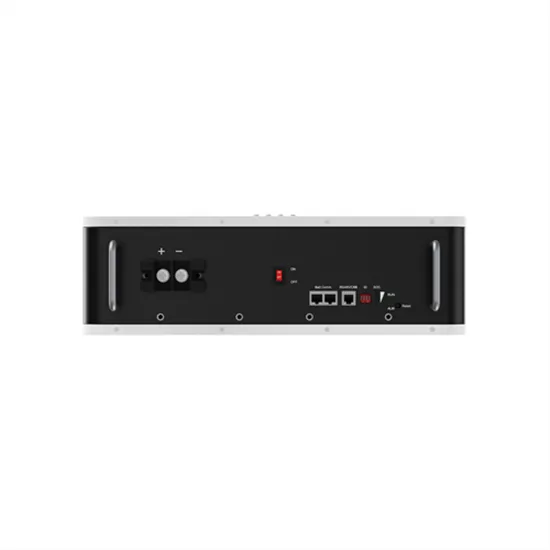
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
By definition, Low frequency power inverters got the name of "low frequency" because they use high speed power transistors to invert the DC
Get a quote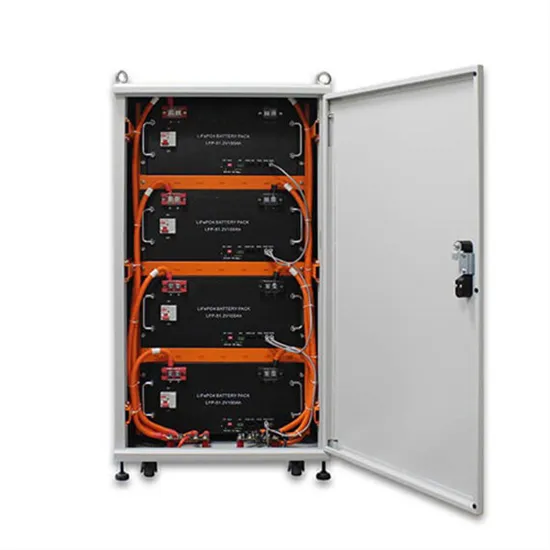
What are the Differences: Pure Sine Wave Inverter vs Modified
Pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters are two common types of inverters. They have some differences in working principle, performance characteristics,
Get a quote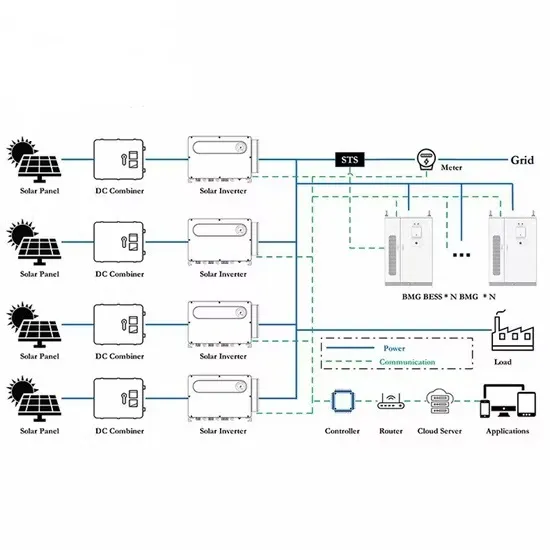
The difference between frequency converter and inverter
The waveform output by the frequency converter is a simulated sine wave, which is mainly used for speed regulation of three-phase asynchronous motors, also called a variable
Get a quote
Modified vs. Pure Sine Wave Inverter: What''s the
Pure sine inverters are more sophisticated devices that can exactly replicate an AC sine wave from a DC power source. Because of their
Get a quote
What are the Differences: Pure Sine Wave Inverter vs Modified Sine Wave
Pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters are two common types of inverters. They have some differences in working principle, performance characteristics,
Get a quote
Inverter Vs Transformer: Key Differences, Pros, And Cons In
Pure Sine Wave Inverters: These are more advanced, provide smoother and more reliable power, and are often used for sensitive electronics. For detailed information, see a 1000-watt pure
Get a quote
Differences between standard industrial power inverters and
Industrial power inverters are really powerful, and at the same time, durable enough to withstand the high power needs of industrial machinery and equipment. While many
Get a quote
Pure Sine Wave Inverter vs. Modified Sine Wave:How to
This article will conduct in-depth analysis from multiple dimensions such as waveform principle, application scenario, cost-effectiveness, etc., to help you accurately match
