How DC/AC Power Inverters Work | HowStuffWorks
Power inverters convert direct current (DC), the power that comes from a car battery, into alternating current (AC), the kind of power supplied to your home and the power
Get a quote
YOUR GUIDE TO DC to AC POWER INVERTERS
A device that converts electricity from DC form to AC form using electronic circuits is known in power industry as inverter. Note that the same term is used in
Get a quote
DC and AC Inverters: What You Need to Know
What is the main difference between a DC inverter and an AC inverter? The main difference is that a DC inverter converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), while
Get a quote
Inverter is Ac or Dc
Inverters are essential for converting the direct current (DC) from sources like solar panels or batteries into alternating current (AC) used in household appliances.
Get a quote
A Guide to Solar Inverters: How They Work & How to Choose Them
An inverter converts the DC electricity from sources such as batteries or fuel cells to AC electricity. The electricity can be at any required voltage; in particular it can operate AC equipment designed for mains operation, or rectified to produce DC at any desired voltage. An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) uses batteries and an inverter to suppl
Get a quote
What is dc and ac converter? Understanding DC to AC Inverters
DC to AC Converter: Commonly called an inverter, this device converts DC power into AC power. It is widely used in solar power systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and vehicles.
Get a quote
The Main Differences Between Inverters and Converters
Understanding the differences between an inverter and a converter is essential for anyone working with electrical systems. Here''s a concise description of their key distinctions:
Get a quote
All About DC Inverter Air Condtioners (2025) | Today''s
Yes, DC inverter air conditioners, also known as AC inverters, can work efficiently in hot climates. Since the compressor''s speed and power are
Get a quote
Amazon : DC To AC Inverter
BELTTT 1000Watt Pure Sine Wave Inverter 12V DC to 120V AC for RV, Truck, Off-Grid Solar Car Power Inverter 12V to 110V Converter with Dual AC Socket and 5V 2.1A USB, Intelligent LCD,
Get a quote
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
What is an Inverter? Inverter is the device which converts DC into AC is known as Inverter. Most of the commercial, industrial, and residential loads require Alternating Current (AC) sources.
Get a quote
Power inverter
An inverter converts the DC electricity from sources such as batteries or fuel cells to AC electricity. The electricity can be at any required voltage; in particular it can operate AC
Get a quote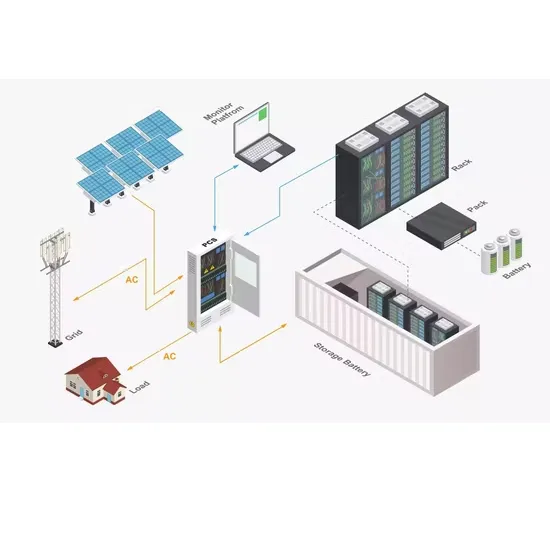
Is an Inverter AC or DC?
Now you know that an inverter is DC. It is designed to convert DC into AC power. You must run an inverter using a DC power source in order for it to operate.
