Solar and wind power in Colombia: 2022 policy overview
Resolution 40284 of 2022 sets the competitive rules for development of ofshore wind power. The CREG Resolution 075 of 2021 regulates access to transmission for renewable energy projects
Get a quote
Scenarios for wind capacity deployment in Colombia by 2050: A
Supported by system dynamics modeling, this paper presents four scenarios that explore possible futures for wind capacity deployment in Colombia between 2020 and 2050.
Get a quote
(PDF) Design of an off-grid hybrid PV/wind power
The study [4] has discussed the energy efficiency of telco base stations with renewable sources integration and the possibility of base stations
Get a quote
Microsoft Word
The purpose of this work is to find a solution based on a low power wind turbine to serve a real telecommunication site located near Palermo, the main city of Sicily (Italy).
Get a quote
Towards greener telecommunication towers: A framework for
The telecommunication towers'' structure depends on tower location, available land, tower surroundings, and wind speed in the considered area (Elhakim et al., 2022), and
Get a quote
Challenges of Power System Operations in Colombia
Supported by system dynamics modeling, this paper presents four scenarios that explore possible futures for wind capacity deployment in Colombia between 2020 and 2050.
Get a quote
(PDF) Small windturbines for telecom base stations
The presentation is a state of the art overview on aspects of coupling small windturbines to telecom basestations. Worldwide thousands of
Get a quote
Challenges of Power System Operations in Colombia
Since the existing regulatory framework in Colombia is not allowing storage systems or behind-the-meter resources to provide the required flexibility services, hydropower will be the more
Get a quote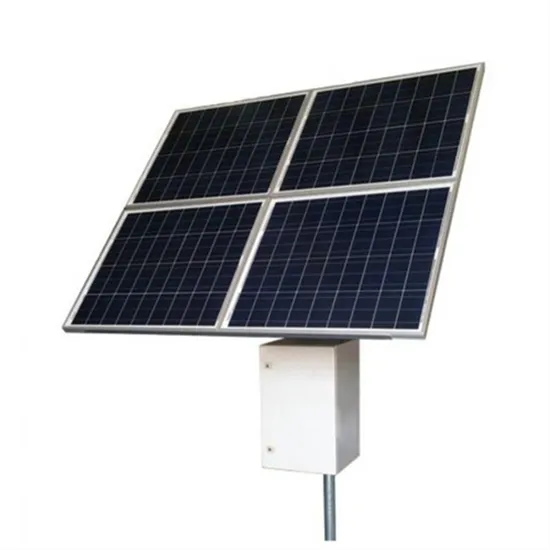
The Role of Hybrid Energy Systems in Powering
Discover how hybrid energy systems, combining solar, wind, and battery storage, are transforming telecom base station power, reducing costs,
Get a quote
(PDF) Wind Turbines to Power Telecommunication Systems: A Case
The ever increasing problems related to air pollution and the difficulties for power lines to reach inaccessible areas are pushing to find new solutions for powering telecommunications
Get a quote
Renewable Energy 2024
Specifically, the Court emphasised that market access is the essential core (núcleo esencial) of the constitutional right to the free market. Therefore, regulations restricting access
Get a quote
WINDExchange: Wind Energy Ordinances
Wind turbine heights can be defined in multiple ways: the distance from the base of the tower to the hub or nacelle, the base of the tower to the tip of a blade when extended
Get a quote
An enabling framework for wind power in Colombia: what are the
This article discusses the existing framework for enabling wind power in Colombia and identifies policy requirements for increasing the share of renewables.
Get a quote
Mobile phone base stations: radio waves and health
Summary Base stations transmit and receive radio waves to connect the users of mobile phones and other devices to mobile communications networks. The strength of the
Get a quote
How to assess and manage energy performance of numerous
1. Introduction Telecommunication base stations (TBSs) are the basic units of the telecommunications network and consume more energy than other public buildings due to
Get a quote
The Influence of Colombia''s Proposed Telecommunications
Colombia''s proposed telecommunications regulation is transforming the industry, focusing on network quality and 5G deployment.
