Empowering smart grid: A comprehensive review of energy storage
The rapid growth in the usage and development of renewable energy sources in the present day electrical grid mandates the exploitation of energy storage technologies to
Get a quote
The role of energy storage in the future electric grid
Three distinct yet interlinked dimensions can illustrate energy storage''s expanding role in the current and future electric grid—renewable energy integration, grid optimization,
Get a quote
What role do energy storage technologies play in
Grid Modernization and Efficiency: Energy storage technologies are integral to grid modernization. They help integrate renewable energy
Get a quote
Battery Storage Advancements: What''s Next for the
Unlocking the Full Potential of Energy Storage The future of battery storage technology holds immense promise for transforming the
Get a quote
The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Stability and
Energy storage technologies, ranging from lithium-ion batteries to pumped hydro storage and beyond, play a pivotal role in addressing the
Get a quote
Energy Storage Technologies for Modern Power Systems: A
Energy storage technologies can potentially address these concerns viably at different levels. This paper reviews different forms of storage technology available for grid
Get a quote
Energy storage technologies: An integrated survey of
Abstract Energy Storage Technology is one of the major components of renewable energy integration and decarbonization of world energy systems. It significantly benefits
Get a quote
Smart grids and renewable energy systems: Perspectives and grid
Abstract The concept of smart grid (SG) was made real to give the power grid the functions and features it needs to make a smooth transition towards renewable energy
Get a quote
Charging Up: The State of Utility-Scale Electricity Storage in the
Grid-scale energy storage has been growing in the power sector for over a decade, spurred by variable wholesale energy prices, technology developments, and state and federal
Get a quote
Grid energy storage
Electricity can be stored directly for a short time in capacitors, somewhat longer electrochemically in batteries, and much longer chemically (e.g. hydrogen), mechanically (e.g. pumped hydropower) or as heat. The first pumped hydroelectricity was constructed at the end of the 19th century around the Alps in Italy, Austria, and Switzerland. The technique rapidly expanded during the 196
Get a quote
How Do Battery Energy Storage Systems Improve Grid Stability?
Learn how Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) help improve grid stability by balancing supply and demand, integrating renewable energy, and providing backup power.
Get a quote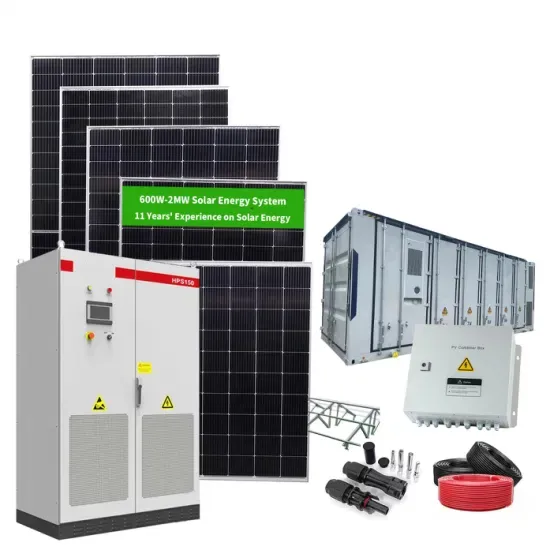
Grid-Scale Battery Storage Is Quietly Revolutionizing
This energy storage technology is harnessing the potential of solar and wind power—and its deployment is growing exponentially.
Get a quote
Energy Storage for a Modern Electric Grid: Technology Trends
Storage technologies can help meet peak demand when power prices are high, provide backup power during power outages, or help the grid adapt to sudden power
Get a quote
Role of energy storage technologies in enhancing grid stability
This paper provides an overview of energy storage, explains the various methods used to store energy (focusing on alternative energy forms like heat and electricity), and then
Get a quote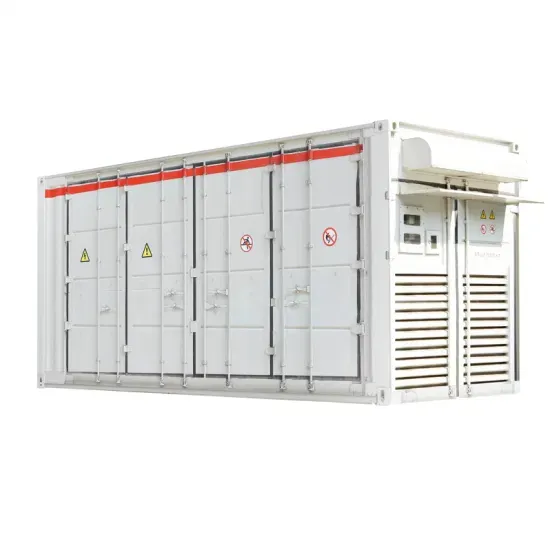
The role of energy storage in the future electric grid
Three distinct yet interlinked dimensions can illustrate energy storage''s expanding role in the current and future electric grid—renewable
Get a quote
What role do energy storage technologies play in stabilizing the grid
Grid Modernization and Efficiency: Energy storage technologies are integral to grid modernization. They help integrate renewable energy efficiently, defer infrastructure upgrades,
Get a quote
The Role of Battery Energy Storage Systems in Grid Reliability
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are emerging as a foundational technology for modernizing the electric grid, offering fast, flexible, and scalable solutions to support
Get a quote
Energy Storage Technologies and Their Role in Grid Stability
Energy storage technologies are essential components of modern power systems, especially as the integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, grows.