Get a quote
DC to AC Converter: Making Efficient Energy Transitions
A DC to AC converter, also known as an inverter, is designed to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). This type of device is crucial for
Get a quote
Introduction to DC/AC Converters
Modern power electronics depend heavily on DC/AC converters because they make it possible to convert DC sources to AC, which is the norm for the majority of electrical applications. These
Get a quote
DC and AC Inverters: What You Need to Know
What is the main difference between a DC inverter and an AC inverter? The main difference is that a DC inverter converts direct current (DC)
Get a quote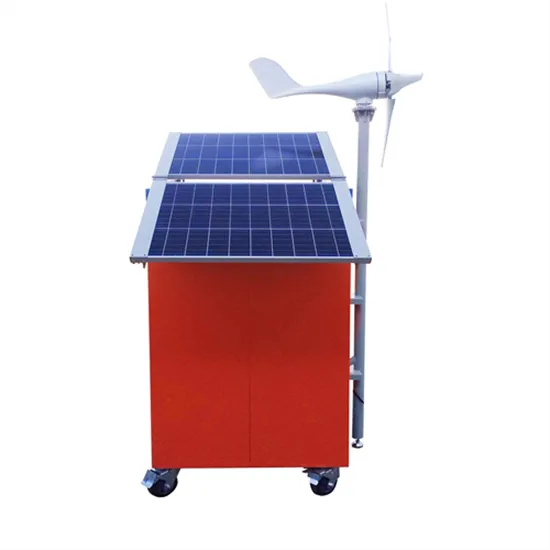
DC-to-AC Converters (Inverters): Design, Working
DC-to-AC converters, also known as inverters, play a crucial role in many different applications due to their ability to convert direct current (DC)
Get a quote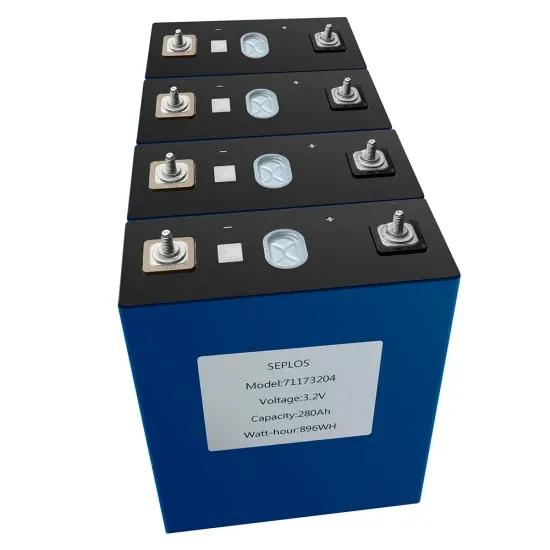
Solar Integration: Inverters and Grid Services Basics
Inverters are just one example of a class of devices called power electronics that regulate the flow of electrical power. Fundamentally, an inverter accomplishes the DC-to-AC conversion by
Get a quote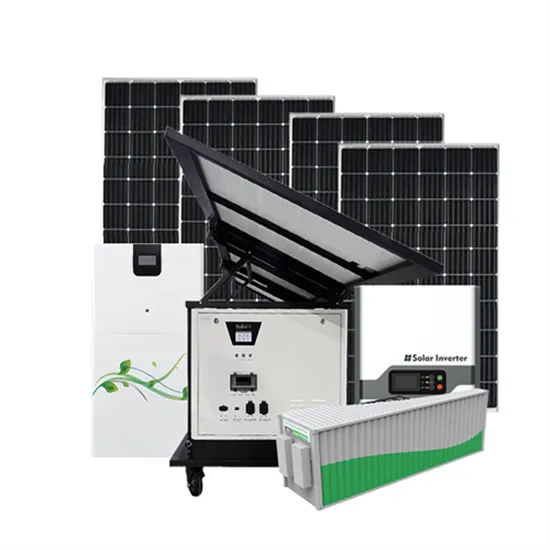
The difference between AC Inverter and DC Inverter
While AC inverters are more versatile and suitable for general household use, DC inverters are specialized and offer high efficiency for particular tasks. By identifying your needs
Get a quote
Solar Integration: Inverters and Grid Services Basics
Inverters are just one example of a class of devices called power electronics that regulate the flow of electrical power. Fundamentally, an inverter accomplishes
Get a quote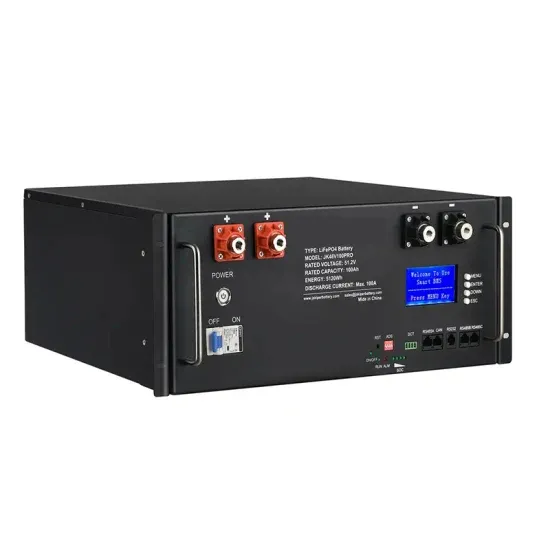
Is an Inverter AC or DC?
