Largest PV power plants list
Solar energy is the fastest growing energy market worldwide, with solar photovoltaic technologies leading the sector. Three fourth of the global renewable energy comes from sunlight. Most
Get a quote
Prediction of long-term photovoltaic power generation in the
On this basis, the future power generation of PV power station for 2025–2034 was predicted using the future meteorological data provided by the downscaling model.
Get a quote
Profiling the five largest solar power plants in India
India has ramped up its solar energy capacity in recent years and the nation is now home to some of the largest power plants. The South Asian
Get a quote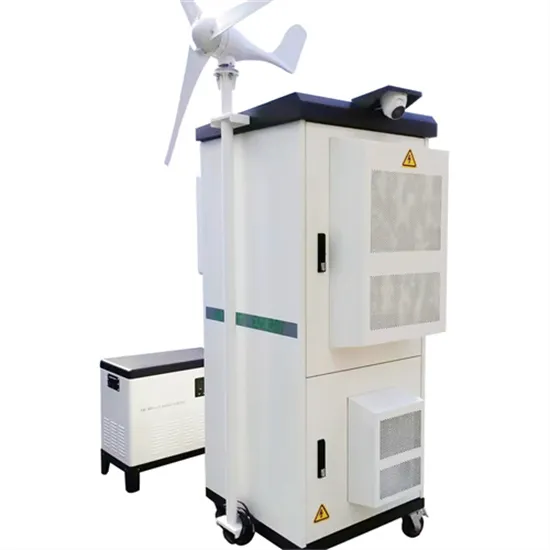
6 Methods for Calculating Photovoltaic Power
6.6.1 The prediction of the power generation of a photovoltaic power station should be based on the solar energy resources of the site, and various factors
Get a quote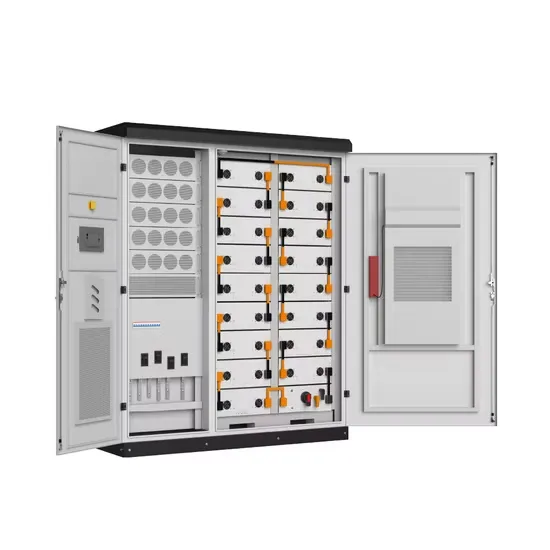
Architecture design of grid-connected exploratory photovoltaic power
Abstract Solar energy, as a prominent clean energy source, is increasingly favored by nations worldwide. However, managing numerous photovoltaic (PV) power generation units
Get a quote
Photovoltaic Cell Generations | Encyclopedia MDPI
Fourth Generation: This generation includes the low flexibility or low cost of thin film polymers along with the durability of "innovative inorganic nanostructures such as metal oxides and
Get a quote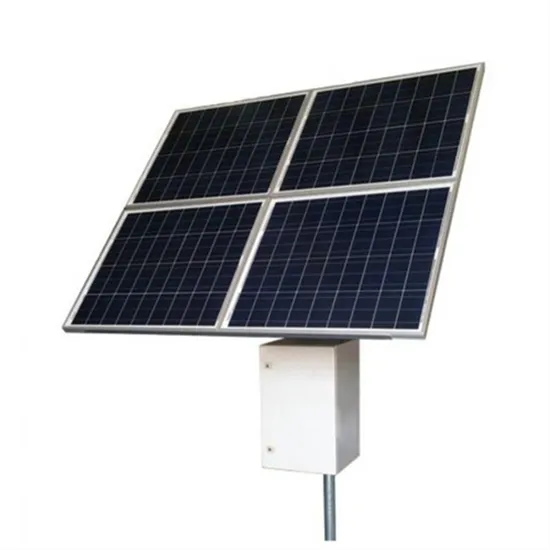
Generation IV Nuclear Reactors
An international task force is sharing R&D to develop six generation IV nuclear reactor technologies. Four are fast neutron reactors. All of these operate at higher
Get a quote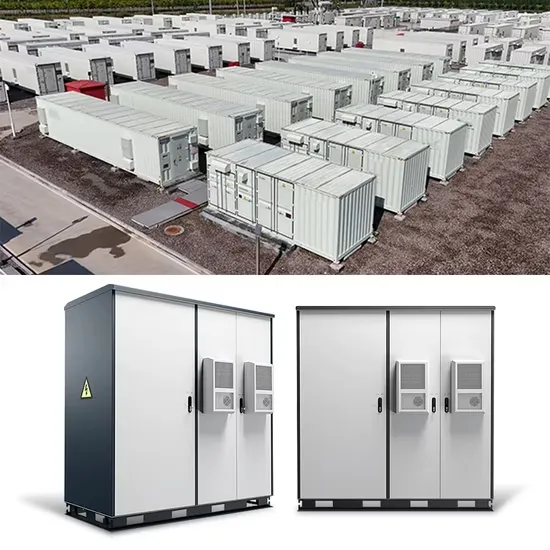
Generation IV nuclear reactors: Current status and future prospects
Generation IV nuclear power plants (GEN IV NPPs) are supposed to become, in many countries, an important source of base load power in the middle–long term (2030–2050).
