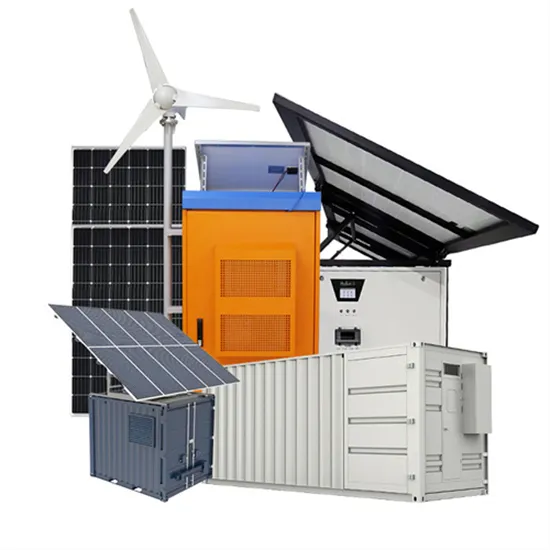
Energy Storage Systems: Batteries
Batteries, as a form of energy storage, offer the ability to store electrical energy for later use, thereby balancing supply and demand, enhancing grid stability, and enabling the integration of
Get a quote
What battery is not energy storage | NenPower
In the realm of energy management systems, batteries emerge as pivotal components for energy storage solutions. However, not all batteries serve the function of
Get a quote
Does Energy Storage Refer to Batteries? Unplugging the Truth
When Someone Says "Energy Storage," Do You Automatically Think of Batteries? Let''s face it—when most people hear energy storage, their minds immediately jump to lithium
Get a quote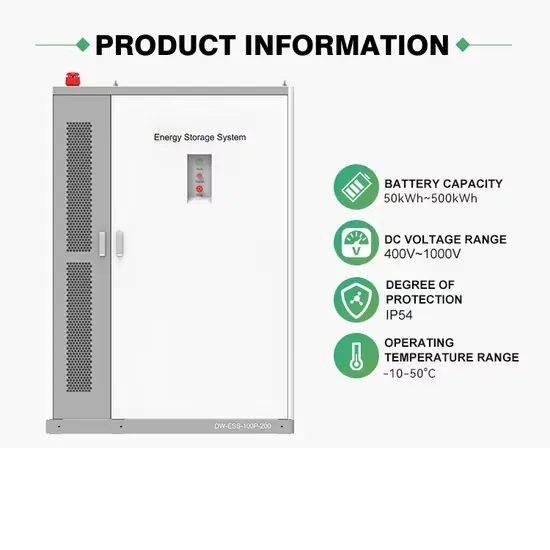
Explaining what is battery energy storage | Duracell
Battery energy storage systems, otherwise known as BESS, are ways of storing the power generated by renewable energy sources until such a time as it is
Get a quote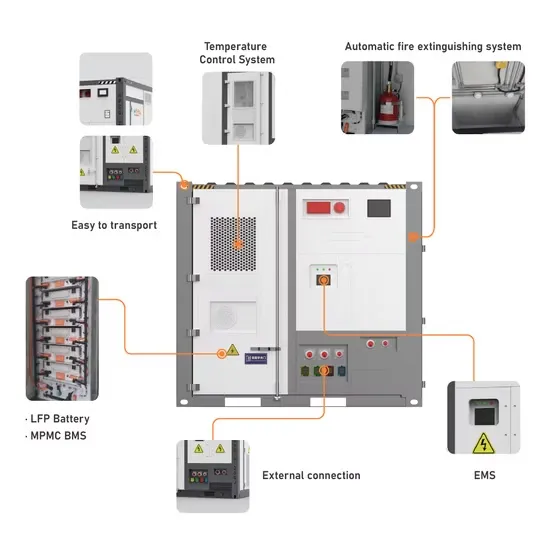
Utility-Scale Battery Storage Systems: Legal Issues
Due to its ready availability, however, the principal focus to meet current energy storage needs is on battery energy storage systems (BESS),
Get a quote
Clean Energy 101: How Batteries Can Support Grid Reliability
In many of these cases, other grid resources that could also support reliability (such as battery energy storage systems) aren''t being considered, even though they can do so just
Get a quote
Why are lithium-ion batteries, and not some other kind of battery,
Some new types of batteries, like lithium metal batteries or all-solid-state batteries that use solid rather than liquid electrolytes, "are pushing the energy density frontier beyond
Get a quote
What is lithium used for in renewable energy?