Get a quote
The Great Inverter Debate: Modified vs. Pure Sine Wave for
The waveform an inverter produces—whether modified sine wave (MSW) or pure sine wave (PSW) —can make the difference between seamless operation and costly
Get a quote
Differences between Modified Sine Wave and Pure Sine Wave Power Inverters
In today''s era of widespread power applications, the choice of power inverter is crucial. Here''s an in-depth look at modified sine wave and pure sine wave inverters to help you
Get a quote
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave inverter & difference
By definition, Low frequency power inverters got the name of "low frequency" because they use high speed power transistors to invert the DC voltage to AC power, but the
Get a quote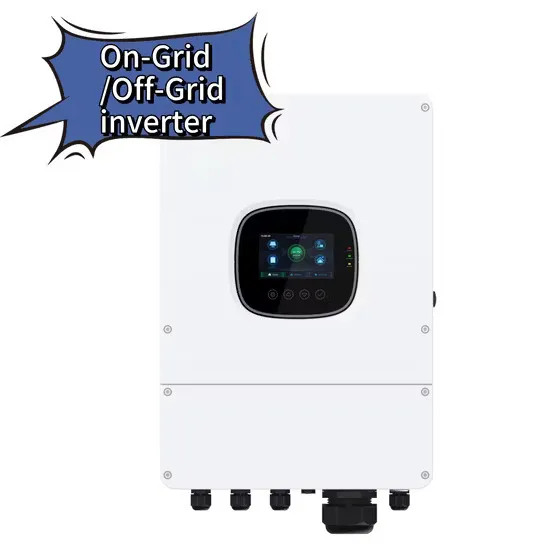
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
Types of Inverters: Inverters are categorized by their output waveforms (square wave, modified sine wave, and sine wave) and by their
Get a quote
Inverter Types & Working Principle | Sine Wave, Square Wave,
The article provides an overview of inverter technology, explaining how inverters convert DC to AC power and detailing the different types of inverters—sine wave, square wave, and modified
Get a quote
Frequency inverters
The tasks and function of a frequency inverter are varied depending on the model, for example the " frequency inverter 400v " or " frequency inverter 230v ", and
Get a quote
Modified vs. Pure Sine Wave Inverter: What''s the Difference?
Pure sine inverters are more sophisticated devices that can exactly replicate an AC sine wave from a DC power source. Because of their added complexity, they''ve historically
Get a quote
Everything You Need to Know About Inverters: Types,
Key Takeaways Familiarize with the inverter size range suited for household use, and why mega-watt units are not typical in residential settings.
