Interfacing Lead Acid batteries with inverter
The data sheet says lead-acid is supported. Yes, it is, but lead acid don''t have CAN BUS for communication. I was wondering whether those need some kind of interface
Get a quote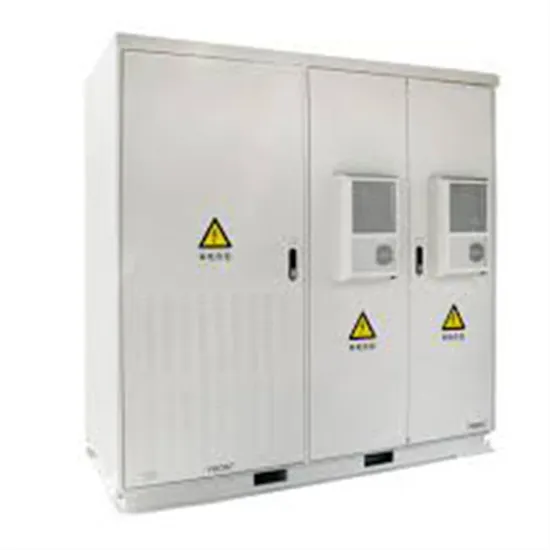
The Differences Between 24v and 48v Inverter: Which
Are you confused about choosing between 24V and 48V inverters? Compare the key differences in efficiency, cost, and battery configuration.
Get a quote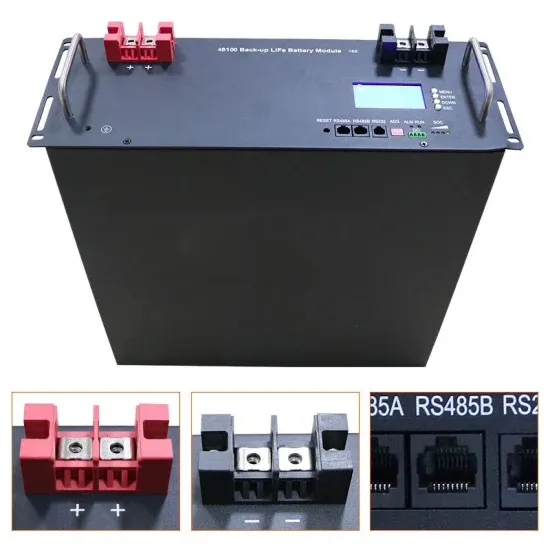
Anybody DYI battery with Enphase micro inverters? : r/solar
You give this thing a 48v battery and a meter at your grid connection point. If whatever (ex. your enphase inverters) are currently generating more than you need and you start selling power,
Get a quote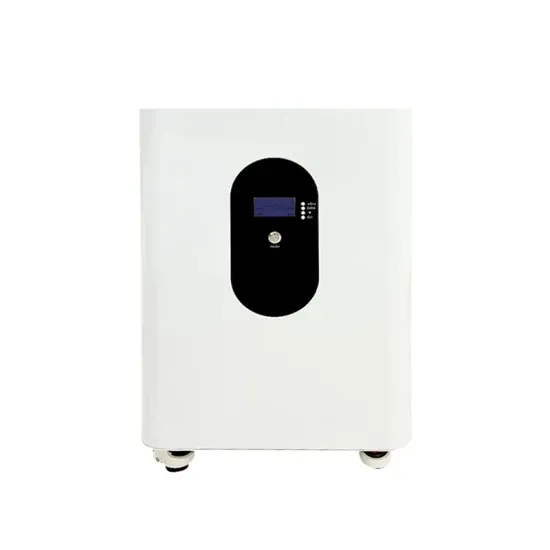
48V Solar Power System Setup Guide: Using Hybrid
In this case, the 48V system can operate at this power using a hybrid inverter and LiFePO₄ battery bank. There would be minimal heat loss
Get a quote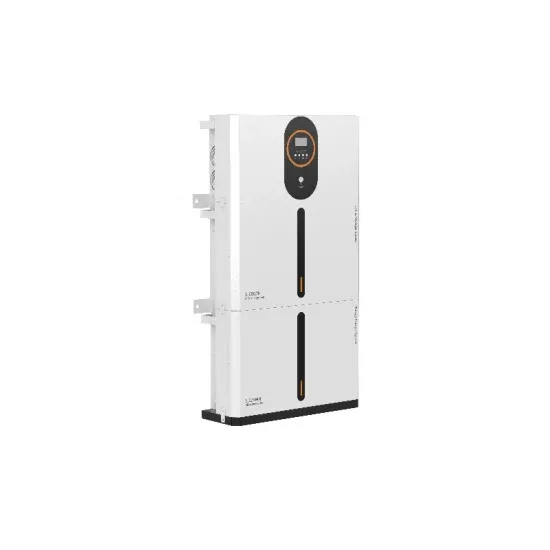
48V Inverter: The Ultimate Guide to Efficient and Scalable Power
Yes, for the most part. 48V inverters are generally more efficient and have thinner wiring, which means less energy loss and lower installation costs. 48V inverters can also
Get a quote
Can an Off Grid Inverter Work Without Batteries?