Get a quote
Comprehensive study on photovoltaic cell''s generation and
The utilization of fossil fuels for power generation results in the production of a greater quantity of pollutants and greenhouse gases, which exerts detrimental impacts on the
Get a quote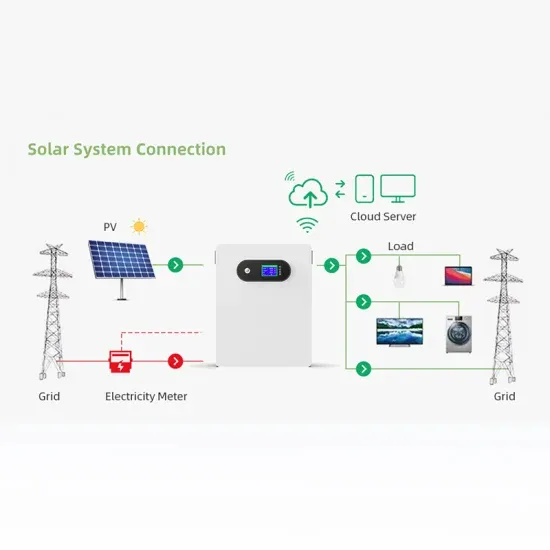
What is the fourth generation of solar energy? | NenPower
Through these advancements, the fourth generation of solar energy aims to create an accessible, efficient, and environmentally friendly approach to harnessing solar power,
Get a quote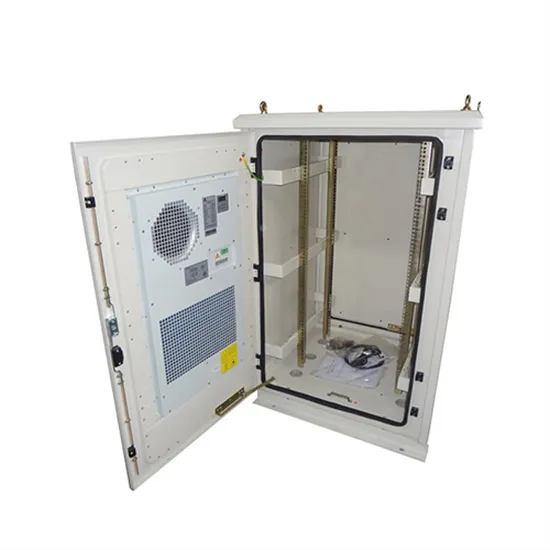
Photovoltaic Cell Generations and Current Research
Fourth-generation photovoltaic cells are also known as hybrid inorganic cells because they combine the low cost and flexibility of polymer thin films, with the
Get a quote
Fourth-generation solar cells: a review
In this review, our objective is to give an overview of contemporary developments, as well as the needs and installation of fourth-generation solar cells, while highlighting their
Get a quote
Solar and battery storage to make up 81% of new U.S.
