Does a larger size inverter draw more energy from a battery bank
Does a larger size inverter draw more energy from a battery bank than a smaller size inverter even if the loads are the same? A customer was considering two different off grid inverters
Get a quote
calculate inverter size for solar + Sizing Formula
What is an Inverter and Why is Sizing Important? An inverter is the heart of a solar power system. It converts DC to AC, as well as optimizes
Get a quote
Grounding a small inverter | Forest River Forums
All of your DC voltage devices are already grounded to the chassis through the converter ground, which is in turn wired to the battery negative through the frame. I think what
Get a quote
What Happens When the Inverter Is Too Big for the Battery?
Using an oversized inverter with a battery can lead to several issues, including reduced energy efficiency, potential damage to connected appliances, and increased operating costs.
Get a quote
Inverter Multiplus 2 3000va battery bank too small
Probably derived from lead-acid where a small battery will suffer immediate voltage drop at high level draw and the inverter will shut down. Victron wants the equipment to work as
Get a quote
What Inverter Size is Best for a 100Ah Battery?
Understanding the Basics What is an Inverter? An inverter converts DC (Direct Current) power from your battery into AC (Alternating Current) power, which is used by most household
Get a quote
What Happens If Your Inverter Is Too Big? Risks,
An oversized power inverter can undermine the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and longevity of your power system. While it might seem like a "safer" choice,
Get a quote
What Size of Inverter is Good for RV? — EASUN POWER Official
What Sise Inverter Is Needed For RV? Here are typical inverter sizes for RVs based on usage: Light Use (small electronics, chargers): 500 to 1000 watts Moderate Use
Get a quote
Can a Power Inverter Be Too Big? Understanding the Risks and
Understanding Power Inverters and Their Functions A power inverter is an electrical device that converts DC (direct current) power from a battery or solar panel into AC (alternating current)
Get a quote
Is my inverter too big? : r/SolarDIY
When using inverters you should try to stick to 100 - 125 amps maximum current draw from the battery. This limits 12V systems to 1-1.5kw, 24V to 2-3kW and anything larger
Get a quote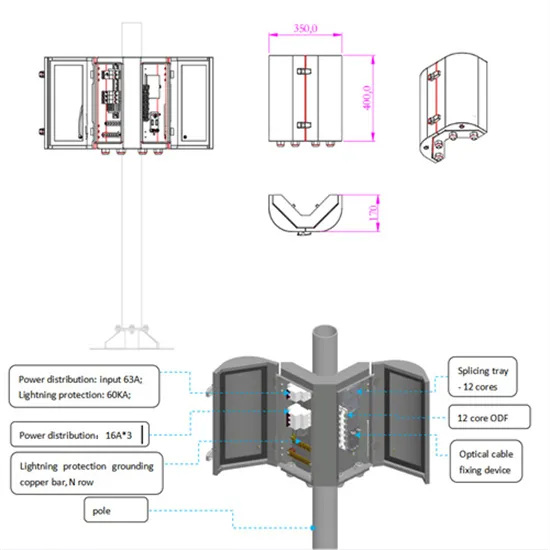
Inverter too small? | Good Sam Community
Inverter too small? I have a 1000w cobra inverter i bought to power a small 5 cubic foot freezer that pulls 4 amps when running. The battery i use for the inverter is 105 amp marine deep
Get a quote
Powerful Car Inverters: How Big Can You Go? | ShunAuto
Power inverters are a great way to add extra plug options to your car for your electronic devices. However, it''s important to be cautious when choosing one as the supply of
Get a quote
Can an Inverter Be Too Big for Your Battery System?
Always check the battery''s max discharge rate (C-rate) to avoid exceeding safe limits. When sizing for 24V or 48V systems, recalculate using the higher voltage.
Get a quote
Solar Inverter Sizing: Everything You Need To Know
What happens if my inverter is too small for my solar panel system? If your inverter is too small, it can''t handle the power from your solar
Get a quote
We Rate the 6 Best Campervan Inverters [2025 RV
We have found that most people choose an inverter that is either too large or too small for their battery bank and power consumption needs.
Get a quote
Inverter Sizing: Can Your Inverter Be Too Big For Your Battery
Using an inverter that is too large for the battery bank can lead to inefficient performance and reduced battery lifespan. An oversized inverter may draw more power than
Get a quote
Big inverters vs smaller inverters
Inverters have an idle power usage. A Victron 48/5000 burns 30W just by being powered on. That''s 0.72kWh/day or 60Ah of 12V battery capacity - would kill a medium size
Get a quote
What Happens If Your Solar Edge Inverter Is Too Small
If your inverter is too small, it may not be able to handle the maximum output of your solar panels. However, if you are far north/south, it could be a good size.