Off-grid inverters can work without batteries, but this depends on the specific inverter model and application scenario. First of all, it should be clear that off-grid inverters are
Get a quote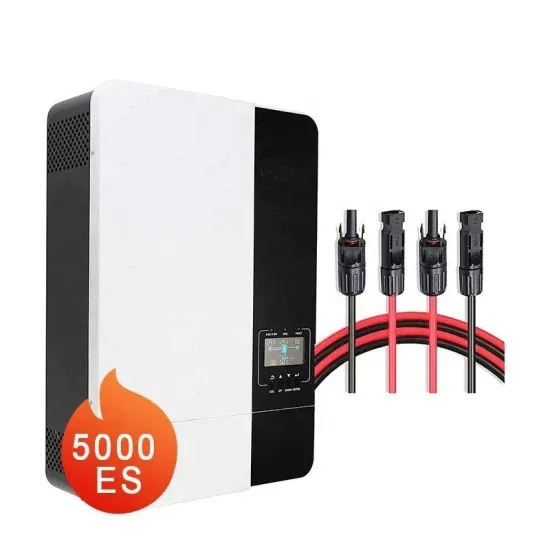
Can I Use A 24V Inverter On A 48V Battery? Compatibility And
No, you should not use a 24V inverter with a 48V battery. A 24V inverter is designed for 24 volts. Connecting it to a 48V battery can lead to overvoltage. This can damage
Get a quote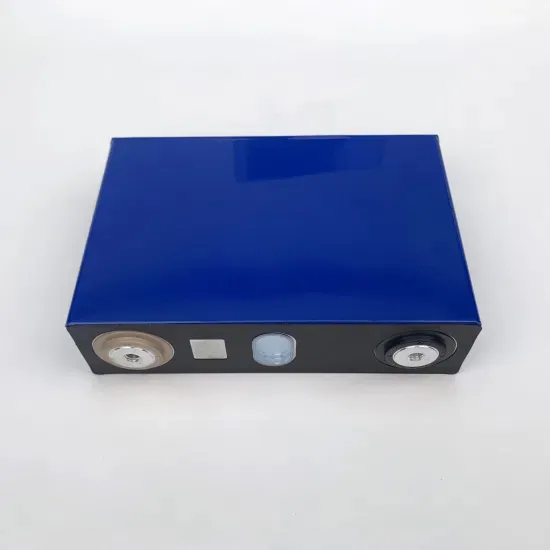
What Will An Inverter Run & For How Long? (With Calculator)
So I''m gonna explain to you guys in simple words about what you can run on your any size inverter and what are the key point to keep in mind. And also how long your inverter
Get a quote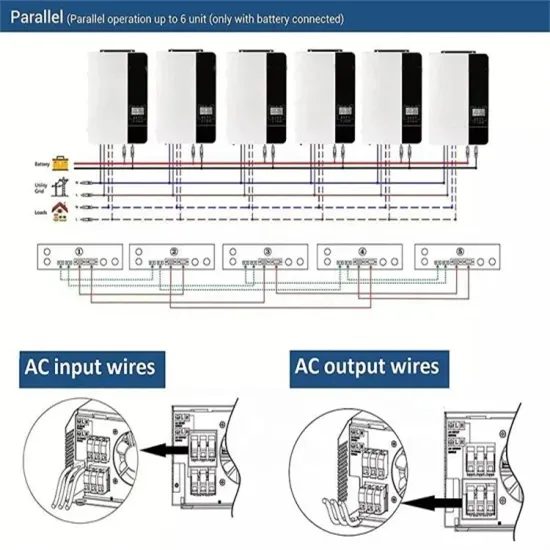
Can I Use A 24V Inverter On A 48V Battery? Compatibility And
No, you should not use a 24V inverter with a 48V battery. A 24V inverter is designed for 24 volts. Connecting it to a 48V battery can lead to overvoltage.
Get a quote
Any Hybrid Inverters work with DIY batteries?
I want to build a 10+kw powerwall & direct DC couple to a hybrid inverter. Aside from being more efficient (i believe), the inverter can manage the direction of power as needed
Get a quote
Inverters: What are they and which ones are suitable
It should be noted that more complex inverters, such as hybrid or grid-tied inverters, can be used as off-grid inverters, but these are not cost
Get a quote
48v low idle inverter for US market
I''m currently looking for a similar inverter that works with US voltage. Here are my requirements, listed in order of priority: I''ve only found very expensive options (like Victron) or
Get a quote
Maximizing Efficiency with 48V Low Frequency Inverters: A
A2: Yes, they are. 48V low frequency inverters can efficiently convert power from renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines into usable AC power.
