Flow Battery vs Solid-State Battery – Which One Will Dominate
This article will explain starting from a general understanding of what a flow battery vs solid-state battery is, how it works, its advantages and disadvantages, to its potential
Get a quote
What are the pros and cons of flow batteries for home energy
In contrasting flow batteries with lithium-ion batteries, significant differences emerge concerning lifespan, environmental impact, and scalability. Flow batteries can endure
Get a quote
Flow batteries for home electricity storage
Flow type batteries can endure deep cycling, meaning they can be discharged and charged regularly without significant performance degradation. They often
Get a quote
The Aluminum-Ion Battery: A Sustainable and
In this review article, we first describe the constraints of a sustainable and seminal battery chemistry. Subsequently, we present an assessment of the chemical
Get a quote
Flow Battery vs Solid-State Battery – Which One Will
This article will explain starting from a general understanding of what a flow battery vs solid-state battery is, how it works, its advantages and
Get a quote
Understanding the Disadvantages of Flow Battery Energy
Summary: Flow battery energy storage systems are gaining traction for renewable energy integration, but they come with limitations. This article explores their key disadvantages,
Get a quote
The Aluminum-Ion Battery: A Sustainable and Seminal Concept?
In this review article, we first describe the constraints of a sustainable and seminal battery chemistry. Subsequently, we present an assessment of the chemical elements in terms of
Get a quote
Advantages and disadvantages of aluminum iron phosphate
The flow battery employing soluble redox couples for instance the all-vanadium ions and iron-vanadium ions, is regarded as a promising technology for large scale energy storage,
Get a quote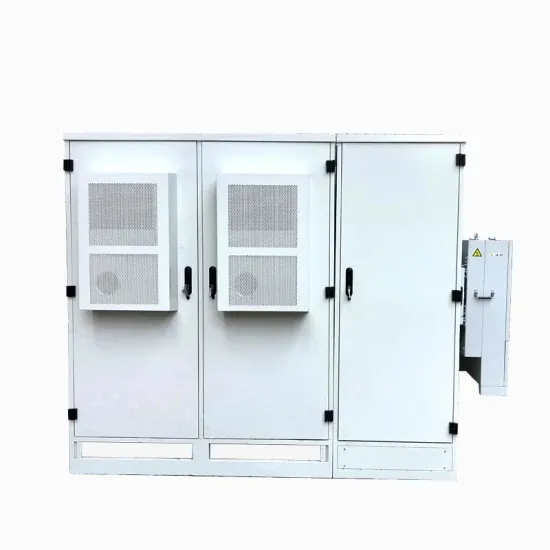
Flow Batteries: Definition, Pros + Cons, Market Analysis & Outlook
But without question, there are some downsides that hinder their wide-scale commercial applications. Flow batteries exhibit superior discharge capability compared to
