Timing & Synchronization technology adopted base
About mobile Base Station GPS As mobile phones advanced from a 1st generation analog system in the 1980''s to a 2nd generation digital system in
Get a quote
Types and Applications of Mobile Communication
The construction of mobile communication base stations is an important part of the investment of mobile communication operators, and is
Get a quote
EMF
Mobile phones work by sending and receiving low power radio signals. The signals are sent to and received from antennas that are attached to radio transmitters and receivers, commonly
Get a quote
Relay station, base station, mobile station, communication
Preferred embodiments of a relay station, a base station, a mobile station, a communication system, and a communication method will be explained with reference to the accompanying...
Get a quote
What is a base station?
In telecommunications, a base station is a fixed transceiver that is the main communication point for one or more wireless mobile client devices. A base station serves as
Get a quote
Mobile station
Mobile Station Diagram A mobile station (MS) [1][2] comprises all user equipment and software needed for communication with a mobile network. The term refers to the global system
Get a quote
Microsoft Word
The Evolution of Base Station Antennas for Mobile Communications C. Beckman† − This paper gives a general overview of the Abstract design of base station antennas for mobile
Get a quote
Base Station Antennas for the 5G Mobile System
The fifth-generation (5G) mobile communication system will require the multi-beam base station. By taking into account millimeter wave use, any antenna types such as an array, reflector and
Get a quote
Base Station
A base station refers to a fixed communication device that serves as a hub for connections in a specific area, such as a wireless telephone system in a cellular network. It
Get a quote
What is the relationship between the Base station and mobile
The MSC is mostly associated with communications switching functions, such as call set-up, release, and routing. However, it also performs a host of other duties, including routing SMS
Get a quote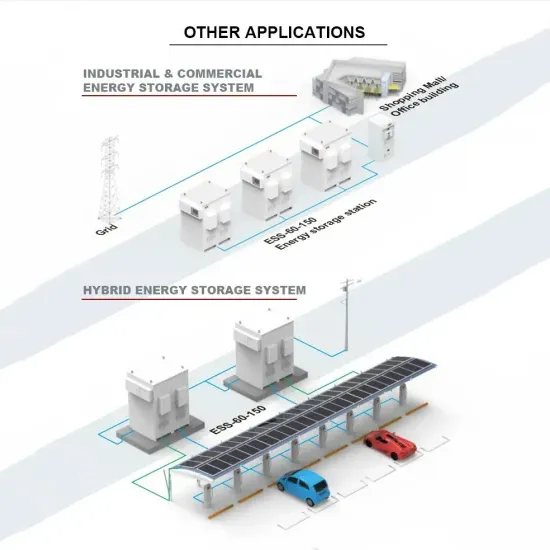
Base Station''s Role in Wireless Communication Networks
What is a base station? A base station is a critical component of wireless communication networks. It serves as the central point of a network that connects various devices, such as
Get a quote
How Incoming Calls To a Mobile Phone are Handled
Whether or not a call is made from the Mobile Station, the Mobile Station (MS) always communicates with the Base Transceiver Station (BTS)
Get a quote
Base station subsystem
OverviewBSS interfacesBase transceiver stationBase station controllerPacket control unitSee also
Um The air interface between the mobile station (MS) and the BTS. This interface uses LAPDm protocol for signaling, to conduct call control, measurement reporting, handover, power control, authentication, authorization, location update and so on. Traffic and signaling are sent in bursts of 0.577 ms at intervals of 4.615 ms, to form data blocks each 20 ms. Abis The interface betw
Get a quote
Movable Base Stations in Mobile Networks for Emergency
Abstract—An emergency communication system is necessary for first responders, who need to enter areas with no network coverage or damaged network infrastructure due to natural or
Get a quote
Understanding Base Station Controller Architecture: A
In this guide, we will delve into the components and functions of base station controller architecture, providing clear insights into how it underpins the mobile
Get a quote
The Evolution of Base Station Antennas for Mobile Communications
This paper gives a general overview of the design of base station antennas for mobile communications. It explains underlying theoretical and practical implementation aspects in
Get a quote
Base Stations
Backhaul Connection: The backhaul connection links the base station to the core network in the mobile communication system. It provides for the interchange of data between
Get a quote
Cellular Concepts
The GSM network is divided into four major systems − Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Mobile Station (MS) Operation and Maintenance Center (OMC) The switching
Get a quote
Types and Applications of Mobile Communication Base Stations
The construction of mobile communication base stations is an important part of the investment of mobile communication operators, and is generally carried out around factors
Get a quote
Base station subsystem
There are vendors in which the BTS is a plain transceiver which receives information from the MS (mobile station) through the Um air interface and then converts it to a TDM (PCM) based
Get a quote
What Is A Base Station?
A base station is an integral component of wireless communication networks, serving as a central point that manages the transmission and reception of signals between
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Base station to mobile station communication]
What is a mobile base station?
A mobile base station, also called a base transceiver station (BTS), is a fixed radio transceiver in any mobile communication network or wide area network (WAN). The base station connects mobile devices to the network and routes them to other terminals in the network or to the core network of a mobile operator Read more Explore Mobile base...