Get a quote
The Role of Battery Storage in Clean Energy Transition
In conclusion, battery storage is not only supporting renewable energy today but is paving the way for a complete transition to clean energy. By enabling energy reliability,
Get a quote
Smart grid energy storage technology ppt
EST can provide more balancing and flexibility to the power system,providing incorporation of intermittent RES to the smart grid. Energy storage technologies have a critical function to
Get a quote
The Role of Energy Storage Systems for a Secure Energy
Energy storage systems will be fundamental for ensuring the energy supply and the voltage power quality to customers. This survey paper offers an overview on potential energy
Get a quote
Storage Futures | Energy Systems Analysis | NREL
Through the SFS, NREL analyzed the potentially fundamental role of energy storage in maintaining a resilient, flexible, and low carbon U.S.
Get a quote
Modeling Energy Storage s Role in the Power System of the
Model resource needs over multiple weather years to capture periods of real grid stress, such as multi-day lulls in renewable energy generation, extreme heat and cold, or periods of high
Get a quote
Emerging and maturing grid-scale energy storage technologies: A
The technologies under investigation are: 1. gravity energy storage, 2. carbon dioxide energy storage, 3. isothermal compressed air energy storage, 4. supercritical
Get a quote
Role of energy storage technologies in enhancing grid stability
Similarly, molten salts'' capacity to store heat wisely for long durations has made them essential for thermal energy storage, especially in concentrating solar power systems.
Get a quote
The Role of Energy Storage in Grid Stability and Management
Energy storage technologies, ranging from lithium-ion batteries to pumped hydro storage and beyond, play a pivotal role in addressing the inherent variability of renewable
Get a quote
The Role of Energy Storage Systems for a Secure Energy
Energy storage systems Grid-forming control Grid services Power hardware in the loop and the electrification of transportation and heating systems. As a consequence, the
Get a quote
Grid energy storage
Energy from fossil or nuclear power plants and renewable sources is stored for use by customers. Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, is a set of technologies
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [The role of energy storage technology in the power grid]
What is grid energy storage?
Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, are technologies connected to the electrical power grid that store energy for later use. These systems help balance supply and demand by storing excess electricity from variable renewables such as solar and inflexible sources like nuclear power, releasing it when needed.
What are energy storage technologies?
Energy storage technologies, ranging from lithium-ion batteries to pumped hydro storage and beyond, play a pivotal role in addressing the inherent variability of renewable energy sources and optimizing grid performance.
Are energy storage technologies viable for grid application?
Energy storage technologies can potentially address these concerns viably at different levels. This paper reviews different forms of storage technology available for grid application and classifies them on a series of merits relevant to a particular category.
What is the role of energy storage in grid stability & management?
In essence, energy storage serves as a crucial bridge between energy generation and consumption, offering flexibility, resilience, and efficiency in managing the complexities of modern power systems. In this blog post, we will delve into the multifaceted role of energy storage in grid stability and management.
How do energy storage systems work?
Electrical grids require precise control of frequency and voltage levels to maintain stable operation. Energy storage systems can respond rapidly to changes in grid conditions, injecting or absorbing power as needed to regulate frequency and voltage and support grid stability.
How can energy storage improve grid management?
As the electricity demand continues to grow and the integration of renewable energy sources increases, energy storage technologies offer solutions to address the challenges associated with grid management. One of the primary contributions of energy storage to grid management is its ability to balance supply and demand.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Angola Energy Storage Power Station Grid Side
Angola Energy Storage Power Station Grid Side
-
 Bahrain power grid energy storage supplier
Bahrain power grid energy storage supplier
-
 Guinea Power Grid Energy Storage System
Guinea Power Grid Energy Storage System
-
 Colombia Southern Power Grid Energy Storage Company
Colombia Southern Power Grid Energy Storage Company
-
 Portugal s power grid energy storage system
Portugal s power grid energy storage system
-
 Energy Storage Smart Grid Virtual Power Plant
Energy Storage Smart Grid Virtual Power Plant
-
 Huawei s power grid energy storage direction
Huawei s power grid energy storage direction
-
 South Korea Power Grid 30kw Energy Storage
South Korea Power Grid 30kw Energy Storage
-
 Morocco Casablanca Energy Storage Power Station Grid Connection Project
Morocco Casablanca Energy Storage Power Station Grid Connection Project
-
 Congo Kinshasa Power Grid Energy Storage Equipment Company
Congo Kinshasa Power Grid Energy Storage Equipment Company
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