Get a quote
The Differences Between 24v and 48v Inverter: Which is Better?
Are you confused about choosing between 24V and 48V inverters? Compare the key differences in efficiency, cost, and battery configuration.
Get a quote
Running Inverters in Parallel: A Comprehensive Guide
Additionally, running inverters in parallel can improve system reliability and redundancy. If one inverter fails, the others can continue to supply power, reducing downtime
Get a quote
What Are the Alternatives If You Need to Use a 24V Inverter with a 48V
Yes, 48V inverters are generally more efficient than lower voltage inverters. They can reduce voltage drop, improve power delivery, and are often better suited for larger
Get a quote
What Will An Inverter Run & For How Long? (With
So I''m gonna explain to you guys in simple words about what you can run on your any size inverter and what are the key point to keep in mind.
Get a quote
Can a 24 Volt 220v Inverter be used for a hair dryer?
12 hours ago· If you''re interested in checking out different inverters, we have a great selection on our website. You can take a look at our Inverter Dc Ac 24v for a reliable 24 - volt option. We
Get a quote
What Are the Alternatives If You Need to Use a 24V Inverter with
Yes, 48V inverters are generally more efficient than lower voltage inverters. They can reduce voltage drop, improve power delivery, and are often better suited for larger
Get a quote
What Are the Alternatives If You Need to Use a 24V Inverter with a 48V
Alternatives to Using a 24V Inverter with a 48V Battery When faced with the challenge of integrating a 24V inverter into a system powered by a 48V battery, several
Get a quote
Can I Use a 24V Inverter with 48V Battery Banks
No, you should not use a 24V inverter with a 48V battery bank because the voltage mismatch can damage the inverter, pose safety hazards, and lead to inefficient power
Get a quote
Can a 48V Inverter Work with a 24V Battery? – A Comprehensive
No, a 48V inverter cannot directly work with a 24V battery. Inverters are designed to work with specific input voltage levels, and a 48V inverter is built to operate with a 48V
Get a quote
What is the Difference Between 24v and 48v Inverter?
24 Volt inverters work at the standard household voltage of 120 volts, and 48V inverter can work at higher voltages in addition to running appliances that are capable of 24v.
Get a quote
48v inverter low voltage cutoff leaves so much on the table.
I have my inverter cutoff set to 3.1 volts per cell as I don''t want my cells going into the low knee at significant current. I''ve observed that the cell temperature jumps up when
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Can inverters below 48v work ]
Is a 24V inverter better than a 48V?
At 48V it drops to a more reasonable 66A. This is actually better than you might think because power loss is proportional to current squared, so if you use your existing wiring and connectors the loss in them will be 4 times higher. A 24V inverter might be a bit cheaper, but you should consider the cost of replacing your wiring and fuses etc.
Do I need a 12V inverter?
To do this, you need to connect an inverter to the battery bank. It is important to match the battery bank voltage with an inverter that can handle that same voltage. Simply put, if you have a 12V system, you need a 12V inverter; a 48V system requires a 48V inverter. Standard Pure Sine Wave inverters simply change DC power to AC power.
How to choose a 48V low frequency inverter?
Efficiency is a key factor when choosing a 48V low frequency inverter. Look for models with high efficiency ratings, as they will ensure optimal power conversion and minimize energy losses. This will ultimately result in lower operating costs and improved overall performance.
Can a 48 volt inverter run a battery?
When you use a 48-Volts inverter, you can use regular and more flexible connectors to connect the inverter to the battery bank. This is so because the thinner the wire, the higher the resistance. And if your DC voltage is lower, you will pass more current through the wires, and they can get very hot, and you lose a lot of battery power.
How long does a 24V inverter last?
Inverters that work on a 24V voltage are very popular in solar-powered RVs, boats, and RV storage systems. For nine hours, a 24V 200Ah lithium-ion battery will power 500W loads. It can also run 100W for just three hours. The runtime depends on the type of battery used and how deeply discharged it is.
What is a 48 volt inverter?
In other words, it is a device that can take current from a bank of batteries (48V) and convert it to the type supplied in the grid to power your appliances and devices. I suggest you use A 24-volt inverter or 36-volt inverter or 48-volt inverter when you need to power appliances over 3000 Watts.