Now you know that an inverter is DC. It is designed to convert DC into AC power. You must run an inverter using a DC power source in order for it to operate. There would be no point in
Get a quote
AC to DC Converter VS DC to AC Inverter
A systematic comparison of the differences and synergies between the two most common power conversion devices: AC to DC converters and DC to AC inverters.
Get a quote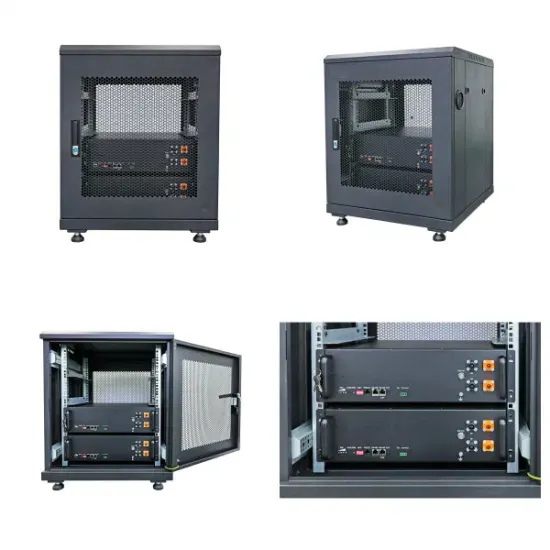
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power
Get a quote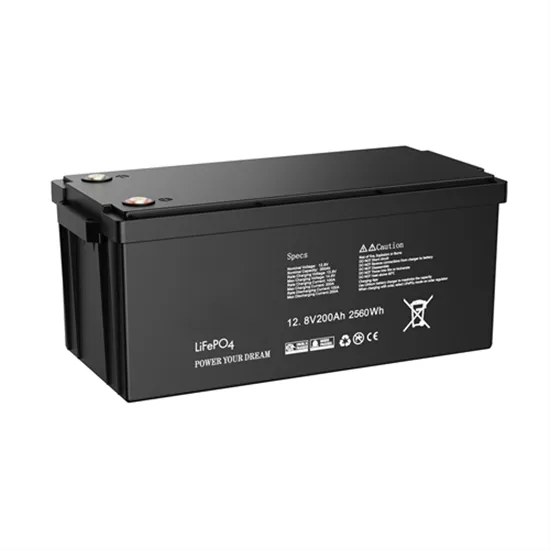
A Guide to Solar Inverters: How They Work & How to Choose Them
Most homes use AC rather than DC energy. DC energy is not safe to use in homes. If you run Direct Current (DC) directly to the house, most gadgets plugged in would smoke and
Get a quote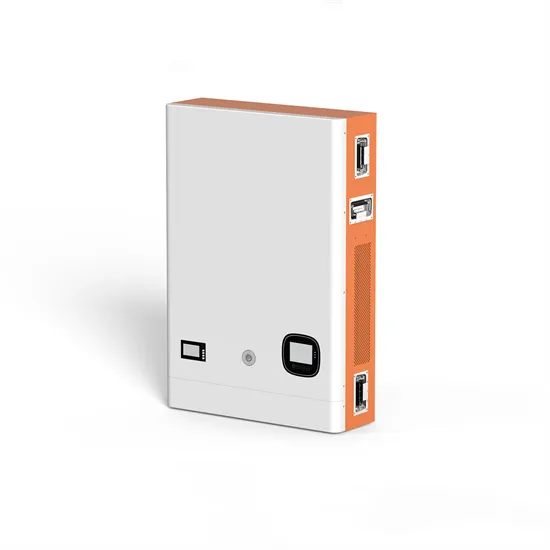
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
Appliances that need DC but have to take power from AC outlets need an extra piece of equipment called a rectifier, typically built from electronic components called diodes,
Get a quote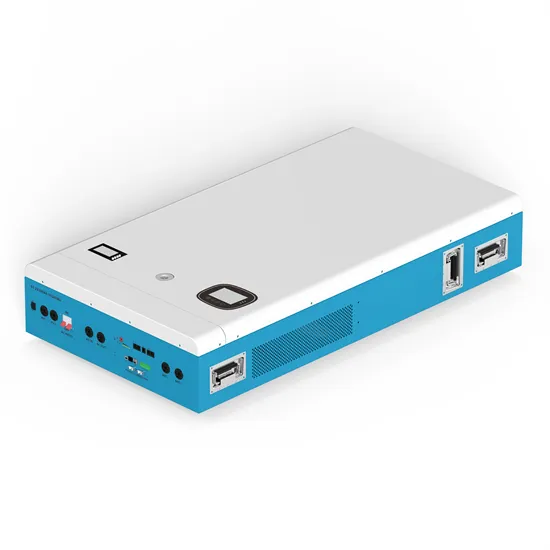
How Do Inverters Convert DC to AC?