Get a quote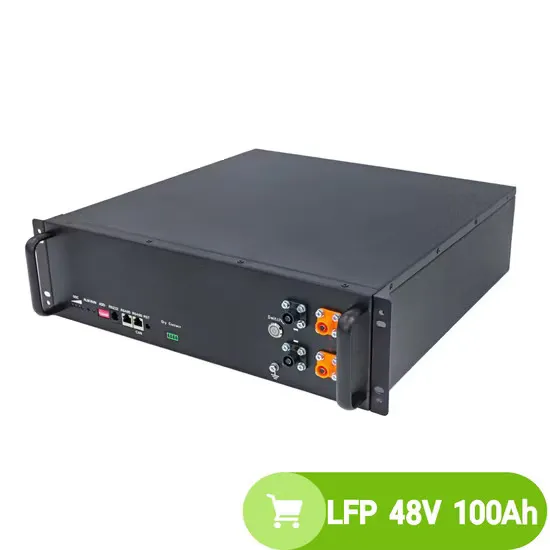
Differences between modular and industrial power inverters
On the other hand, buying a modular inverter instead of a standard industrial power inverter will only lead to future damage. This is because modular inverters cannot
Get a quote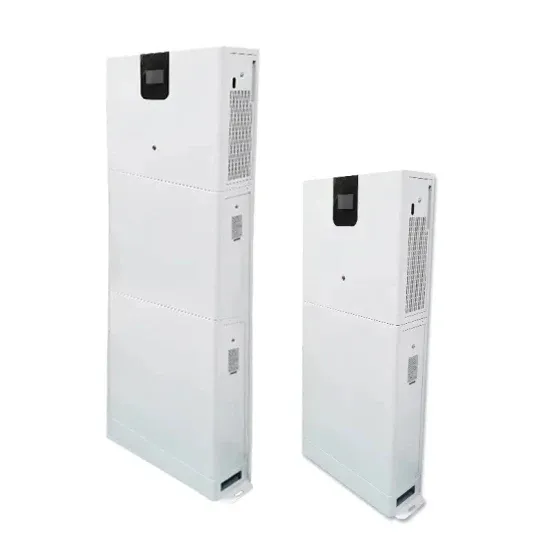
What Is A Pure Sine Wave Inverter? | Definition, Benefits,
A Pure Sine Wave Inverter is a critical component in the world of power conversion, known for delivering clean and stable electrical energy. This article delves deeply
Get a quote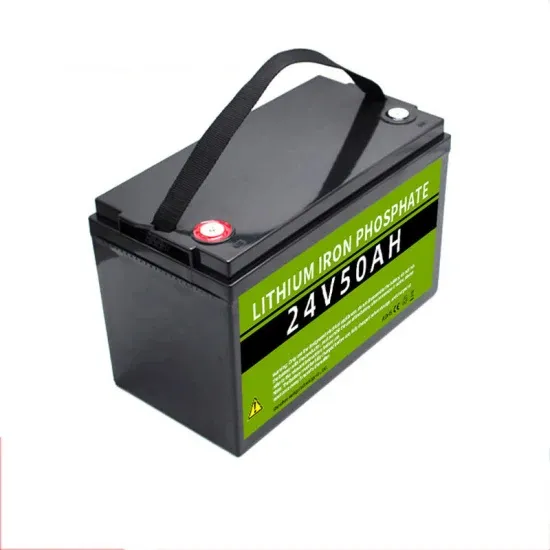
The Great Inverter Debate: Modified vs. Pure Sine Wave for Industrial
The waveform an inverter produces—whether modified sine wave (MSW) or pure sine wave (PSW) —can make the difference between seamless operation and costly
Get a quote
Sine Wave vs Square Wave: What You Need to Know
Sine waves deliver smooth, consistent power that is ideal for sensitive electronics, while square waves provide basic, less efficient energy
Get a quote
Key Differences Between Frequency Inverters and Inverters
Understand the key differences between frequency inverters for motor control and power inverters for DC to AC conversion. Learn their unique applications.