The versatility of lithium batteries means they can be used for EVs and energy grids, and can utilize similar supply chains that can be optimized
Get a quote
Sodium-ion batteries need breakthroughs to compete
A thorough analysis of market and supply chain outcomes for sodium-ion batteries and their lithium-ion competitors is the first by STEER, a
Get a quote
Solar energy and the batteries making it available
Renewable energy, when it comes to solar and wind power, has always had a caveat: it can only run when the wind blows or the sun shines.
Get a quote
Is a Battery a Renewable Source of Energy? Its Crucial Role in
No, batteries are generally not considered renewable energy solutions. Instead, they are classified as energy storage devices that can store energy from both renewable and
Get a quote
A battery by any other name: Rethinking energy storage
It''s time to radically expand our thinking about what constitutes a battery, expanding it to include other forms of energy storage. The term battery doesn''t refer to any single
Get a quote
Battery Energy Storage: Are Batteries Energy Storage Systems?
1 day ago· Electrochemical energy storage (batteries) Among these solutions, battery storage stands out as the most scalable and versatile option, particularly suited for residential,
Get a quote
Explaining what is battery energy storage | Duracell Energy
Battery energy storage systems, otherwise known as BESS, are ways of storing the power generated by renewable energy sources until such a time as it is needed. Simply put, they are
Get a quote
Solving renewable energy''s sticky storage problem
Importantly, lithium-ion batteries aren''t suitable for long-duration storage, explains Meng. Despite monumental price declines in recent years, they remain costly due to their
Get a quote
How Do Batteries Work? The Physics of Stored Energy
Quantum batteries—a concept still largely theoretical—envision energy storage at the level of quantum states, potentially allowing ultra-fast
Get a quote
What Is Energy Storage? Different Types And Uses
Energy storage systems capture energy from a source and store it for later use. They can be designed to store electrical, mechanical or thermal energy.
Get a quote
Is Battery Storage Considered Renewable Energy?
Batteries act as energy storage devices that absorb and release energy on demand, with lithium-ion being the predominant chemistry used. They do not produce electricity
Get a quote
Are Batteries Considered Renewable Energy? Exploring Storage
Batteries, however, are energy storage systems (ESS) that hold electricity for later use. They bridge gaps between renewable generation and demand but aren''t energy sources
Get a quote
What Is Energy Storage? Different Types And Uses
Energy storage systems capture energy from a source and store it for later use. They can be designed to store electrical, mechanical or thermal energy. Energy is typically stored in
Get a quote
Comprehensive review of energy storage systems technologies,
Battery, flywheel energy storage, super capacitor, and superconducting magnetic energy storage are technically feasible for use in distribution networks. With an energy density
Get a quote
The Flow Battery Tipping Point is Coming | EnergyTech
If you haven''t heard, the energy storage market is booming. Residential, commercial and grid-scale battery technologies are being called
Get a quote
Energy Storage
Lithium-ion batteries account for more than 50% of the installed power and energy capacity of large-scale electrochemical batteries. Flow batteries are an emerging storage technology;
Get a quote
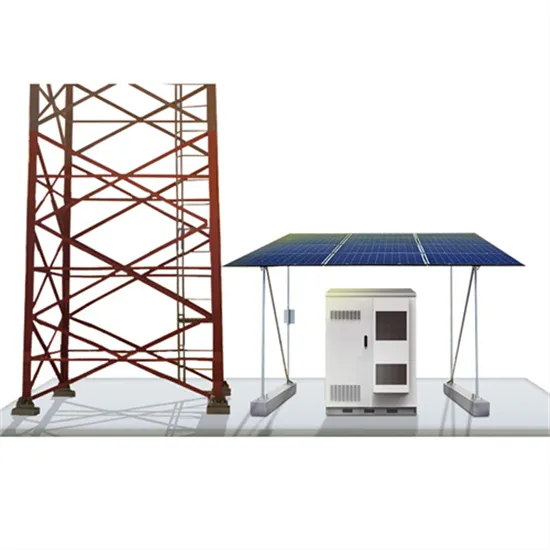
Energy Storage Systems: Batteries
Batteries, as a form of energy storage, offer the ability to store electrical energy for later use, thereby balancing supply and demand, enhancing grid stability,
Get a quote
A battery by any other name: Rethinking energy storage
It''s time to radically expand our thinking about what constitutes a battery, expanding it to include other forms of energy storage. The term
Get a quote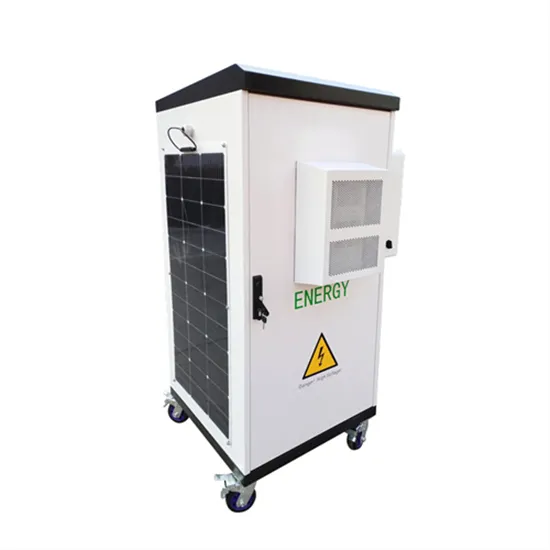