Understand how inverters convert DC (Direct Current) to AC (Alternating Current) in power systems, along with applications and benefits provided by Power
Get a quote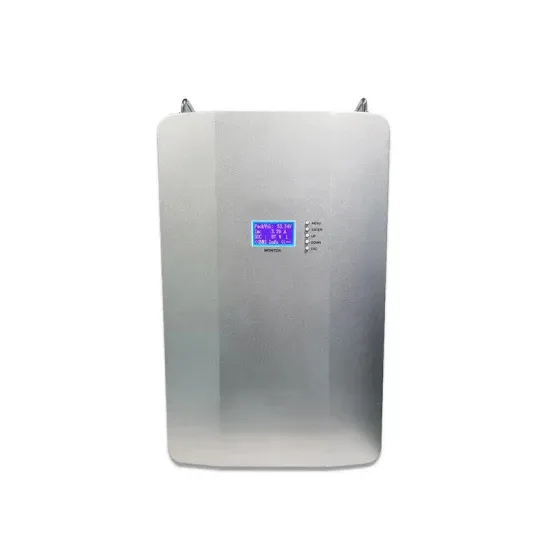
DC-to-AC Converters (Inverters): Design, Working & Applications
DC-to-AC converters, also known as inverters, play a crucial role in many different applications due to their ability to convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC).
Get a quote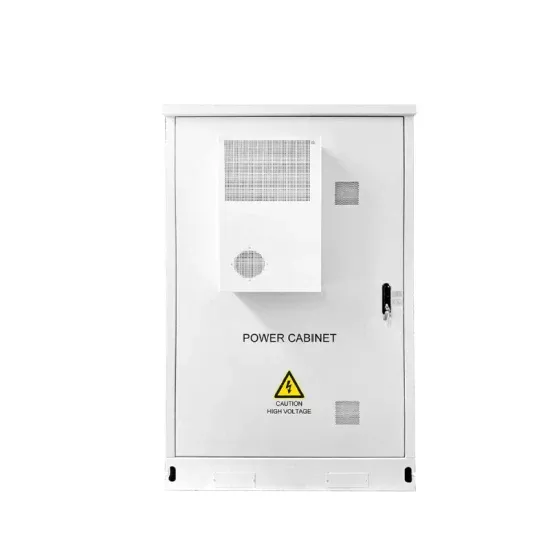
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
Appliances that need DC but have to take power from AC outlets need an extra piece of equipment called a rectifier, typically built from
Get a quote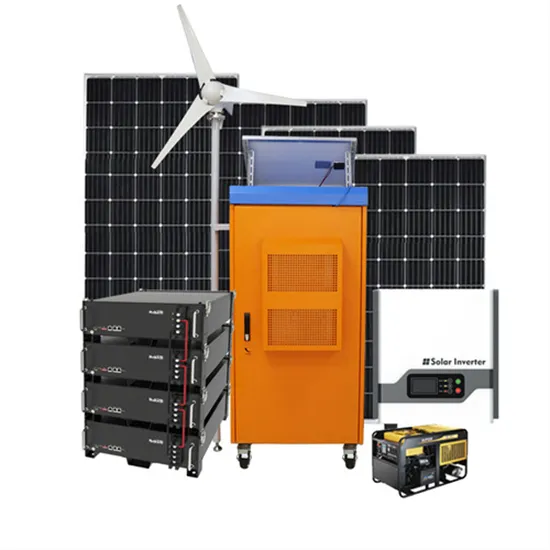
6 FAQs about [Are inverters DC or AC ]
What is a DC inverter?
An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). The conversion is crucial because most home appliances require AC power to operate. There are different types of inverters designed to meet various needs, primarily categorized as AC inverters and DC inverters.
What are AC inverters used for?
You’ll find AC inverters in a multitude of applications, especially in renewable energy setups. They are used in: DC inverters convert AC power from the grid into DC power. The conversion of AC to DC is often necessary for devices that internally run on DC power, ensuring better efficiency and reducing power wastage.