Get a quote
(PDF) Small windturbines for telecom base stations
The presentation will give attention to the requirements on using windenergy as an energy source for powering mobile phone base stations.
Get a quote
Wind-solar-diesel hybrid model for telecommunication base stations
In the present study, a procedural approach to design of a wind-solar-diesel hybrid energy system for remote telecommunication base station was attempted, by using weather
Get a quote
(PDF) Power Consumption: Base Stations of Telecommunication
In this paper, the work consists of categorizing telecommunication base stations (BTS) for the Sahel area of Cameroon according to their power consumption per month. It consists also of
Get a quote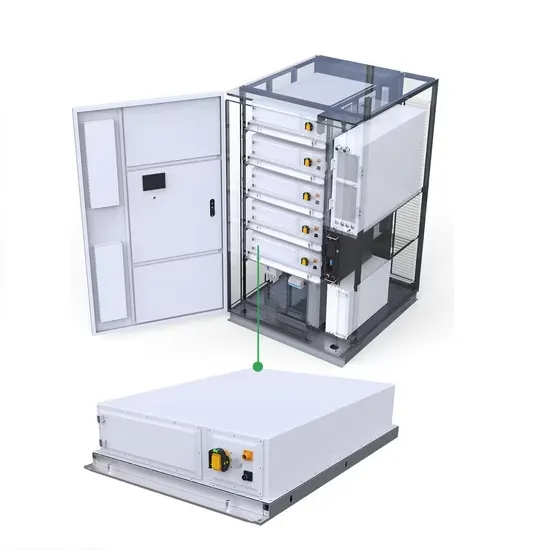
Offshore Wind Roadmap for Colombia O
Particular recognition is given to the wider RCG team and the ERM Bogotá office for their dedication and enthusiasm to provide a thorough strategic analysis and advice on the role that
Get a quote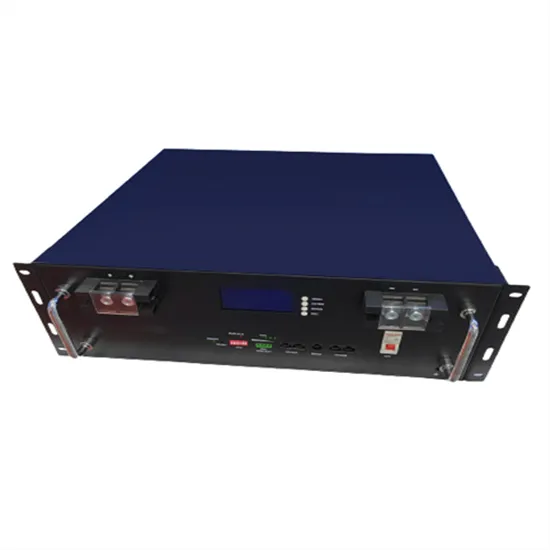
World Bank Document
If these barriers are successfully addressed, wind energy may contribute substantially to maintain the current, relatively lowcarbon footprint of Colombias power sector, aided by a strong hydro
Get a quote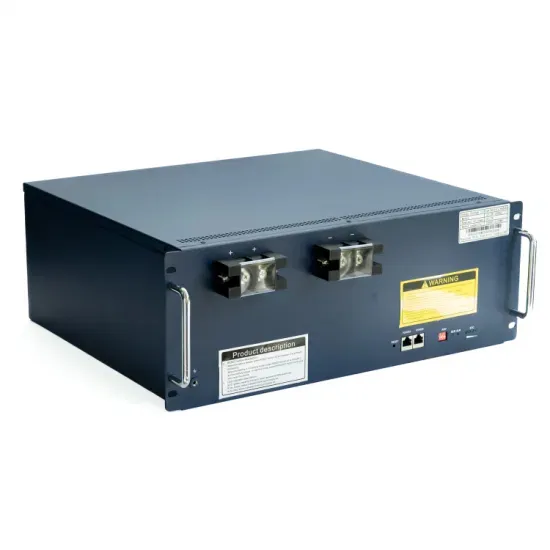
(PDF) Small windturbines for telecom base stations
The presentation will give attention to the requirements on using windenergy as an energy source for powering mobile phone base stations.