The $2.5 trillion reason we can''t rely on batteries to
Fluctuating solar and wind power require lots of energy storage, and lithium-ion batteries seem like the obvious choice—but they are far too
Get a quote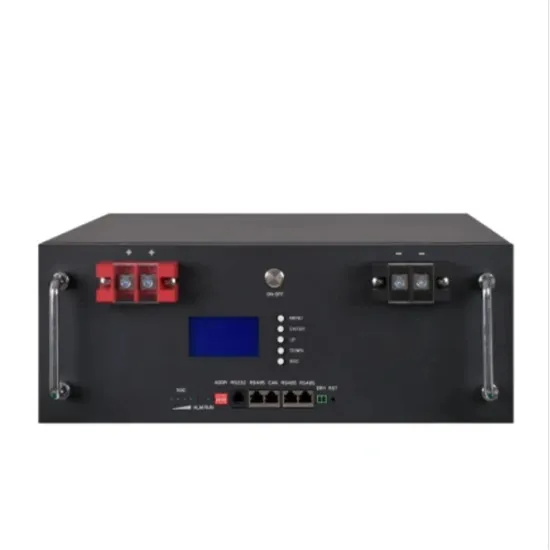
Why Aren''t Supercapacitors Widely Used for Energy Storage?
Meet the supercapacitor – the energy storage world''s most fascinating underdog. While lithium-ion batteries hog the spotlight, these electrochemical powerhouses quietly excel
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Aren t batteries considered energy storage ]
What are battery energy storage systems?
This article delves into the fundamentals, historical development, applications, advanced topics, challenges, and future trends of battery energy storage systems. Batteries are electrochemical devices that convert chemical energy into electrical energy through redox reactions.
What is battery storage es?
Battery storage is one of the most widely used ES technologies. It involves using batteries, typically lithium-ion batteries, to store electrical energy. These batteries are commonly used in electric vehicles and can also be used in home ES systems, allowing homeowners to store excess solar power for later use.
Is battery storage enough to reach city scale?
While some places, like California, are adding traditional battery storage to their electric energy mix, that may not be enough to rapidly reach city scale. As we grapple with increasingly complex energy challenges, many are looking for innovative and longer-term energy storage solutions.
What is the difference between a battery and a fuel cell?
Batteries store energy in chemical form and can release it as electrical energy, while fuel cells generate electricity from chemical reactions. These technologies have the advantage of storing energy for long periods and being used for a range of applications. Compressed air energy storage
What are energy storage systems & why are they important?
Energy storage systems, particularly batteries, play a pivotal role in modern energy systems engineering. As the world transitions towards renewable energy sources, the need for efficient, reliable, and scalable energy storage solutions has never been more critical.
Are batteries enough to meet our energy needs?
Solar panels produce electricity when the sun shines, wind turbines spin when winds are strong, but our energy needs don’t always conveniently align with these intermittent sources. This disconnect makes batteries an essential part of our energy future—but today’s batteries aren’t enough to meet the need.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Why aren t energy storage cabinet batteries used as energy storage charging piles
Why aren t energy storage cabinet batteries used as energy storage charging piles
-
 Batteries are also considered energy storage
Batteries are also considered energy storage
-
 Which company produces energy storage batteries
Which company produces energy storage batteries
-
 Battery lifespan of energy storage batteries at base stations in the Republic of South Africa
Battery lifespan of energy storage batteries at base stations in the Republic of South Africa
-
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Lithium Batteries for Home Energy Storage
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lithium Batteries for Home Energy Storage
-
 Cost structure of energy storage batteries
Cost structure of energy storage batteries
-
 Does the Electrical Engineering Department have a major in energy storage batteries
Does the Electrical Engineering Department have a major in energy storage batteries
-
 Prices of home energy storage batteries in West Africa
Prices of home energy storage batteries in West Africa
-
 DC power supply to charge energy storage batteries
DC power supply to charge energy storage batteries
-
 What are the types of photovoltaic energy storage batteries
What are the types of photovoltaic energy storage batteries
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