Do inverters convert DC to AC?
Inverters are complex devices, but they are able to convert DC-to-AC for general power supply use. Inverters allow us to tap into the simplicity of DC systems and utilize equipment designed to work in a conventional AC environment. The most commonly used technique in inverters is called Pulse Width Modulation (PWM).
What are the different types of inverters?
There are different types of inverters designed to meet various needs, primarily categorized as AC inverters and DC inverters. AC inverters convert DC power, generally sourced from batteries or solar panels, into AC power. This AC power can be used to run household appliances, machines, and other electronic devices.
What is a power inverter?
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC.
Is a solar inverter a converter?
A solar inverter is really a converter, though the rules of physics say otherwise. A solar power inverter converts or inverts the direct current (DC) energy produced by a solar panel into Alternate Current (AC.) Most homes use AC rather than DC energy. DC energy is not safe to use in homes.
Guess what you want to know
-
 What are inverters and AC motors
What are inverters and AC motors
-
 AC to DC inverter
AC to DC inverter
-
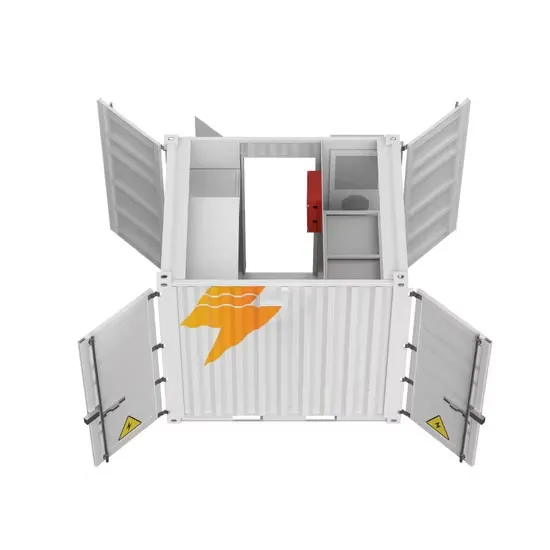
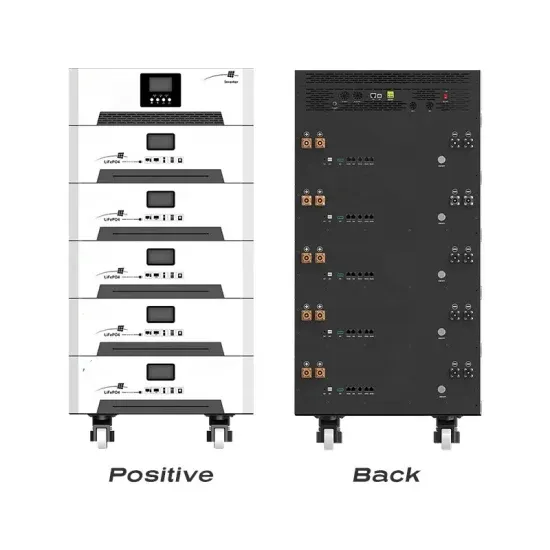 Details of energy storage DC and AC side equipment
Details of energy storage DC and AC side equipment
-
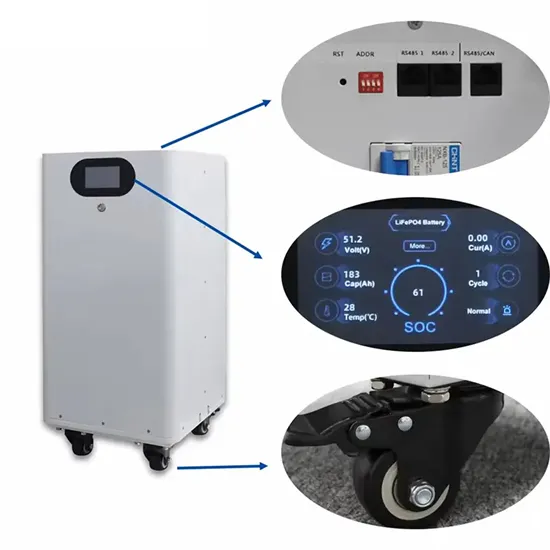 Poland portable AC DC power supply
Poland portable AC DC power supply
-
 Is AC or DC inverter better
Is AC or DC inverter better
-
 Is there a 96V DC to AC inverter
Is there a 96V DC to AC inverter
-
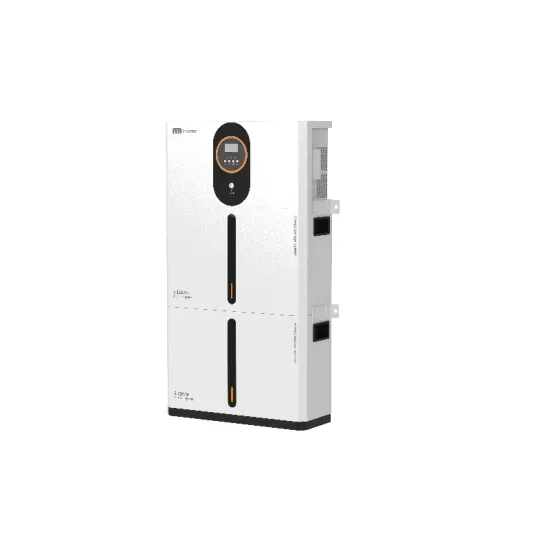 DC inverter to AC
DC inverter to AC
-
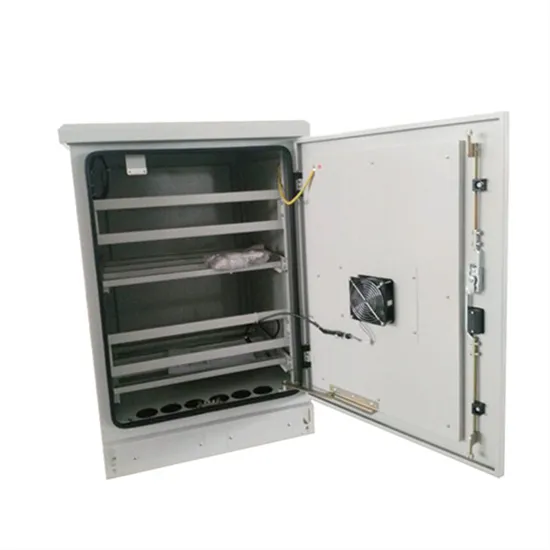 Tuvalu Portable AC DC Power Supply
Tuvalu Portable AC DC Power Supply
-
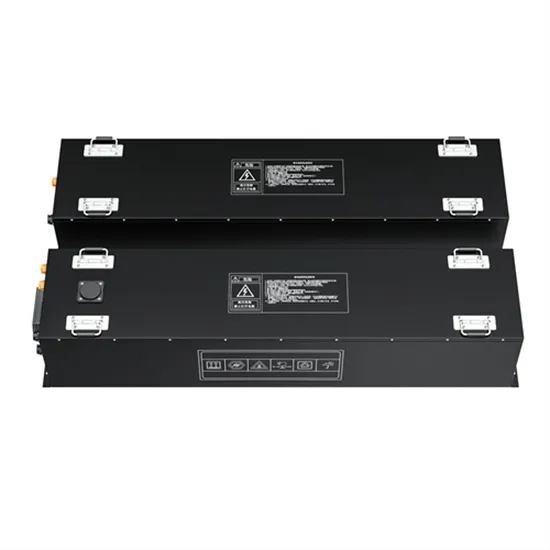 Inverter DC to AC 380V high power 9kw
Inverter DC to AC 380V high power 9kw
-
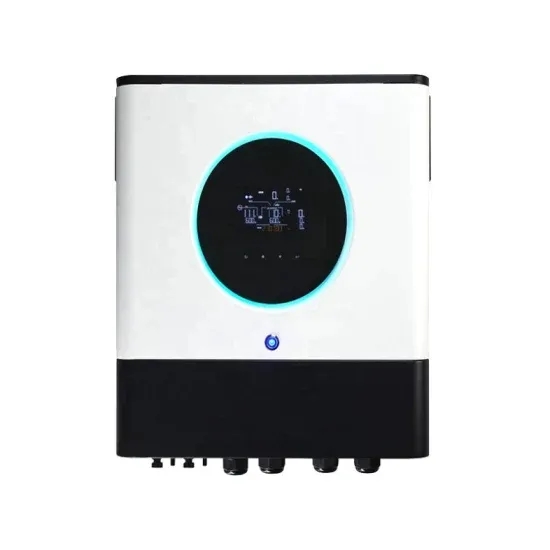 Energy storage power station DC AC
Energy storage power station DC AC
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