Developers and power plant owners plan to add 62.8 gigawatts (GW) of new utility-scale electric-generating capacity in 2024, according to our
Get a quote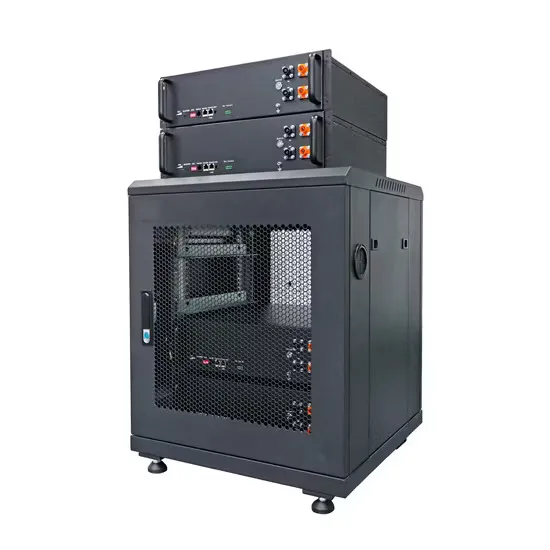
Solar energy—A look into power generation,
These challenges can be met by developing an efficient energy storage system and developing cheap, efficient, and abundant PV solar cells.
Get a quote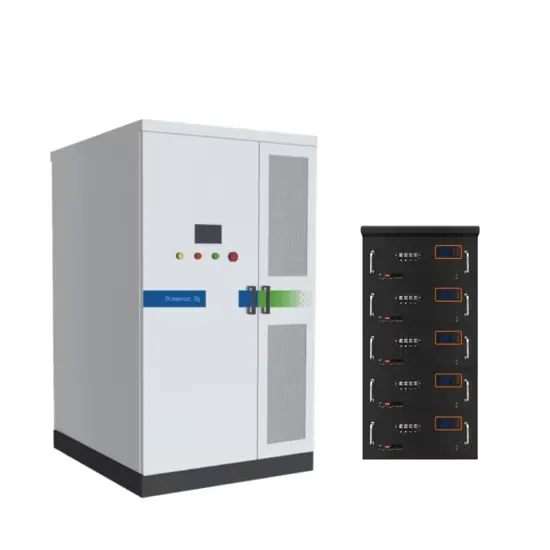
Photovoltaic Cell Generations and Current Research Directions
Fourth-generation photovoltaic cells are also known as hybrid inorganic cells because they combine the low cost and flexibility of polymer thin films, with the stability of organic
Get a quote
Could Generation IV Nuclear Reactors Play a Role in the
Scientists have started researching unconventional ways to generate nuclear energy, and recent experiments have shown the possibility of eliminating its safety concern.
Get a quote
Nio unveils cutting-edge battery tech: 4th-gen swap
Nio introduced a fourth-generation battery swap station and a robust 640-kW DC charger, complemented by ambitious installation targets for
Get a quote
Generation IV nuclear reactors: Current status and future prospects
Photovoltaic power plant composed by modules of multi-crystalline silicon with a net electrical efficiency of 19% (Peters et al., 2011, Raugei and Frankl, 2009).
Get a quote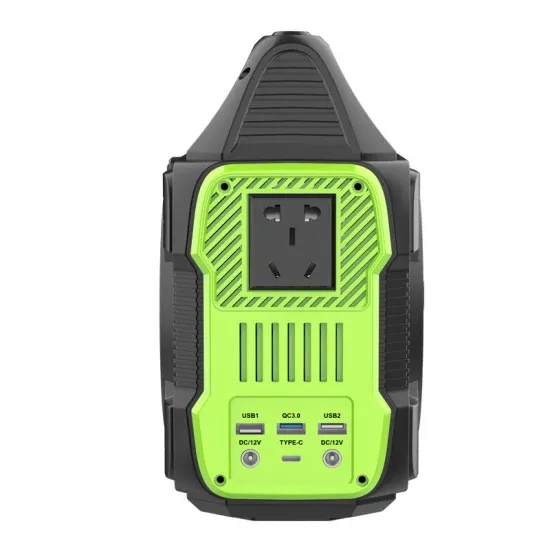
What is the fourth generation of solar energy?