Get a quote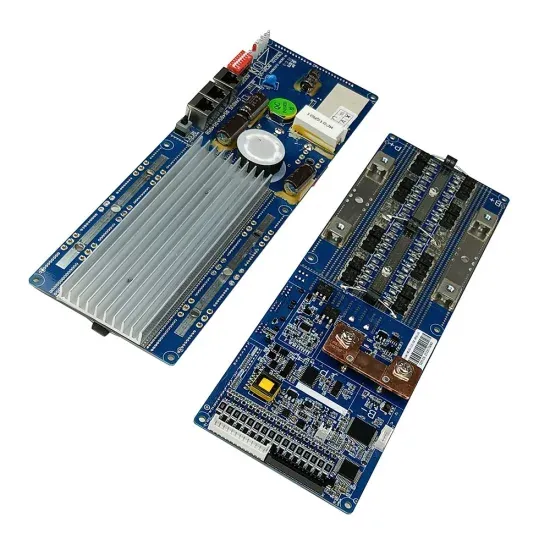
A comprehensive review on recent progress in aluminum–air batteries
Download: Download high-res image (322KB) Download: Download full-size image In this comprehensive review article, we present the various perspectives of the fundamentals,
Get a quote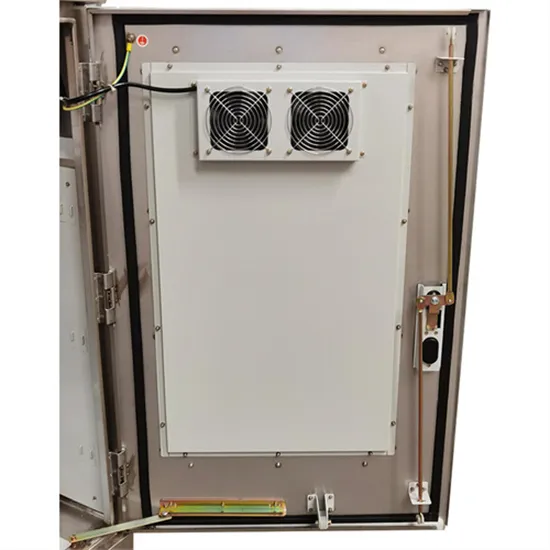
Aluminum batteries: Opportunities and challenges
Aluminum (Al) is promising options for primary/secondary aluminum batteries (ABs) because of their large volumetric capacity (Cυ∼8.04 A h cm−3, four times higher than Li),
Get a quote
Despite technological advances, flow batteries struggle against
But some of the disadvantages for flow batteries include expensive fluids that are also corrosive or toxic, and the balance of system costs are relatively high along with the
Get a quote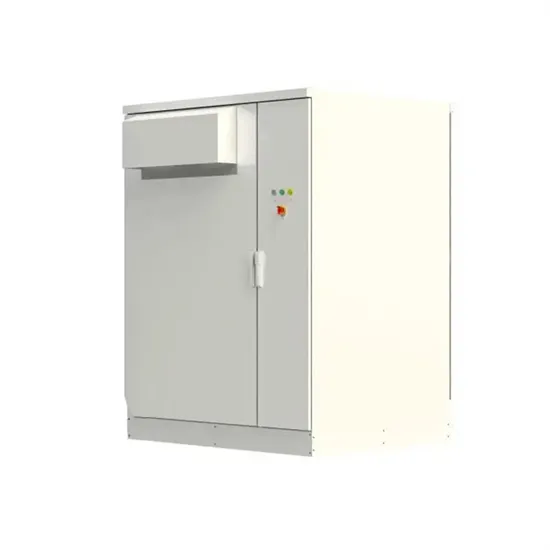
Current Challenges, Progress and Future Perspectives of Aluminum
Abstract Today, the ever-growing demand for renewable energy resources urgently needs to develop reliable electrochemical energy storage systems. The rechargeable
Get a quote
Flow Batteries: Definition, Pros + Cons, Market
But without question, there are some downsides that hinder their wide-scale commercial applications. Flow batteries exhibit superior discharge
Get a quote
Rusty metal could be the battery the energy grid needs
We need more ways to store renewable energy. These scientists are finding ways to overcome metal-air batteries current shortcomings.
Get a quote
Flow Batteries: A Game-Changer in Energy Storage
The safety aspect presents another compelling advantage for flow batteries. Their non-flammable electrolytes eliminate the risk of thermal
Get a quote
Aluminum-ion battery outperforms lithium
Retains capacity after thousands of cycles with improved safety, sustainability, and affordability. Researchers have developed an aluminum-ion battery that outperforms lithium
Get a quote
What are problems associated with Al ion battery instead of Li ion
However, there are serious obstacles to the practical development of Al batteries such as the complicated nature of trivalent Al3+ intercalation into the cathode of Al-ion batteries and...