Get a quote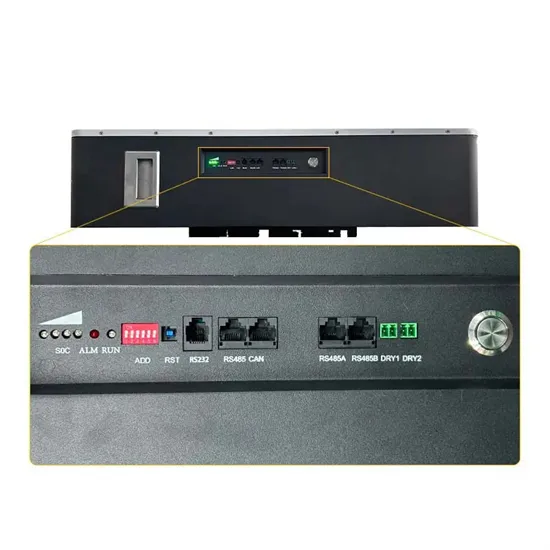
Can a Battery Be Too Big for an Inverter?
Yes, a battery can be too big for an inverter, leading to inefficiencies and potential safety issues. Oversized batteries may not discharge correctly or could exceed the inverter''s
Get a quote
How does the size of an inverter affect its performance
Undersized Inverter: If the inverter is too small, it cannot handle the full output of the solar panels, leading to energy losses due to "clipping" during peak production times. This
Get a quote
Lesson 5: Solar inverter oversizing vs. undersizing
When you pair an inverter that is underrated for the amount of power the system is designed to generate, that''s called undersizing. There is also a situation where it may make sense to pair
Get a quote
Is my inverter too big? : r/SolarDIY
When using inverters you should try to stick to 100 - 125 amps maximum current draw from the battery. This limits 12V systems to 1-1.5kw, 24V to 2-3kW and anything larger you''d use 48v.
Get a quote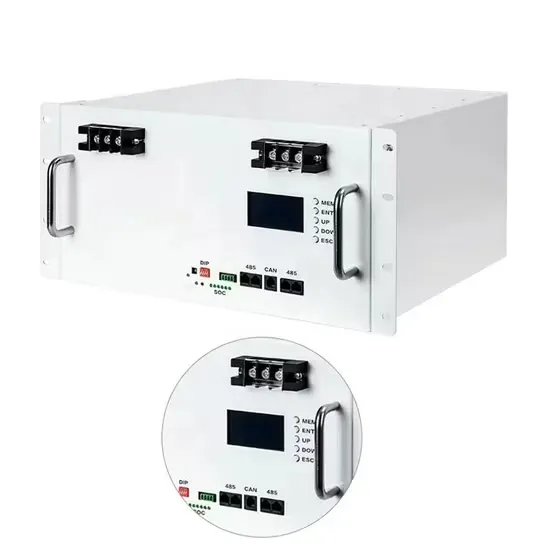
Lesson 5: Solar inverter oversizing vs. undersizing
When you pair an inverter that is underrated for the amount of power the system is designed to generate, that''s called undersizing. There is also a situation
Get a quote
Should I get an extra battery for the inverter?
And if you leave a small load on the inverter, say, just the inverter''s own quiescent load with no appliances running, or maybe a laptop or something, that''ll drain
Get a quote
Can an Inverter be Too Big for a Battery? Understanding the
In this article, we''ll explore the concept of an inverter being too big for a battery and the potential risks and consequences associated with it. Understanding Inverter and Battery Compatibility
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [The battery is too small and the inverter is too large]
What happens if a solar inverter is too big?
Oversized Inverter: An inverter that is too large may operate less efficiently during periods of low solar production, such as on cloudy days or early morning/late afternoon when sunlight is less intense. This can result in reduced efficiency and less optimal usage of the inverter’s capacity. 2. System Compatibility and Compliance
What happens if you undersize an inverter?
When you undersize an inverter, you pair it with a system that can produce more power than the inverter is rated for. That can cause inverter clipping. Clipping happens when there is more DC power being fed into the inverter than it is rated for. When that happens, the inverter will produce its maximum output and no more.
Do inverters use a lot of power?
Generally, yes. Inverters have an idle power usage. A Victron 48/5000 burns 30W just by being powered on. That's 0.72kWh/day or 60Ah of 12V battery capacity - would kill a medium size car battery in 24 hours even if no loads are supplied. The MPP Solar/Growatt units and most all-in-ones are notorious for high idle energy consumption.
How does inverter size affect performance?
Here are several key ways that inverter size impacts performance: 1. Energy Conversion Efficiency Undersized Inverter: If the inverter is too small, it cannot handle the full output of the solar panels, leading to energy losses due to “clipping” during peak production times.
Is oversized inverter a good idea?
The only time that oversizing is a good idea is when the customer plans to add capacity in the future. By providing an oversized inverter, the customer would be saved the future expense of upgrading their inverter when they add panels to their system.
What is undersizing a solar inverter?
