What''s Currently Happening in Sodium-Ion Batteries? 2025
As of 2025, sodium-ion batteries are well-positioned to achieve cost parity with lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) batteries, a key milestone for market competitiveness. With
Get a quote
Evaluation and economic analysis of battery energy storage in
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used because of their excellent performance, and sodium-ion batteries have a similar version to lithium-ion batteries and are more suitable for
Get a quote
Sodium Batteries for Use in Grid-Storage Systems and Electric
However, sodium-ion batteries remain particularly advantageous for stationary energy storage systems, such as solar and wind energy storage, where their lower cost and
Get a quote
Sodium‐Ion Batteries Paving the Way for Grid Energy
Moreover, new developments in sodium battery materials have enabled the adoption of high-voltage and high-capacity cathodes free of rare
Get a quote
PNNL-Led Grid-Focused Alliance Drives Sodium-Ion
The Sodium-ion Alliance for Grid Energy Storage, led by PNNL, is focused on demonstrating high-performance, low-cost, safe sodium-ion
Get a quote
Sodium-ion batteries: state-of-the-art technologies and future
The study''s findings are promising for advancing sodium-ion battery technology, which is considered a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative to lithium-ion batteries,
Get a quote
Recent Progress in Sodium-Ion Batteries: Advanced Materials,
For energy storage technologies, secondary batteries have the merits of environmental friendliness, long cyclic life, high energy conversion efficiency and so on, which
Get a quote
A 30-year overview of sodium-ion batteries
Although sodium metal can be adopted as the counter electrode in the half cell, specific requirements in terms of the equipment and operating environment
Get a quote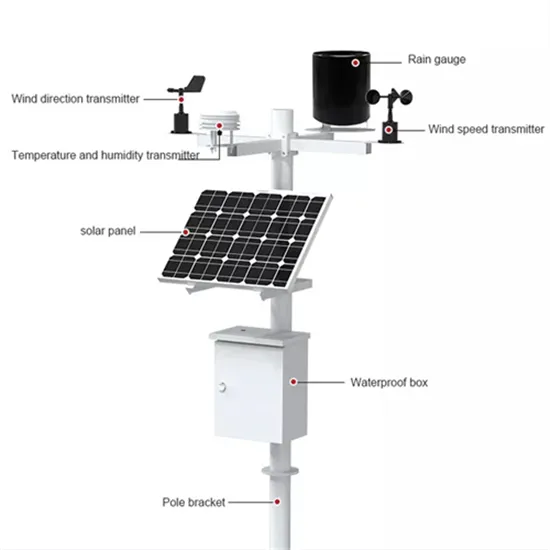
Peak Energy Plans Sodium-Ion Grid-Scale Battery Storage
Peak Energy is challenging the conventional wisdom when it comes to battery energy storage systems for grid scale applications.
Get a quote
Toward Emerging Sodium‐Based Energy Storage Technologies:
As one of the potential alternatives to current lithium-ion batteries, sodium-based energy storage technologies including sodium batteries and capacitors are widely attracting
Get a quote
(PDF) Recent advances of electrode materials for low
Recent advances of electrode materials for low-cost sodium-ion batteries towards practical application for grid energy storage January 2017
Get a quote
A 30-year overview of sodium-ion batteries
Although sodium metal can be adopted as the counter electrode in the half cell, specific requirements in terms of the equipment and operating environment are necessary, which
Get a quote
Energy storage costs
Wider deployment and the commercialisation of new battery storage technologies has led to rapid cost reductions, notably for lithium-ion batteries, but also for high-temperature sodium-sulphur
Get a quote
Interview: Sodium ion batteries: The future of energy storage?