Guess what you want to know
-
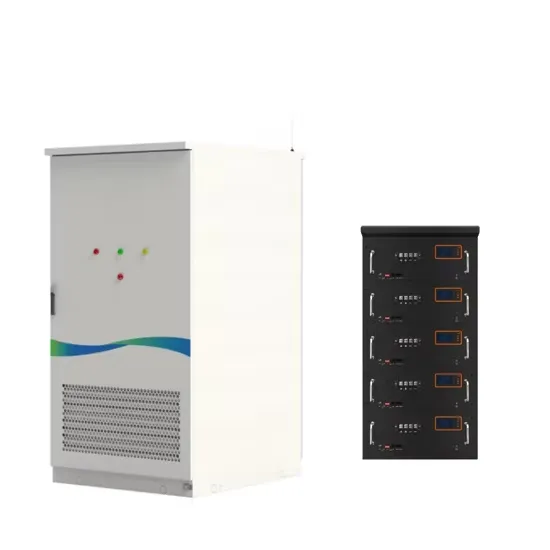 How many inverters are needed to generate 48v 30A
How many inverters are needed to generate 48v 30A
-
 Home 12V and 24v 48V inverters
Home 12V and 24v 48V inverters
-
 Is it good to use 48V and 60V inverters
Is it good to use 48V and 60V inverters
-
 What is the difference between 48v and 60v inverters
What is the difference between 48v and 60v inverters
-
 48v 200W inverters
48v 200W inverters
-
 Spanish 48v inverter
Spanish 48v inverter
-
 How many amps is a 48V lithium battery pack
How many amps is a 48V lithium battery pack
-
 Inverter 48v to 230
Inverter 48v to 230
-
 48V 8kW inverter
48V 8kW inverter
-
 1200w with 48v inverter or 12
1200w with 48v inverter or 12
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
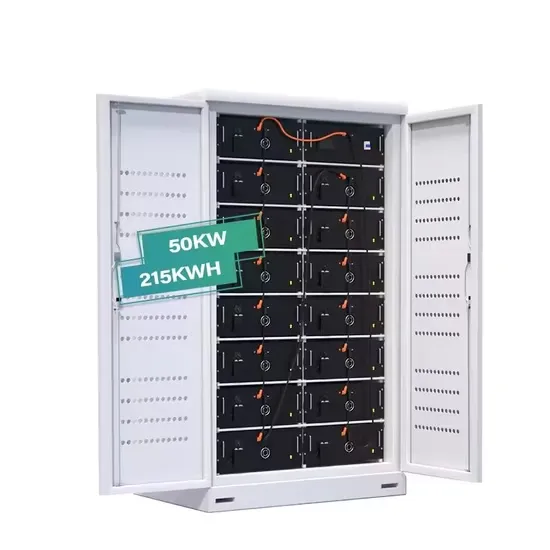
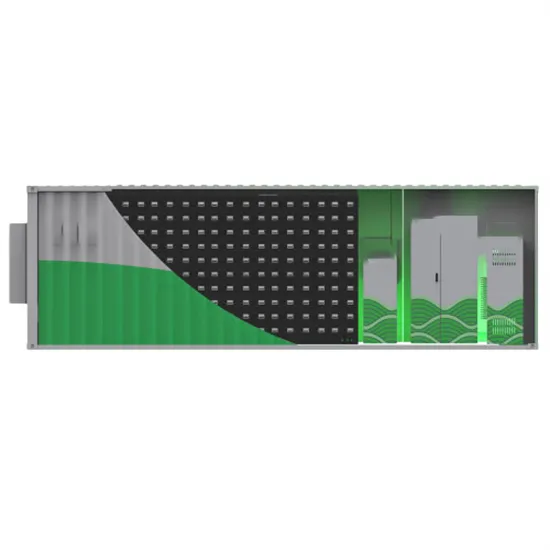
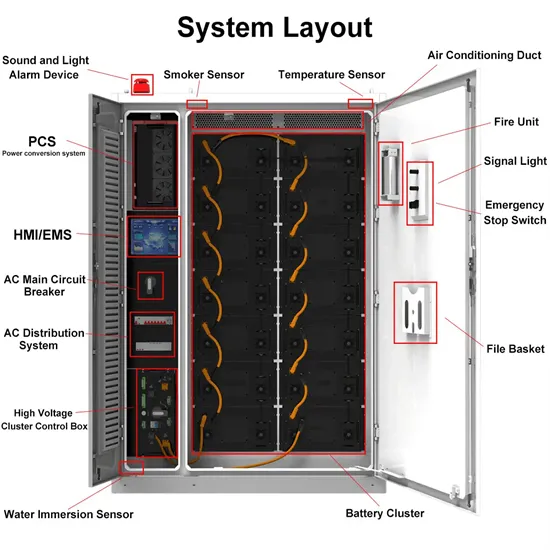
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