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Colombian Telecommunication Base Station Wind Power Regulations]
Are Colombia's wind energy plans stalling?
(AP Photo/Ivan Valencia, File) BOGOTA, Colombia (AP) — Colombia’s ambitious plans for wind energy development, especially in the resource-rich La Guajira region, are facing serious setbacks as major companies pull out and projects stall, industry experts say.
How much wind power does Colombia have?
Colombia’s rich wind and solar energy potential is estimated at 30 GW and 32 GW, respectively, according to SER Colombia, which is more than Colombia’s current installed capacity of 18.8 GW. Of particular interest is La Guajira region, with world-class wind resources (average wind speeds of 9.8 m/s) and 18 GW of Colombia’s wind power potential.
How can wind and solar energy be used in Colombia?
The expected large deployment of wind and solar resources in Colombia can be used to leverage creation of local employment, gender equality and benefits to local communities and Indigenous peoples. This will require strengthened policy frameworks to avoid negative efects on these areas.
Did Colombia start a wind farm without a regulatory framework?
Diego Patron, manager of the Jemeiwaa Ka’I wind project, a large-scale wind farm cluster in La Guajira, acknowledged the pioneering nature of Colombia’s early wind efforts, which began in a regulatory vacuum without clear institutional frameworks.
What is energy policy in Colombia?
Energy policy in Colombia is defined by the National Energy Plan (PEN) 2020–2050, which includes solar and wind in its diferent scenarios, including for both grid-connected and unconnected areas. Electricity planning is outlined by the 15-year Generation and Transmission Expansion Plans, which are updated yearly.
What is the energy transition in Colombia?
