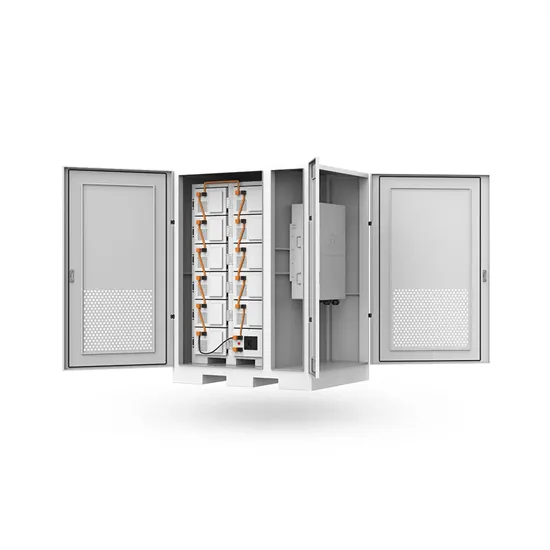
Use of grid-forming inverters to support nearby grid-following inverter
New Zealand is on the brink of a boom in solar generation, wind generation, and battery energy storage system deployment, which connect to the grid via inverter-based power
Get a quote
AS/NZS 4777.2 2020 Updates – What You Need to Know
Standard specifies safety and installation requirements for inverter energy systems (IES) intended for the injection of electric power through an electrical installation to the grid.
Get a quote
Solar Inverters in NZ
Grid-tied Inverters As the name implies, grid-tied inverters are connected straight to the grid. This means that they can''t be used in conjunction with solar batteries but work well
Get a quote
Next generation power inverter for grid resilience: Technology
This paper highlights the limitations of current inverter technology and points the way forward to the next generation of inverters that overcome those limitations. A more
Get a quote
Comprehensive Guide to AS/NZS 4777.1 and AS/NZS
This standard outlines installation requirements for grid-connected inverters. It specifies the processes and practices needed to ensure the
Get a quote
Standards New Zealand
Standard specifies safety and installation requirements for inverter energy systems (IES) intended for the injection of electric power through an electrical installation to the grid.
Get a quote
How Long Do Solar Inverters Last? Maximizing Inverter Lifespan
Regular maintenance and professional assistance are key to maximizing the lifespan of solar inverters and, consequently, reaping the full benefits of clean, renewable
Get a quote
Optimal configuration of 5G base station energy storage
A multi-base station cooperative system composed of 5G acer stations was considered as the research object, and the outer goal was to maximize the net profit over the
Get a quote
Inverter life expectancy.
I run an off-grid system using dual 12,000w AIMS (ETL) 48v inverters - since May 2018 - so a bit over 3 years now. They run on a daily cycle - on after the battery charges up bit
Get a quote
Australian/New Zealand StandardTM
This Standard was prepared by the Joint Standards Australia/Standards New Zealand Committee EL-042, Renewable Energy Power Supply Systems and Equipment, and is based on
Get a quote
Our Summary : AS/NZS 4777.1:2024 – Grid
Stakeholders involved in specifying, installing, or maintaining grid-connected inverters should carefully review these changes and ensure full compliance
Get a quote
Our Summary : AS/NZS 4777.1:2024 – Grid Connection of
Stakeholders involved in specifying, installing, or maintaining grid-connected inverters should carefully review these changes and ensure full compliance with AS/NZS 4777.1:2024, AS/NZS
Get a quote
Regulatory application of AS/NZS 4777
Information on when the latest versions of AS/NZS 4777 apply in relation to the supply and installation of inverters in photo-voltaic installations
Get a quote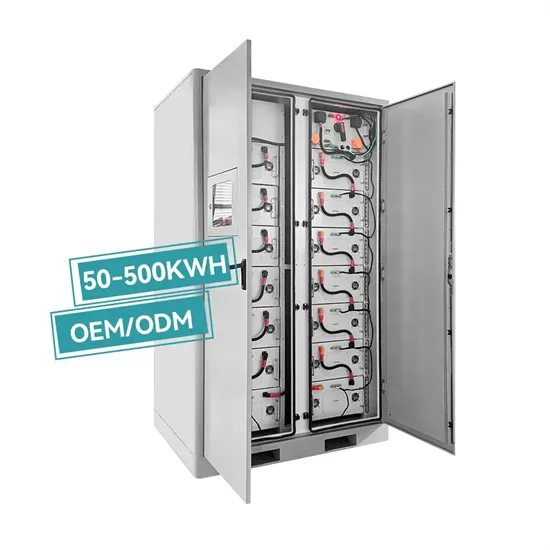
AS/NZS 4777.2 2020 Updates – What You Need to Know
There is a chance that some inverters will become non-compliant if they cannot operate according to these setpoints, meaning they could not be legally installed in Australia or
Get a quote
Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study