Get a quote
What Is A Flow Battery? Overview Of Its Role In Grid-Scale
A flow battery is a type of rechargeable battery. It stores energy using electroactive species in liquid electrolytes. These electrolytes are stored in external tanks and pumped
Get a quote
Aluminum: The future of Battery Technology
2. How Lithium and Aluminum ion Batteries work Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) dominate the battery market as they provide high energy density and long cyclability, meaning it can endure
Get a quote
Scientific issues of zinc‐bromine flow batteries and mitigation
Zinc-bromine flow batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that uses zinc and bromine in the electrolytes to store and release electrical energy. The relatively high energy
Get a quote
Aluminum Batteries: An Overview of Pros, Cons and
This article explores the advantages and disadvantages of aluminum-based batteries, how to choose the right one for your needs, and
Get a quote
Cost-effective iron-based aqueous redox flow batteries for large
In order to solve the current energy crisis, it is necessary to develop an economical and environmentally friendly alternative energy storage system in order to provide potential
Get a quote
Aluminum Batteries: An Overview of Pros, Cons and Latest
This article explores the advantages and disadvantages of aluminum-based batteries, how to choose the right one for your needs, and the latest developments in
Get a quote
Aluminum-air batteries: A review of alloys, electrolytes and design
This manuscript first takes a broader look at metal-air battery performance before focusing on a summary of data and electrochemical performance for aluminum and aluminum
Get a quote
What Are Flow Batteries? A Beginner''s Overview
Part 1. What is the flow battery? A flow battery is a type of rechargeable battery that stores energy in liquid electrolytes, distinguishing itself from conventional batteries, which
Get a quote
Flow batteries for home electricity storage
Flow type batteries can endure deep cycling, meaning they can be discharged and charged regularly without significant performance degradation. They often have longer cycle life
Get a quote
Redox Flow Batteries: Recent Development in Main Components
Redox flow batteries represent a captivating class of electrochemical energy systems that are gaining prominence in large-scale storage applications. These batteries offer
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Disadvantages of all-aluminum flow batteries]
What are the disadvantages of flow batteries?
They can also be scaled to match growing needs relatively by increasing the amount of fluid in the tanks. But some of the disadvantages for flow batteries include expensive fluids that are also corrosive or toxic, and the balance of system costs are relatively high along with the parasitic (on-site) load needed to power the pumps.
What are the pros and cons of aluminum-based batteries?
When comparing aluminum-based batteries to other battery types, it’s important to consider the pros and cons of each option. On the plus side, aluminum-based batteries are lightweight, have a high energy density, are non-toxic, and can be recharged quickly and easily.
Are aluminum batteries bad for the environment?
This has however, not been reported to date. Despite its low cost, simple operation, and reduced environmental impact, aluminum batteries based on aqueous or protic systems exhibit fatal drawbacks, such as the passivating oxide film formation decreasing the battery voltage and efficiency, hydrogen side reactions, and material corrosion.
Are flow batteries a good choice for commercial applications?
But without question, there are some downsides that hinder their wide-scale commercial applications. Flow batteries exhibit superior discharge capability compared to traditional batteries, as they can be almost fully discharged without causing damage to the battery or reducing its lifespan.
Why is a secondary aluminum-ion battery unfeasible?
A secondary aluminum-ion battery based on pure aluminum-metal as negative electrode and an aqueous electrolyte is unfeasible (Liu et al., 2017), because aluminum deposition only occurs at potentials far outside the stability region of water (see Figure 3). The electrolyte would decompose, and the ion transport gets disrupted.
Why are flow batteries so expensive?
Flow batteries have a higher initial cost compared to other battery types due to their complex design, which includes separate tanks for storing electrolytes, pumps, plumbing, and control systems. Moreover, their relatively low charge and discharge rates necessitate the use of substantial quantities of materials.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Disadvantages of zinc-iron flow batteries
Disadvantages of zinc-iron flow batteries
-
 Disadvantages of Iron-Cadmium Flow Batteries
Disadvantages of Iron-Cadmium Flow Batteries
-
 Requirements for flow batteries for communication base stations
Requirements for flow batteries for communication base stations
-
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Instant Energy Storage Batteries
Advantages and Disadvantages of Instant Energy Storage Batteries
-
 Cost of zinc-iron flow batteries
Cost of zinc-iron flow batteries
-
 Flow batteries for mobile base station equipment
Flow batteries for mobile base station equipment
-
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Huawei s Energy Storage Batteries
Advantages and Disadvantages of Huawei s Energy Storage Batteries
-
 Zinc-based flow batteries and vanadium batteries
Zinc-based flow batteries and vanadium batteries
-
 Do vanadium liquid flow batteries require phosphoric acid
Do vanadium liquid flow batteries require phosphoric acid
-
 Advantages and disadvantages of interchangeable energy storage batteries
Advantages and disadvantages of interchangeable energy storage batteries
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