Interview: Sodium ion batteries: The future of energy storage? Sustainable alternatives to lithium ion batteries are crucial to a carbon-neutral society, and in her Wiley
Get a quote
Sodium-Ion Battery Price Trends: A Comprehensive Guide for 2023
As reported by poweringautos , the projected price for sodium-ion batteries in 2024 is approximately $85 per kWh, which is lower than the estimated $89 per kWh for lithium
Get a quote
An overview of sodium-ion batteries as next
Installed capacity projection of Na-ion battery by potential application [16]. (Figure reprinted with permission.) Although Na-ion and Li-ion batteries share a
Get a quote
How does the cost of sodium-ion batteries compare to lithium-ion
Overall, sodium-ion batteries offer a cost-effective alternative to lithium-ion batteries, especially for applications that prioritize sustainability and cost over high energy
Get a quote
A cost and resource analysis of sodium-ion batteries
This article explores the economic and resource-based aspects of sodium-ion batteries, offering a comprehensive analysis of their cost-effectiveness and resource
Get a quote
A 30-year overview of sodium-ion batteries
This review delves into the frequently underestimated relationship between half- and full-cell performances in sodium-ion batteries, emphasizing the necessity of balancing cost and
Get a quote
Sodium-Ion Batteries for Stationary Energy Storage
Cost-Effectiveness: Sodium-ion batteries are theoretically cost-effective due to their reliance on abundant materials like sodium (cheaper than lithium) and aluminum (less
Get a quote
Why Sodium-Ion Batteries Are a Promising Candidate
As sodium-ion batteries start to change the energy storage landscape, this promising new chemistry presents a compelling option for next
Get a quote
Sodium-ion Batteries: Inexpensive and Sustainable Energy
There is also rapidly growing demand for behind-the-meter (at home or work) energy storage systems. Sodium-ion batteries (NIBs) are attractive prospects for stationary storage
Get a quote
Why Sodium-Ion Batteries Are a Promising Candidate for
As sodium-ion batteries start to change the energy storage landscape, this promising new chemistry presents a compelling option for next-generation stationary energy
Get a quote
Advancements and challenges in sodium-ion batteries: A
Sodium is abundant and inexpensive, sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) have become a viable substitute for Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). For applications including electric vehicles
Get a quote
A cost and resource analysis of sodium-ion batteries
This article explores the economic and resource-based aspects of sodium-ion batteries, offering a comprehensive analysis of their cost
Get a quote
Sodium-Ion Batteries for Stationary Energy Storage
Cost-Effectiveness: Sodium-ion batteries are theoretically cost-effective due to their reliance on abundant materials like sodium (cheaper than
Get a quote
Recent advances of electrode materials for low-cost sodium-ion
We believe that low-cost and long-life room-temperature sodium-ion batteries would ultimately become a reality through the unremitting scientific research, and will have promising
Get a quote
Sodium Batteries for Use in Grid-Storage Systems
However, sodium-ion batteries remain particularly advantageous for stationary energy storage systems, such as solar and wind energy storage,
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Application cost of sodium-ion batteries in energy storage]
Are sodium ion batteries the future of energy storage?
There is also rapidly growing demand for behind-the-meter (at home or work) energy storage systems. Sodium-ion batteries (NIBs) are attractive prospects for stationary storage applications where lifetime operational cost, not weight or volume, is the overriding factor.
Are sodium-ion batteries a viable option for stationary storage applications?
Sodium-ion batteries (NIBs) are attractive prospects for stationary storage applications where lifetime operational cost, not weight or volume, is the overriding factor. Recent improvements in performance, particularly in energy density, mean NIBs are reaching the level necessary to justify the exploration of commercial scale-up.
Are sodium ion batteries a viable option?
Scalability: The scalability of sodium-ion battery production promises substantial economies of scale. As production ramps up, the per-unit cost of batteries is expected to decrease, making them an even more attractive option for large-scale energy storage and electric vehicles.
Why are sodium ion batteries so popular?
One of the main attractions of sodium-ion batteries is their cost-effectiveness. The abundance of sodium contributes to lower production costs, paving the way for more affordable energy storage solutions. Furthermore, recent advancements have improved their energy density.
What is a sodium ion battery?
Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) represent a significant shift in energy storage technology. Unlike Lithium-ion batteries, which rely on scarce lithium, SIBs use abundant sodium for the cathode material. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element on Earth’s crust and can be efficiently harvested from seawater.
Are sodium ion batteries cheaper than lithium?
Additionally, sodium is about 50 times cheaper than lithium, making it an attractive option for large-scale applications. One of the main attractions of sodium-ion batteries is their cost-effectiveness. The abundance of sodium contributes to lower production costs, paving the way for more affordable energy storage solutions.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Cost of home energy storage batteries in Ethiopia
Cost of home energy storage batteries in Ethiopia
-
 Do home energy storage batteries cost money
Do home energy storage batteries cost money
-
 Application of energy storage batteries in factories
Application of energy storage batteries in factories
-
 Application scenarios of energy storage batteries
Application scenarios of energy storage batteries
-
 Full life cycle of energy storage batteries
Full life cycle of energy storage batteries
-
 Batch shipment of energy storage lithium batteries
Batch shipment of energy storage lithium batteries
-
 Can photovoltaic energy storage batteries be placed indoors
Can photovoltaic energy storage batteries be placed indoors
-
 What are the fire protection requirements for energy storage batteries
What are the fire protection requirements for energy storage batteries
-
 Home energy storage batteries in Sao Tome and Principe
Home energy storage batteries in Sao Tome and Principe
-
 Overall conversion efficiency of energy storage batteries
Overall conversion efficiency of energy storage batteries
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