This approach ensures stable operation in both islanded and grid-connected modes, providing essential grid support functions such as frequency and voltage regulation. Its
Get a quote
Changes to Inverter Standards
In December 2020, Standards Australia released a new version of AS/NZS 4777.2 Grid connection of energy systems via inverters Part 2: Inverter requirements (AS/NZS
Get a quote
How to Maximize the Lifespan of Solar Inverter
This article examines essential factors that influence the lifespan of solar inverters, including manufacturing quality, system compatibility, installation
Get a quote
ESP005 Technical Requirements for the connection of
Guideline for the Connection of inverter based distributed generation less than 10kW capacity published by the EEA. 1. INTRODUCTION. The purpose of this standard is to define the
Get a quote
用户手册
The wireless communication module can be connected to the inverter through the standard RS485 interface, thereby obtaining inverter running data. The running data is transmitted to
Get a quote
Addressing larger voltage deviations and network
In particular, we expect that co-ordinating the real-time operation of New Zealand''s power system to supply electricity to consumers at the level of reliability they want will become more difficult
Get a quote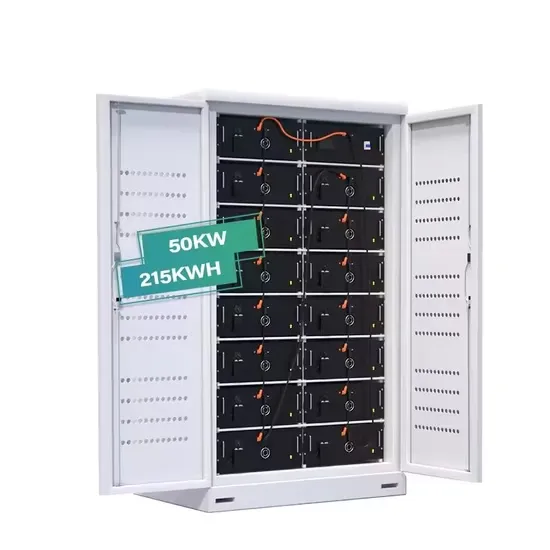
SG110CXPV Grid-Connected InverterUser ManualSG110CX
The manual mainly describes the product information, guidelines for installation, operation and maintenance. The manual cannot include complete information about the photovoltaic (PV)
Get a quote
China''s Largest Grid-Forming Energy Storage Station
This marks the completion and operation of the largest grid-forming energy storage station in China. The photo shows the energy storage station supporting the Ningdong
Get a quote
Comprehensive Guide to AS/NZS 4777.1 and AS/NZS 4777.2
This standard outlines installation requirements for grid-connected inverters. It specifies the processes and practices needed to ensure the safety, reliability, and proper
Get a quote
Optimised configuration of multi-energy systems considering the
Additionally, exploring the integration of communication base stations into the system''s flexibility adjustment mechanisms during the configuration is important to address the
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [The lifespan of New Zealand communication base station inverters connected to the grid]
How do inverters work in New Zealand?
The most common inverter-based resources used in New Zealand rely on a high-quality system voltage waveform to determine the active and reactive power outputs that the inverter can generate. 2.23.
When will inverters be certified in Australia and New Zealand?
In December 2020, the Standard was updated to reflect changing conditions in the industry. These changes could affect your business, so knowledge is key to minimise risk before transitioning to the updated version. In December 2021, all new inverters in Australia and New Zealand will need to be certified to AS/NZS 4777.2:2020.
What is a standard for inverter energy systems?
Standard specifies safety and installation requirements for inverter energy systems (IES) intended for the injection of electric power through an electrical installation to the grid. IES are distributed energy resources when connecting to the grid and need to ensure overall safe operation of the installation and interaction with the broader grid.