Get a quote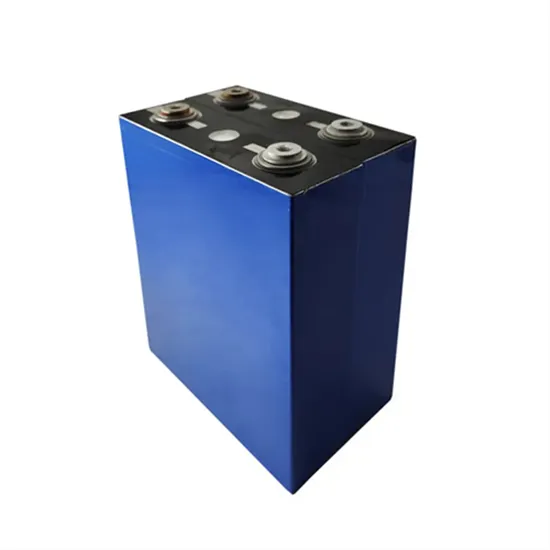
A comprehensive guide to understanding and
Pure sine wave inverters: These inverters produce a near-perfect sine wave output, making them suitable for powering sensitive electronic
Get a quote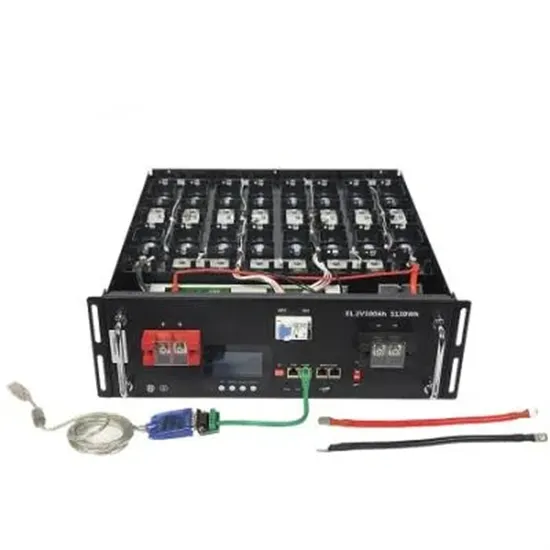
The difference between frequency converter and inverter
The waveform output by the frequency converter is a simulated sine wave, which is mainly used for speed regulation of three-phase asynchronous
Get a quote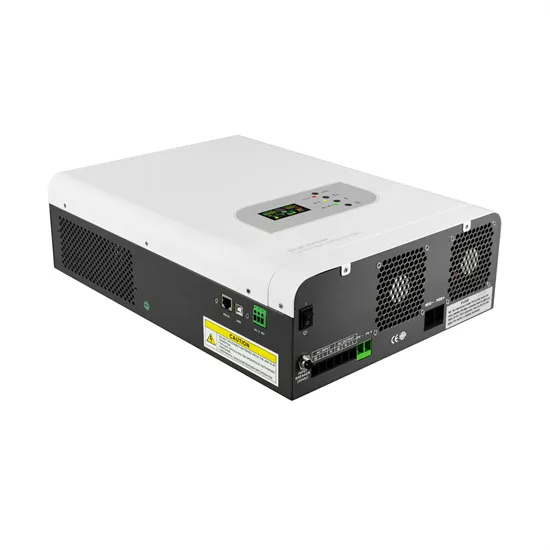
Modified Vs. Pure Sine Wave Power Inverters [Purchasing Guide]
What''s the difference between pure sine and modified sine wave power inverters? Which inverter should you buy for sensitive electronics?
Get a quote
What is the Difference Between a Power Inverter and
Explore the differences between pure sine wave and standard power inverters to choose the right solution for your commercial or industrial
Get a quote
Inverter Types & Working Principle | Sine Wave,
The article provides an overview of inverter technology, explaining how inverters convert DC to AC power and detailing the different types of inverters—sine
Get a quote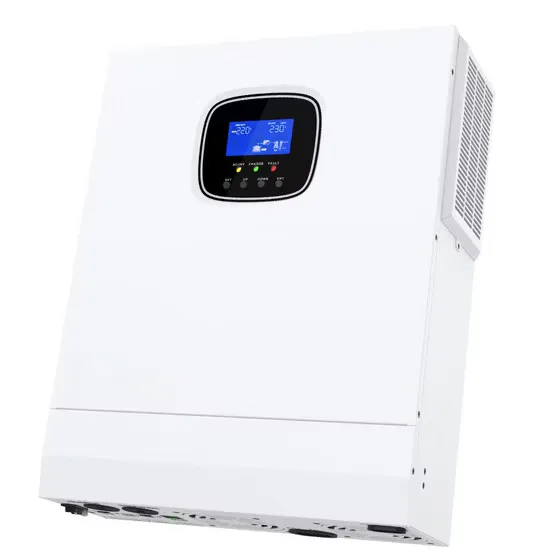
Pure Sine Wave Inverter: All You Need to Know
In this blog post, we will explore the fundamentals of pure sine wave inverters, including what they are, how they work, the differences between modified and pure sine wave
Get a quote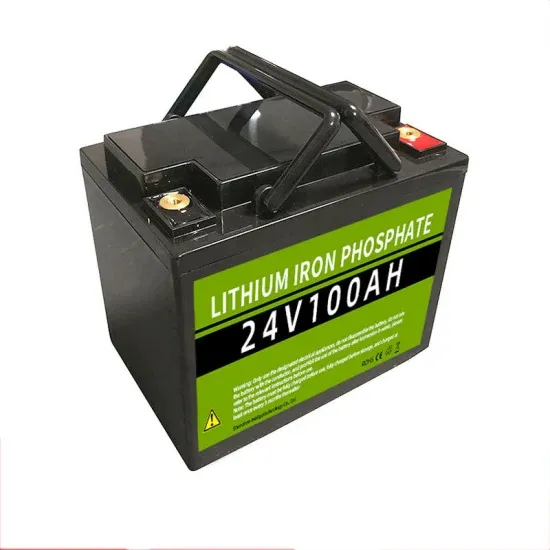
What is the Difference Between a Power Inverter and a Pure Sine Wave
Explore the differences between pure sine wave and standard power inverters to choose the right solution for your commercial or industrial applications.
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Difference between sine wave and industrial frequency inverter]
What is the difference between pure sine wave inverter and modified sine wave?
Pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters are two common types of inverters. They have some differences in working principle, performance characteristics, application field, waveform, and compatibility. Next, we will explain the differences between pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters in various aspects.
What is a pure sine wave inverter?
A pure sine wave inverter is a type of power inverter that converts DC (direct current) power from batteries or other DC sources into AC power that can be used to power a wide range of electronic devices and appliances, including sensitive equipment such as laptops, refrigerators, air conditioners, and more.