What is a base station in telecommunications?
In telecommunications, a base station is a fixed transceiver that is the main communication point for one or more wireless mobile client devices. A base station serves as a central connection point for a wireless device to communicate.
What is a base station in a cellular network?
A base station, also known as a cell site or cell tower, is an integral part of a cellular network. It serves as a central hub for communication between mobile devices and the network infrastructure. Here is a simplified explanation of how a base station works: 1.
Why are base stations important in cellular communication?
Base stations are important in the cellular communication as it facilitate seamless communication between mobile devices and the network communication. The demand for efficient data transmission are increased as we are advancing towards new technologies such as 5G and other data intensive applications.
How does a mobile phone connect to a base station?
The first step in the process is for the phone to check that there is coverage in the area that the call is made. Once the phone has verified that there is sufficient signal strength to make the call, the phone establishes a connection with a nearby mobile phone base station.
How does a base station communicate with a client device?
Generally, if client devices wanted to communicate to each other, they would communicate both directly with the base station and do so by routing all traffic through it for transmission to another device. Base stations in cellular telephone networks are more commonly referred to as cell towers.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Venezuela Mobile s communication base station flow battery
Venezuela Mobile s communication base station flow battery
-
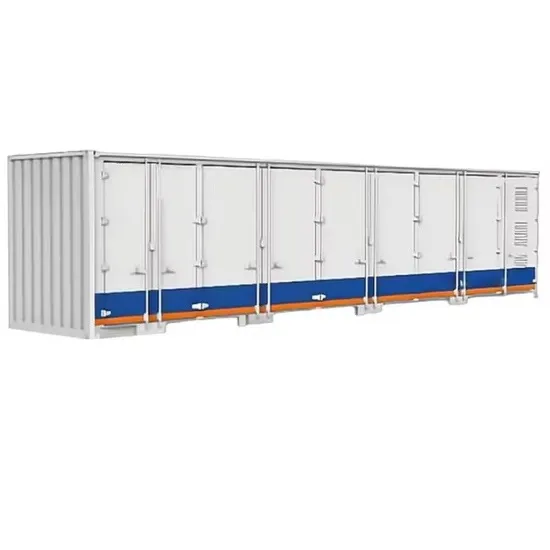 Cellular mobile communication system base station
Cellular mobile communication system base station
-
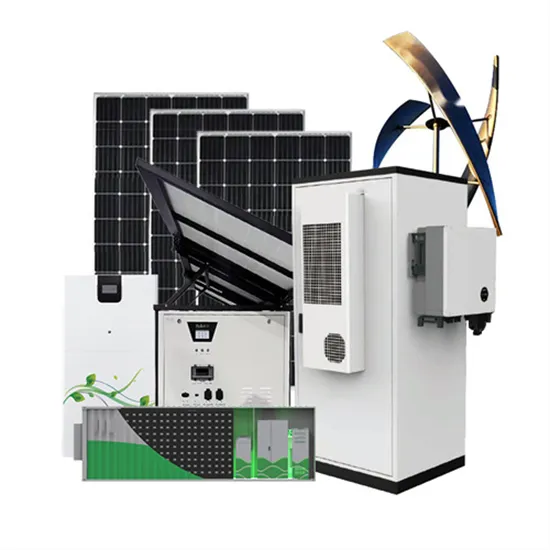 Mobile base station inverter communication power supply
Mobile base station inverter communication power supply
-
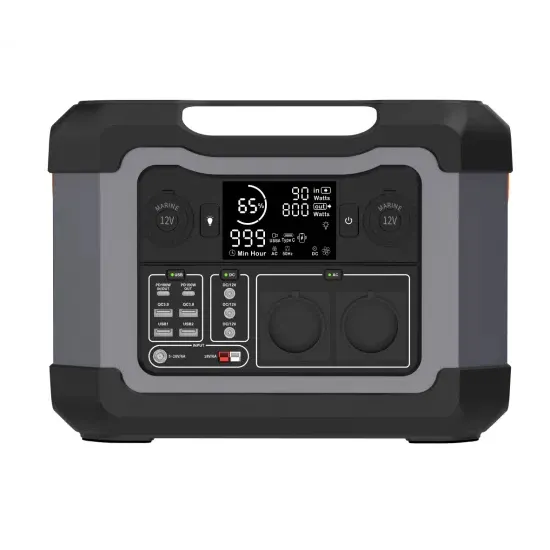 Mobile communication green base station deployment requirements
Mobile communication green base station deployment requirements
-
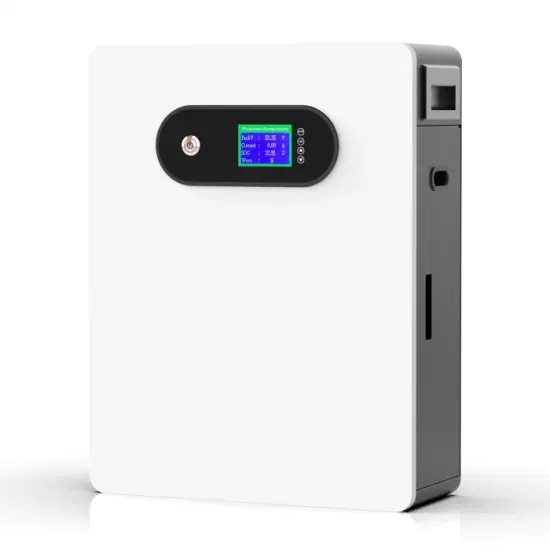 5g mobile communication base station wind and solar complementarity
5g mobile communication base station wind and solar complementarity
-
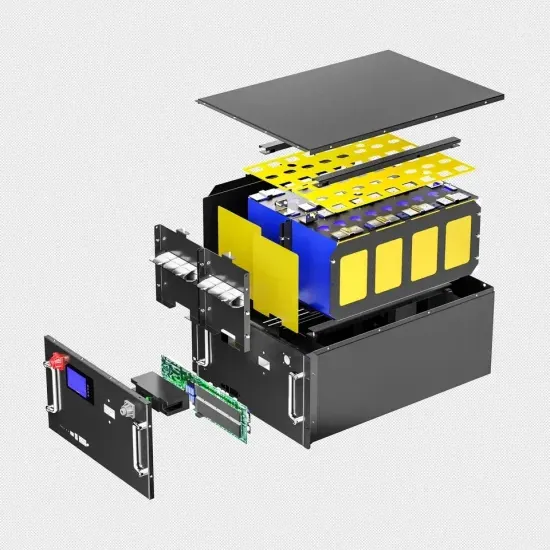 Mobile base station communication cabinets
Mobile base station communication cabinets
-
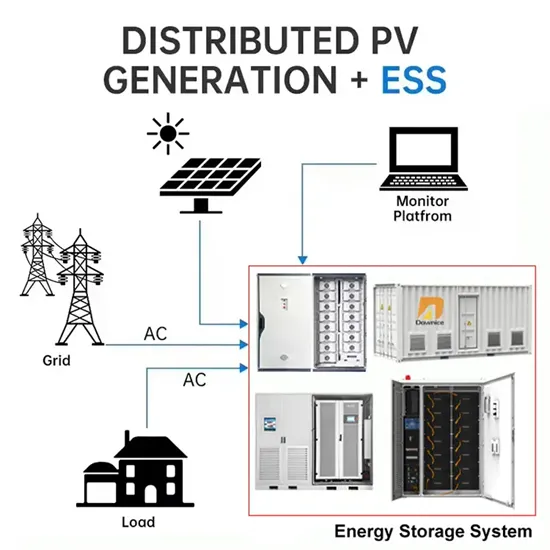 Communication between base station and mobile station
Communication between base station and mobile station
-
 Sao Tome and Principe mobile communication wind power base station photovoltaic power generation system
Sao Tome and Principe mobile communication wind power base station photovoltaic power generation system
-
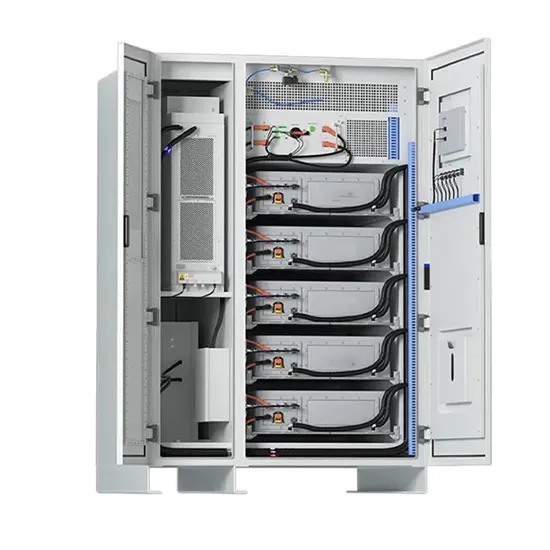 Mobile Base Station Communication Tower Battery
Mobile Base Station Communication Tower Battery
-
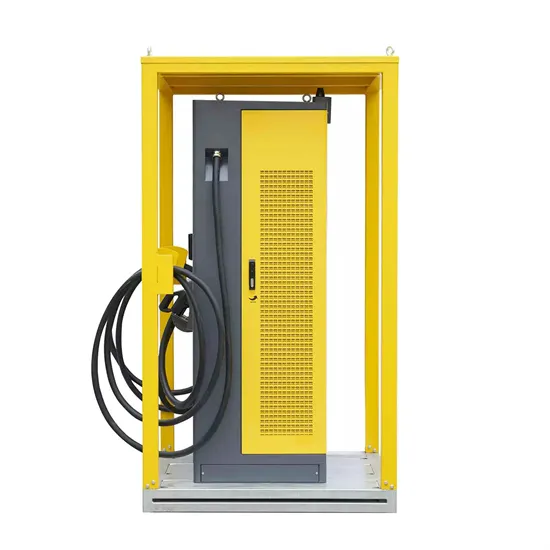 Brazil Mobile Communication Wind Power Base Station Photovoltaic Power Generation System
Brazil Mobile Communication Wind Power Base Station Photovoltaic Power Generation System
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