Can inverters be legally installed in Australia or New Zealand?
Inverter manufacturers will need to ensure their inverters comply with the updated Standard prior to the transition date. There is a chance that some inverters will become non-compliant if they cannot operate according to these setpoints, meaning they could not be legally installed in Australia or New Zealand until compliance is demonstrated.
How complex is New Zealand's power system?
New Zealand’s power system is becoming increasingly complex to operate, as generation and energy storage system investments are made across transmission and distribution networks. The management of stable voltages across networks will increasingly require greater co-operation between the system operator and distributors.
How long will a weak transmission system last in New Zealand?
Inadequate system strength may become an issue on New Zealand’s transmission network in 3–7 years. 2.21. A distorted voltage waveform can cause maloperation of inverter controls, resulting in inverter-based resources performing in a manner that is less desirable from a network operations standpoint.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Togo has several military communication base station inverters connected to the grid
Togo has several military communication base station inverters connected to the grid
-
 What types of equipment are connected to the grid for communication base station inverters
What types of equipment are connected to the grid for communication base station inverters
-
 Does the inverter for the Philippine communication base station have a battery when connected to the grid
Does the inverter for the Philippine communication base station have a battery when connected to the grid
-
 How high a temperature can a communication base station inverter withstand when connected to the grid
How high a temperature can a communication base station inverter withstand when connected to the grid
-
 Unmanned communication base station inverter connected to the grid 6 9MWh
Unmanned communication base station inverter connected to the grid 6 9MWh
-
 Senegal communication base station inverter connected to the grid 100KWh
Senegal communication base station inverter connected to the grid 100KWh
-
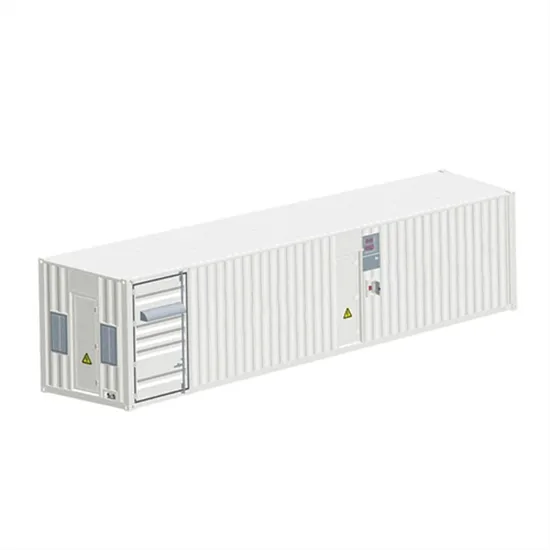 Can Huawei communication base station inverter be domestically produced and connected to the grid
Can Huawei communication base station inverter be domestically produced and connected to the grid
-
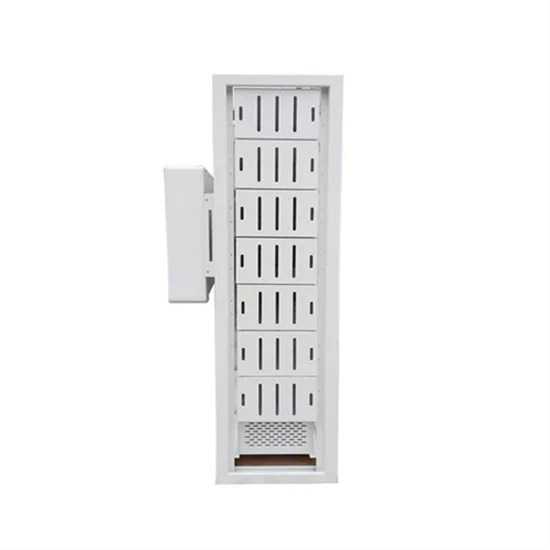 The small one should be equipped with a communication base station inverter and connected to the grid
The small one should be equipped with a communication base station inverter and connected to the grid
-
 Australia s small photovoltaic communication base station inverter is connected to the grid
Australia s small photovoltaic communication base station inverter is connected to the grid
-
 France wants to connect several communication base station inverters to the grid
France wants to connect several communication base station inverters to the grid
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