Through these advancements, the fourth generation of solar energy aims to create an accessible, efficient, and environmentally friendly
Get a quote
Fourth-generation solar cells: a review
In this review, our objective is to give an overview of contemporary developments, as well as the needs and installation of fourth-generation solar
Get a quote
Photovoltaic Cell Generations | Encyclopedia MDPI
Fourth Generation: This generation includes the low flexibility or low cost of thin film polymers along with the durability of "innovative inorganic nanostructures
Get a quote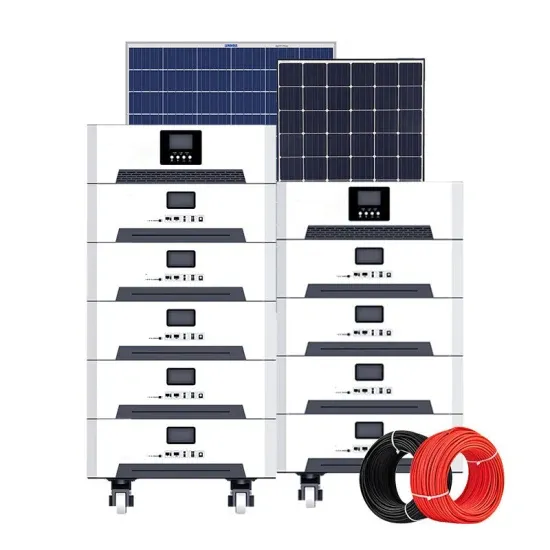
What Is a Photovoltaic Power Station and How Does
Discover how a photovoltaic power station harnesses sunlight to provide clean and sustainable energy in a world moving towards green power.
Get a quote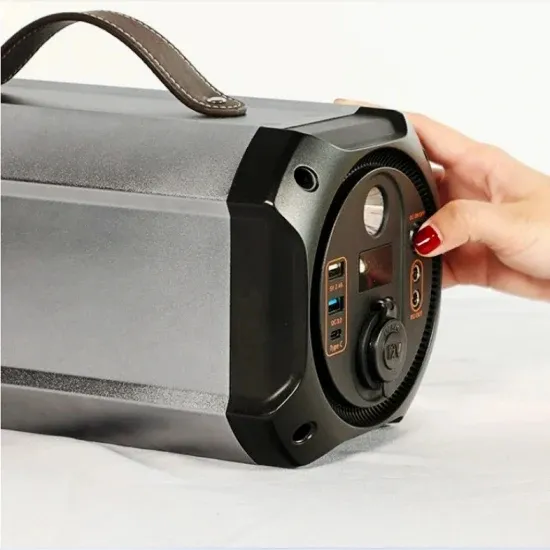
Solana Generating Station
The Solana Generating Station is a solar power plant near Gila Bend, Arizona, about 70 miles (110 km) southwest of Phoenix. It was completed in 2013. When commissioned, it was the
Get a quote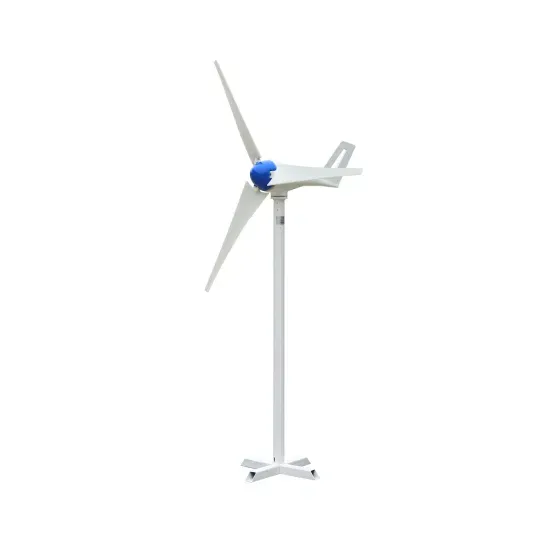
Nio Power Swap Station 4.0 now operational | Automotive World
The first batch of NIO Power Swap Station 4.0 went live. The fourth generation supports automated battery swap for multiple brands and different vehicle models
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Fourth generation photovoltaic power station power generation]
What is a fourth generation photovoltaic cell?
Fourth Generation of Photovoltaic Cells Fourth-generation photovoltaic cells are also known as hybrid inorganic cells because they combine the low cost and flexibility of polymer thin films, with the stability of organic nanostructures such as metal nanoparticles and metal oxides, carbon nanotubes, graphene, and their derivatives.
What is a generation 4 reactor?
Generation IV (Gen IV) reactors are nuclear reactor design technologies that are envisioned as successors of generation III reactors.
What is a Generation IV reactor?
No precise definition of a Generation IV reactor exists. The term refers to nuclear reactor technologies under development as of approximately 2000, and whose designs were intended to represent 'the future shape of nuclear energy', at least at that time.
How many Generation 4 nuclear reactors are there?
An international task force is sharing R&D to develop six generation IV nuclear reactor technologies. Four are fast neutron reactors. All of these operate at higher temperatures than today's reactors. In particular, four are designated for hydrogen production.
