or fuel cells to AC electricity. The electricity can be at any required voltage; in particular it can operate AC equipment designed for mains operation, or rectified to produce DC at any desired voltage. An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) uses batteries and an inverter to suppl
Get a quote
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
Most modern inverters utilize some form of H-Bridge circuity to change the polarity of direct current. In most cases, the lower voltage DC
Get a quote
Inverter Vs. Converter – When Do We Need One And
Inverter Vs. converter is confusing to inexperienced. Even when the inverter itself is a type of converter, but in common terms, a converter is used for the
Get a quote
What to Know about DC to AC Voltage Conversion?
Learn everything you need to know about DC to AC voltage conversion, including why it''s necessary, how it works, the role of inverters, and common applications like solar
Get a quote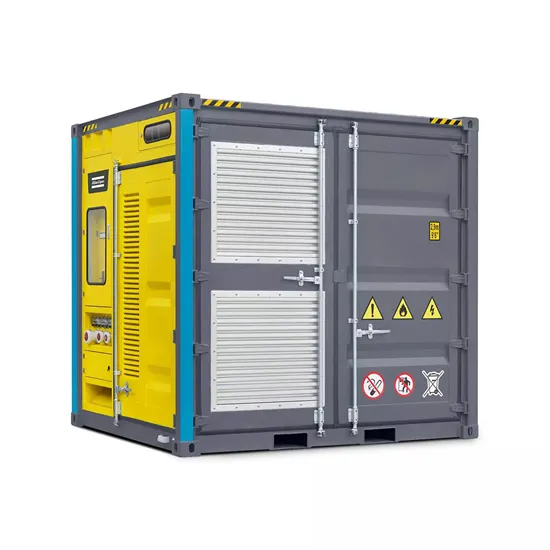
Benefits of Parallel Inverters | DIY Solar Power Forum
If both inverters are the same, and allow paralleling, they will provide double the power output. If you have 2 ea. 6000 watt inverters, you will have one 12000 watt output
Get a quote
Transformer vs Inverter: What are Differences
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another or to multiple circuits. An inverter is a converter that converts DC power
Get a quote
ELI5: How does an inverter convert 12v dc to 120v ac? What''s
The power the inverter draws from the source is always going to be more than that being drawn by the device. (Some energy is lost during the conversion). Also, this results in a current being
Get a quote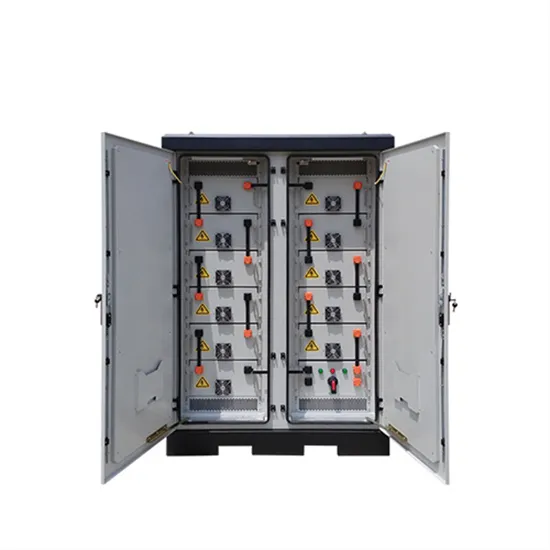
How to Increase Voltage for AC and DC Sources?
For AC circuits, you can use a step-up transformer or an autotransformer to get a higher voltage output. Another way is to connect the voltage sources in series. For DC circuits, connecting
Get a quote
ELI5: How does an inverter convert 12v dc to 120v ac? What''s
They still use an oscillator, but a much higher frequency one, because they can use a smaller, more efficient transformer to change the voltage. They go through more steps,
Get a quote
How to Increase Voltage for AC and DC Sources?
For AC circuits, you can use a step-up transformer or an autotransformer to get a higher voltage output. Another way is to connect the voltage sources in series.
Get a quote
How Power Inverter Generates Reactive Power
Inverter Operation: A power inverter converts DC (Direct Current) to AC (Alternating Current) by switching the DC voltage on and off rapidly, generating an AC
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Can an inverter increase DC voltage ]
Does a power inverter produce power?
The inverter does not produce any power; the power is provided by the DC source. Power inverters are primarily used in electrical power applications where high currents and voltages are present. Buy Online... Kan 12v. 220AH Solar Tubular Battery
How fast does an inverter work?
It does this very quickly — 60 times per second in most U.S. electrical systems. AC power works well at high voltages, and can be "stepped up" in voltage by a transformer more easily than direct current can. An inverter increases the DC voltage, and then changes it to alternating current before sending it out to power a device.
Do inverters convert AC to DC?
The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC. The input voltage, output voltage and frequency, and overall power handling depend on the design of the specific device or circuitry.
Can you use direct current without an AC to DC inverter?
You can't use straight direct current without the AC to DC inverter because the device's power supply needs the AC power in order to properly step down and regulate the voltage. There are many types of inverters that facilitate the integration of various energy sources and systems into our daily electrical applications.
How do inverters absorb reactive power?
To absorb reactive power, it will generate a voltage still in phase with the grid voltage but with a lower amplitude. Inverters generate reactive power by use of the freewheeling diodes on each of the power switches. The inductive nature of the load makes it want to draw current even after the power switch has been turned OFF.
How many volts does an inverter produce?
Hundreds of thousands of volts, where the inverter is part of a high-voltage direct current power transmission system. An inverter may produce a square wave, sine wave, modified sine wave, pulsed sine wave, or near-sine pulse-width modulated wave (PWM) depending on circuit design.
Guess what you want to know
-
 96v inverter to increase voltage
96v inverter to increase voltage
-
 DC panel inverter input voltage
DC panel inverter input voltage
-
 Inverter intermediate DC voltage
Inverter intermediate DC voltage
-
 Three-phase inverter DC voltage
Three-phase inverter DC voltage
-
 Inverter DC maximum voltage
Inverter DC maximum voltage
-
 Inverter DC side rated voltage
Inverter DC side rated voltage
-
 270v high voltage DC to 220v inverter
270v high voltage DC to 220v inverter
-
 AC voltage of single-phase inverter
AC voltage of single-phase inverter
-
 Does it need to boost the voltage after the photovoltaic inverter
Does it need to boost the voltage after the photovoltaic inverter
-
 Wide voltage inverter 48v 60v 72v universal
Wide voltage inverter 48v 60v 72v universal
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