The Colombian energy transition is centered around large and small-scale wind and solar power integration that will increase the requirements of flexibility services, inertia and grid expansion at transmission and distribution levels, but also that will make the generation mix even greener.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Telecommunication base station wind power Peak shaving and valley filling
Telecommunication base station wind power Peak shaving and valley filling
-
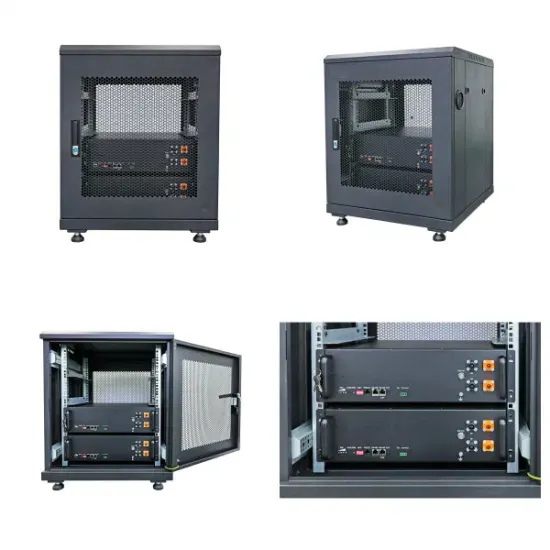
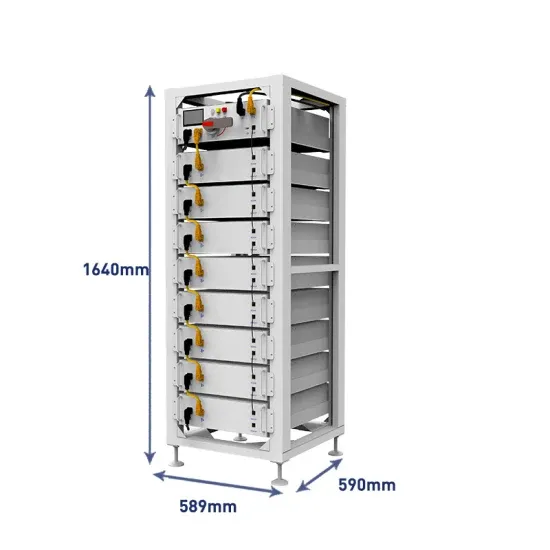 Israel Telecommunication Base Station Hybrid Energy Wind Power
Israel Telecommunication Base Station Hybrid Energy Wind Power
-
 Wind power communication base station energy storage cabinet business
Wind power communication base station energy storage cabinet business
-
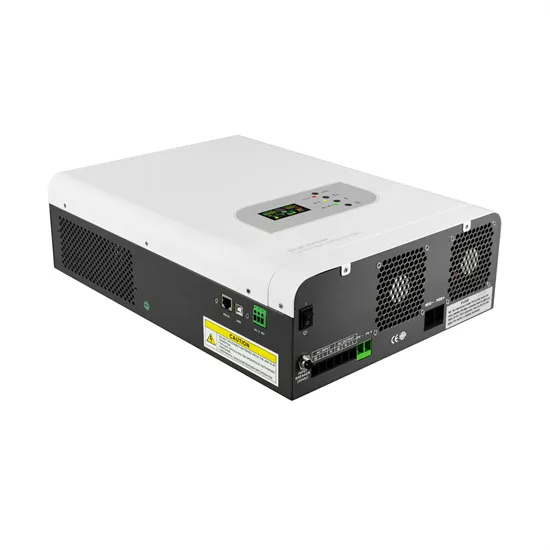 Guatemala 5G communication base station wind power planning
Guatemala 5G communication base station wind power planning
-
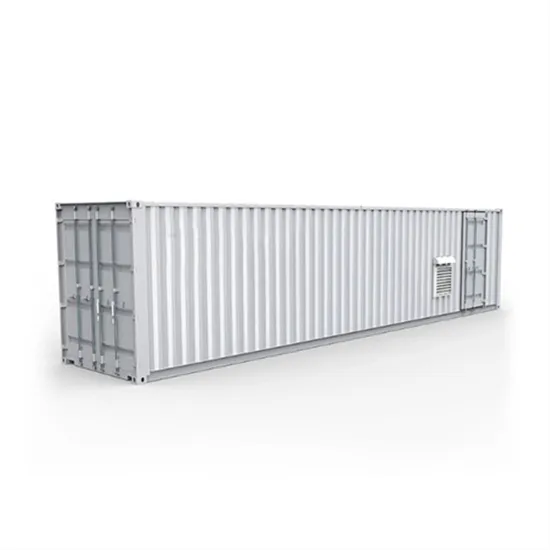 Base station communication equipment wind power
Base station communication equipment wind power
-
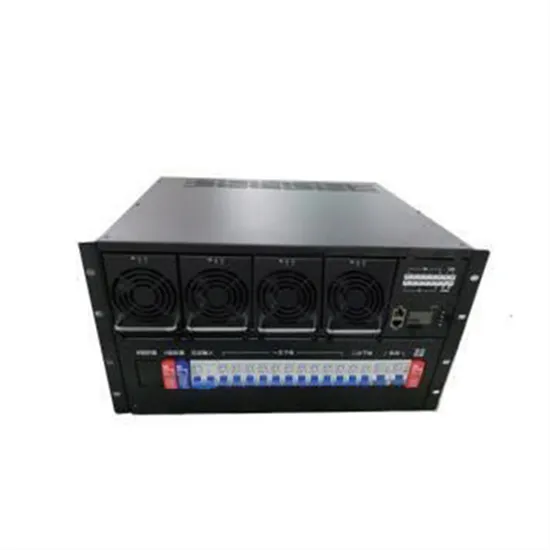 China Green Communication Base Station Wind Power
China Green Communication Base Station Wind Power
-
 Cook Islands Communication Base Station Wind and Solar Complementary Regulations
Cook Islands Communication Base Station Wind and Solar Complementary Regulations
-
 Communication base station wind power energy saving system
Communication base station wind power energy saving system
-
 Sofia Communication Base Station Wind Power Planning
Sofia Communication Base Station Wind Power Planning
-
 Eastern European communication base station wind power technology
Eastern European communication base station wind power technology
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