What is 3rd generation photovoltaic technology?
Third Generation: This generation counts photovoltaic technologies that are based on more recent chemical compounds. In addition, technologies using nanocrystalline “films,” quantum dots, dye-sensitized solar cells, solar cells based on organic polymers, etc., also belong to this generation.
Are Gen 4 nuclear power plants a viable source of base load power?
Generation IV nuclear power plants (GEN IV NPPs) are supposed to become, in many countries, an important source of base load power in the middle–long term (2030–2050). Nowadays there are many designs of these NPPs but for political, strategic and economic reasons only few of them will be deployed.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Cascade photovoltaic power station power generation
Cascade photovoltaic power station power generation
-
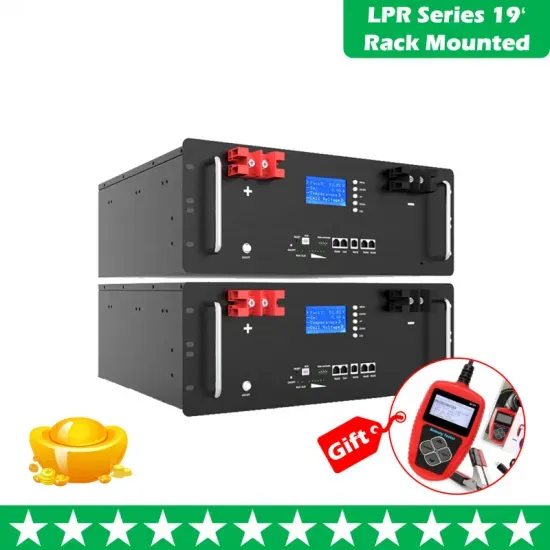 Abkhazia emergency communication base station photovoltaic power generation system
Abkhazia emergency communication base station photovoltaic power generation system
-
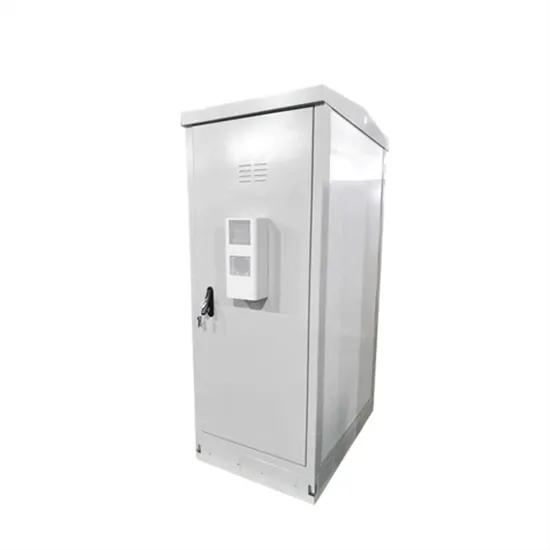 Mongolia communication base station wind power and photovoltaic power generation energy saving
Mongolia communication base station wind power and photovoltaic power generation energy saving
-