What are the different types of sine wave inverters?
The square wave, modified sine wave, and quasi-sine wave all have a number of harmonics, which, as you know, are sine waves with frequencies that are odd multiples of the fundamental frequency and different amplitudes. Harmonics are especially troublesome in some applications, so high-quality sine wave inverters are the most widely used type.
What is the output current waveform of a pure sine wave inverter?
The output current waveform of a pure sine wave inverter is of high quality and can achieve low harmonic distortion when interfaced with a grid power supply.
What is a modified sine inverter?
The major advantage of modified sine inverters is that they are less expensive than pure sine models. Pure sine inverters are more sophisticated devices that can exactly replicate an AC sine wave from a DC power source. Because of their added complexity, they've historically cost a lot more than modified sine inverters.
Can you use a modified sine wave inverter without a motor?
Devices without AC motors tend to work as expected with modified sine wave inverters, and any device with a rectifier cleans up that rough AC wave as it turns it into DC power. So lamps, TVs, and other devices are OK for modified inverter use. The major advantage of modified sine inverters is that they are less expensive than pure sine models.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Branded industrial frequency pure sine wave inverter
Branded industrial frequency pure sine wave inverter
-
 48v industrial frequency sine wave inverter
48v industrial frequency sine wave inverter
-
 Photovoltaic power frequency inverter and pure sine wave inverter
Photovoltaic power frequency inverter and pure sine wave inverter
-
 Industrial grade pure sine wave inverter
Industrial grade pure sine wave inverter
-
 Sine wave inverter power frequency inverter
Sine wave inverter power frequency inverter
-
 Power frequency inverter sine wave
Power frequency inverter sine wave
-
 Power frequency pure sine wave control inverter
Power frequency pure sine wave control inverter
-
 High frequency pure sine wave inverter 12V to 48V
High frequency pure sine wave inverter 12V to 48V
-
 Production of industrial frequency sine wave inverters
Production of industrial frequency sine wave inverters
-
 The difference between inverter and sine wave
The difference between inverter and sine wave
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