When you pair an inverter that is underrated for the amount of power the system is designed to generate, that’s called undersizing. There is also a situation where it may make sense to pair an inverter that’s rated higher than the solar array’s output. That’s known as oversizing.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Lithium battery large monomer inverter
Lithium battery large monomer inverter
-
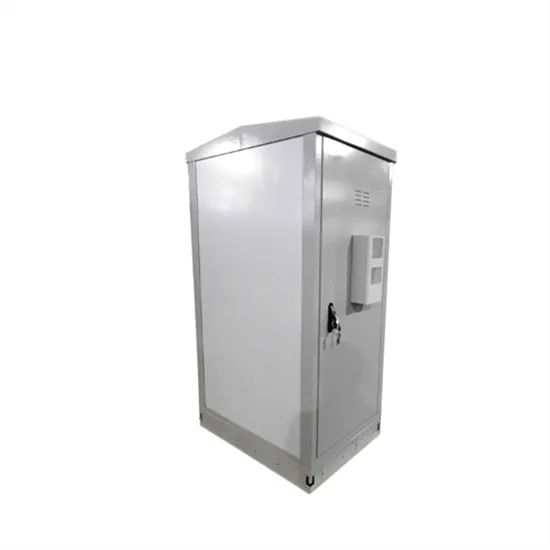 Small size large energy storage battery
Small size large energy storage battery
-
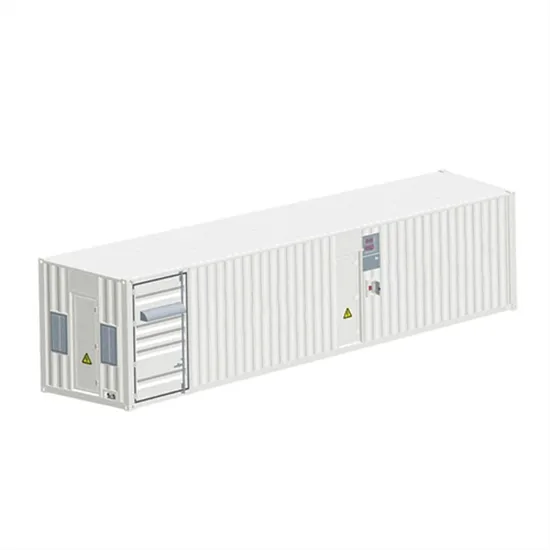 Outdoor 220V large battery with inverter 24v
Outdoor 220V large battery with inverter 24v
-
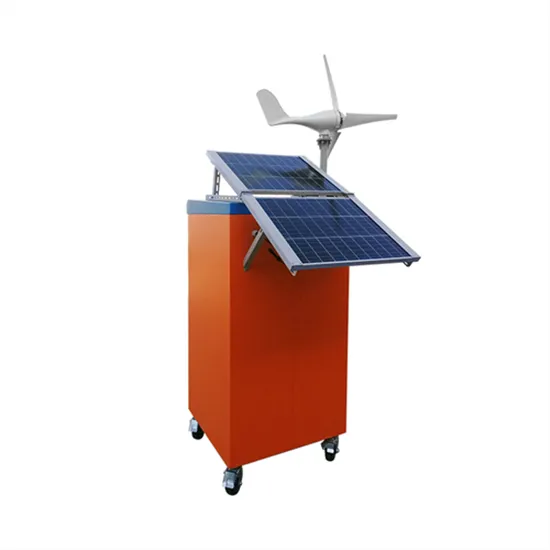 How to eliminate the problem of small grid-connected battery in inverter of communication base station
How to eliminate the problem of small grid-connected battery in inverter of communication base station
-
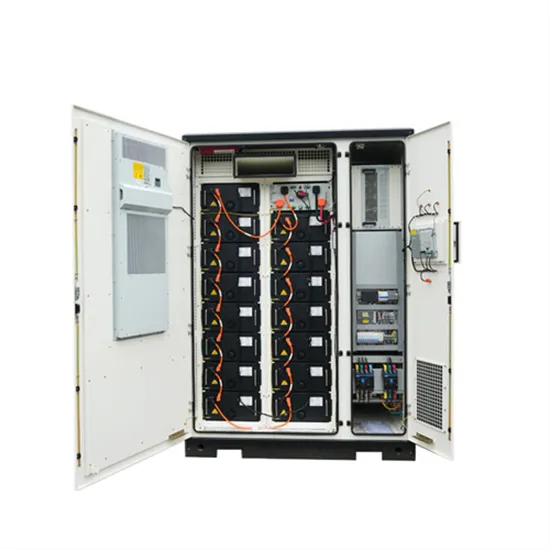 Is there a battery inside the small inverter
Is there a battery inside the small inverter
-
 How many small solar panels are needed for a 2kw water pump inverter
How many small solar panels are needed for a 2kw water pump inverter
-
 Inverter battery put together
Inverter battery put together
-
 Eritrea Small Inverter Manufacturer
Eritrea Small Inverter Manufacturer
-
 Micro super small inverter
Micro super small inverter
-
 Small high frequency inverter
Small high frequency inverter
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