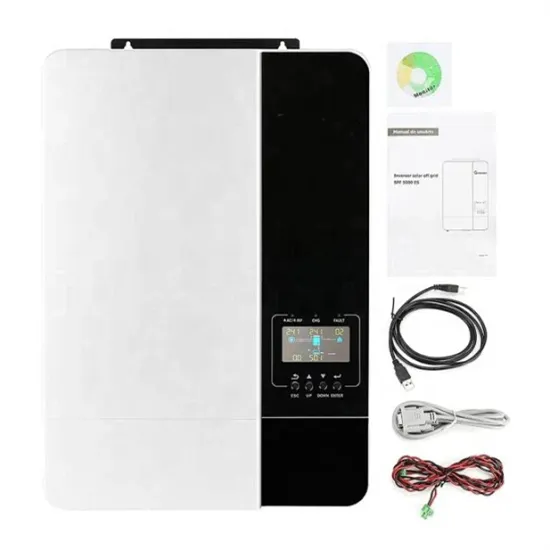 Vaduz 5G base station photovoltaic power generation system communication cabinet manufacturer
Vaduz 5G base station photovoltaic power generation system communication cabinet manufacturer
-
 48v communication base station photovoltaic power generation
48v communication base station photovoltaic power generation
-
 Small photovoltaic power station installation and power generation
Small photovoltaic power station installation and power generation
-
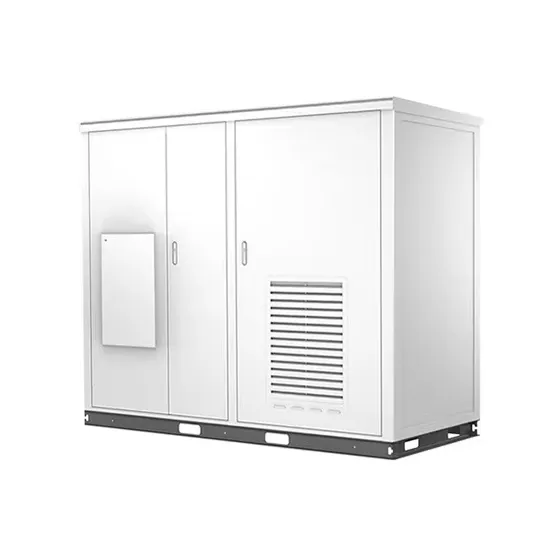 Chad communication base station grid-connected photovoltaic power generation
Chad communication base station grid-connected photovoltaic power generation
-
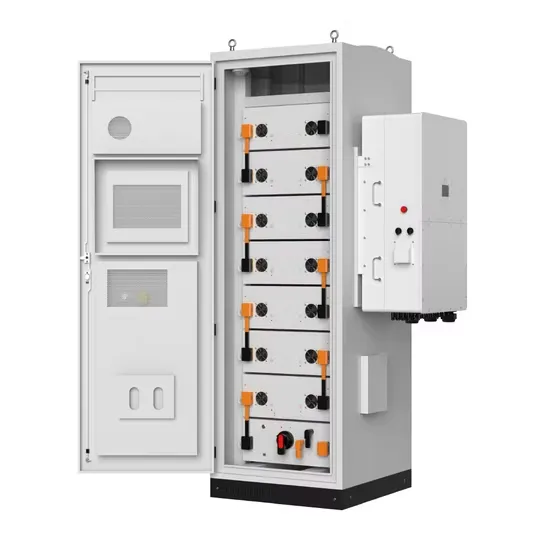 Haiti 5g base station photovoltaic power generation system communication cabinet manufacturer
Haiti 5g base station photovoltaic power generation system communication cabinet manufacturer
-
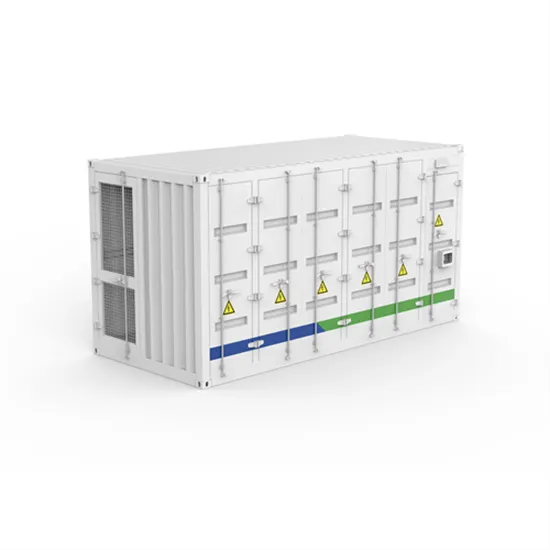 Power generation weight of the photovoltaic power station in Paraguay
Power generation weight of the photovoltaic power station in Paraguay
-
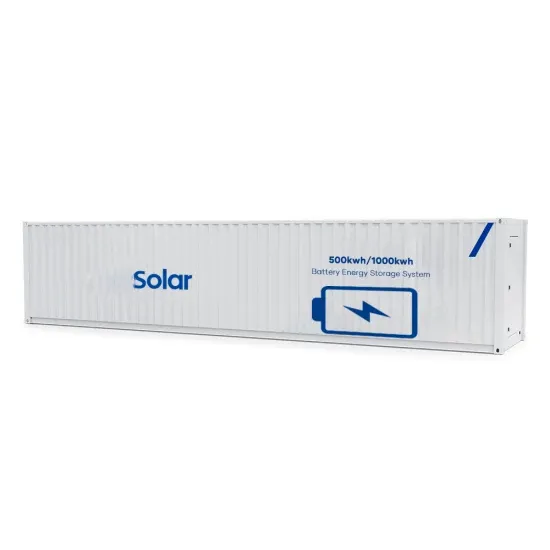 How is the photovoltaic power generation of Estonia s green base station
How is the photovoltaic power generation of Estonia s green base station
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


